OCR Chemistry Revision - Chemical Bonding
The Noble Gases
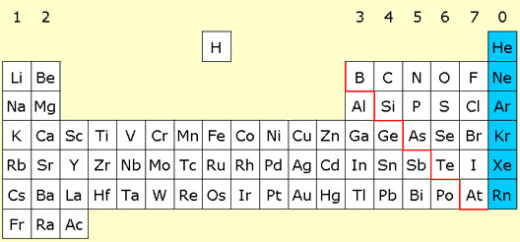
The only 6 elements on the periodic table that exist naturally as single, unbonded atoms are Helium, Neon, Argon, Krypton, Xenon and Radon.
These elements are collectively known as the Noble Gases and they make up Group 0 of the Periodic Table.
The outermost shell of every Noble Gas atom is full, this makes the atom very stable and thus very unreactive.
Atoms always want a full outer shell and in order for an atom to react it has to be unstable or willing to give/lose electrons to achieve this.
Facts about Noble Gases:
- Argon is the most abundant noble gas in the air.
- Krypton is used in lasers for eye surgery.
- The first noble gas (helium) was discovered in 1868, and the rest were discovered in the 32 years after this.
- Noble gases only make up about 1% of the air.

Different Types of Bonding
There are three main types of chemical bonding; ionic, covalent and metallic.
When atoms of different elements chemically bond together in any of these 3 ways, a compound is formed.
The atoms of the different elements in the compound are always proportional to each other, For instance, water (H2O) always has two hydrogen atoms to every oxygen atom.
Ionic Bonding
Definition of ionic bond:
'The electrostatic attraction between two oppositely charged ions.'
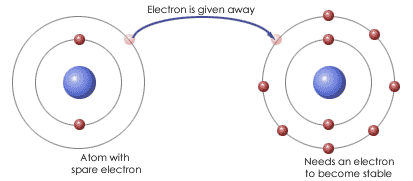
Ionic bonding occurs between the atoms of a compound consisting of a metal and a non-metal.
The electrons of the metal atom are transferred to the non-metal atom and this forms oppositely charged ions (a positive metal ion and a negative non-metal ion).
These ions are then bonded together by electrostatic attraction, otherwise known as an ionic bond.
Take the compound sodium oxide (Na2O) for example. Sodium oxide consists of two sodium atoms and one oxygen atom. In order for these two atoms to ionically bond one electron is transferred from each one of the sodium atoms to the one oxygen atom.
The sodium atoms then form Na+ ions (because they have lost an electron) and the oxygen atom forms an O2− ion (because it has gained 2 electrons).
The electrostatic attraction between these oppositely charged ions forms an ionic bond.
However, the two Na+ ions and the one O2− ion were not the only ions involved in the ionic bonding. In the case of sodium oxide each ion is surrounded by oppositely charged ions that attract each other in all different directions.
The attraction of all of these ions forms a giant ionic lattice structure.
A giant lattice structure is a 3D structure of oppositely charged ions that are held together by strong ionic bonds.

Covalent Bonding
Definition of covalent bond:
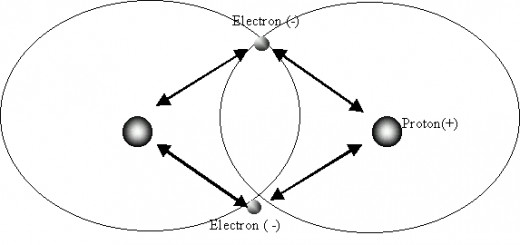
'A bond formed by a shared pair of electrons.'
Covalent bonds occur between compounds that consist of non-metal atoms.
The negatively charged pair of electrons of the atom are attracted to the other atom's positive nuclei.
This attraction is stronger than the repulsion between the two positive nuclei and thus the pair of electrons occupy the space between the two nuclei of the atoms and the atoms are held together in a covalent bond.
The pair of electrons are shared in order for the atom to have a full outer shell.
Hydrogen (H2) is an example of a covalent bond.
Each hydrogen atom has one electron in its outer shell and for a full outer shell it needs two electrons, therefore two hydrogen atoms will share their electron in a covalent bond.
Some non-metal compounds have multiple covalent bonds. This happens when an atom shares more than one pair of electrons.
For instance oxygen shares two pairs of electrons and forms a double bond and atoms that share three pairs of electrons form triple bonds.

Metallic Bonding
Definition of metallic bonding:
'The electrostatic attraction between positive metal ions and delocalised electrons.'
The atoms in a solid metal compound are held together by metallic bonds.The positive metal ions are in fixed positions in a lattice.
The outermost electrons that originated from the metal atoms (now metal ions) are all delocalised and are shared between the different metal atoms in the lattice.
The bonding occurs between the positive metal ions and the negative delocalised electrons. The electrons are free to move around the structure but the metal ions are not.
The delocalised electrons are often referred to as a 'sea of electrons'.
Metal Lattices have the following properties:
- High melting and boiling points.
- Good electrical conductivity.
- Malleability and ductility.

Definitions
Lattice: A three-dimensional arrangement of atoms, ions, or molecules in a metal or other solid.
Delocalised Electrons: Electrons that are not associated with a single atom.
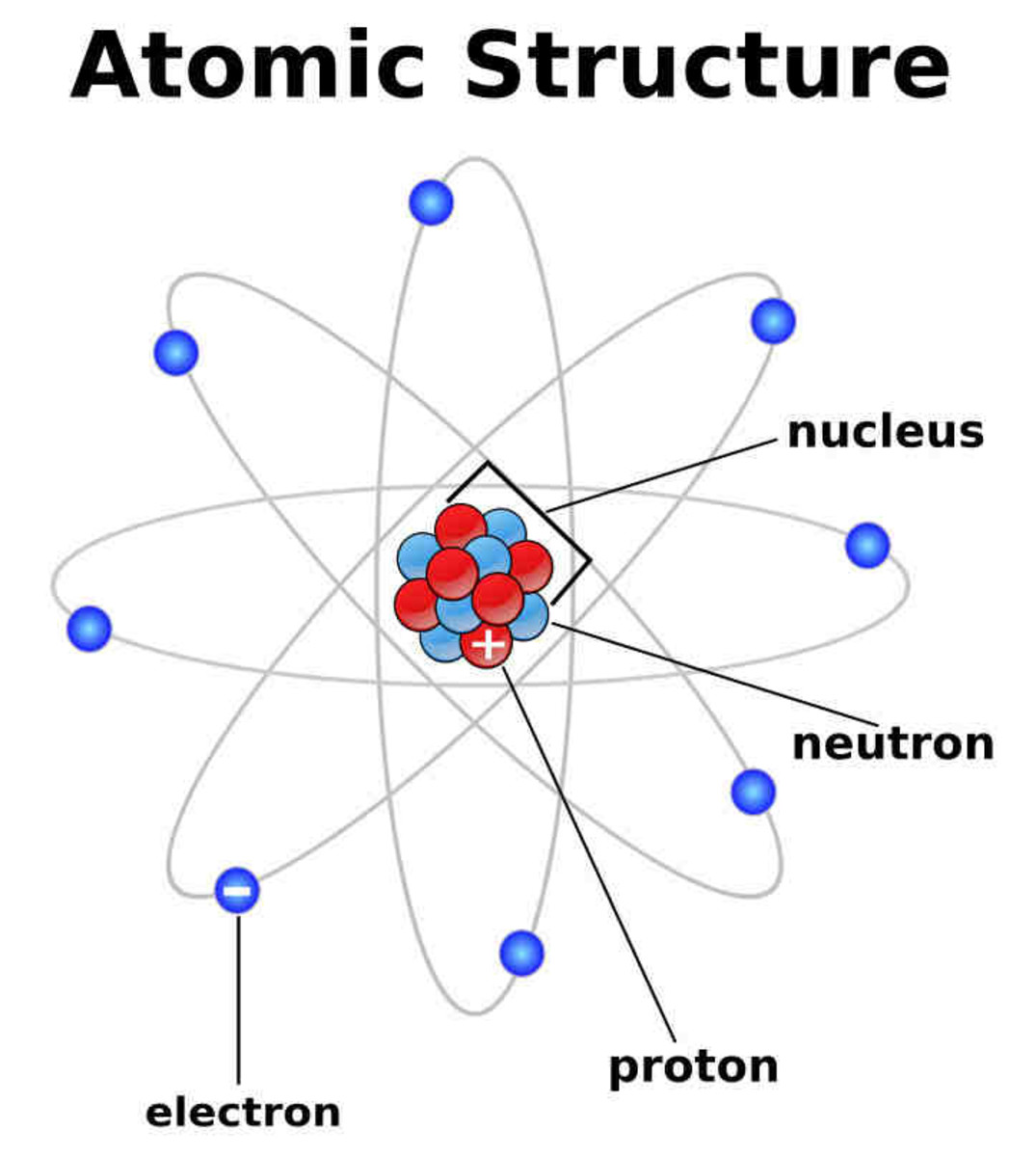
Ion: An atom with either a positive or negative charge due to the loss or gain of electrons.
Compound: A substance formed when two or more elements bond.