Binaural Beats, Sounds and Tones: What They Are and How They Work
Nature is a Great Place to Meditate, and Binaural Beats Can Enhance Your Experience

This Meditation Set Utilizes Binaural Beats to Enhance Meditation and Trance
What are Binaural Beats and Sounds?
Binaural beats, also known as binaural sounds, are repetitive notes believed to stimulate the brain and influence brain functions in ways that don't involve hearing.
The way a brain functions when it is exposed to binaural sounds is known as the frequency following response.
Entrainment, the process where a predominant brainwave frequency moves towards additional stimuli, is a practice that can be produced by binaural sounds. It can also be achieved by those who happen to be extremely advanced when it comes to meditation.
Binaural beats have been scientifically proven to have a direct correction to a person's spatial perception, as well as auditory recognition. Depedning on the frequency of the beats, various places in the brain can become activated.
Humans hear in the frequency range of 20 Hz to 20,000 Hz, however brainwave frequencies all fall below 40 Hz.
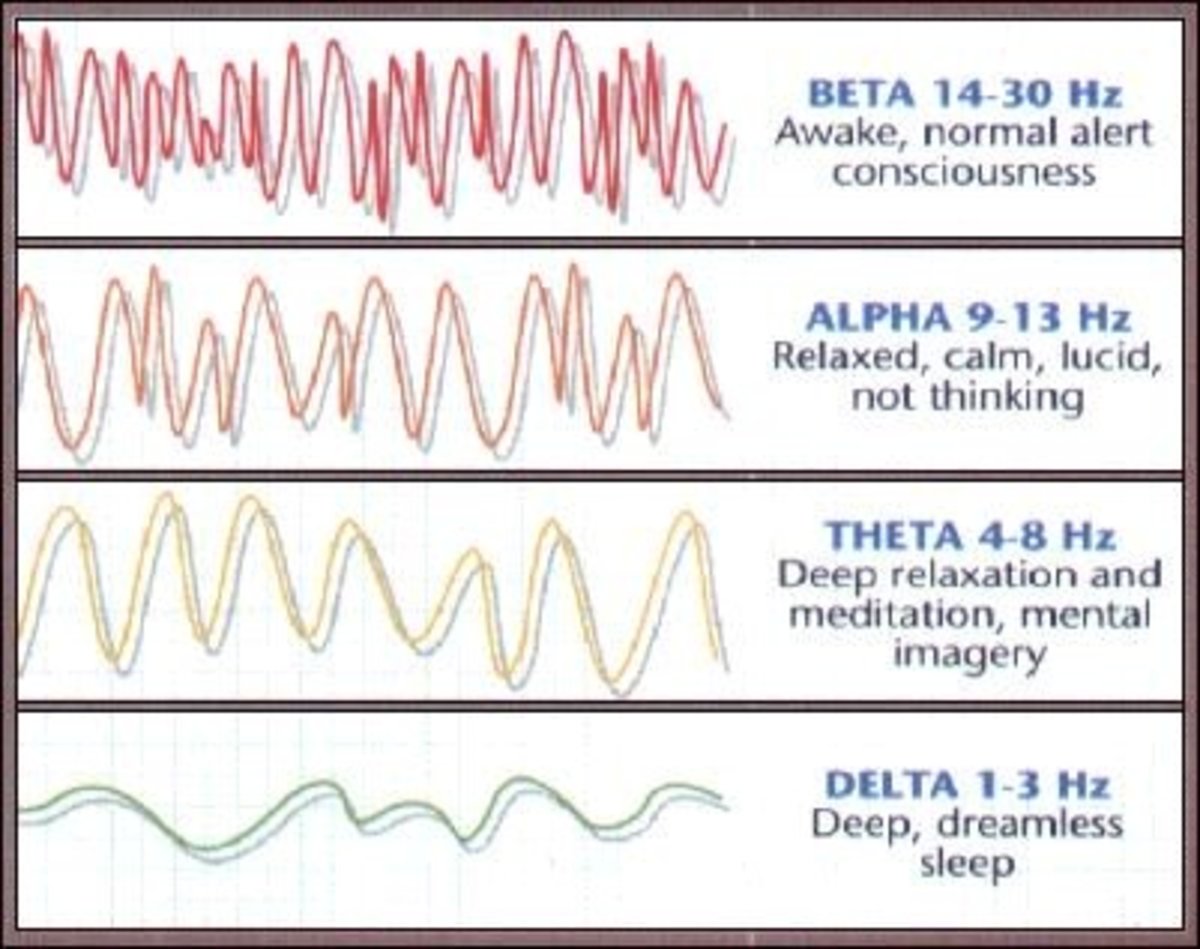
Binaural beats are designed to correspond to one of the five brain frequencies: delta, theta, alpha, beta and gamma. If a person is listening to music at 455 Hz in the left ear, and 430 Hz in the right ear, the brain waves shift towards the difference, 25 Hz, which is within the beta range of brain frequencies.
Beta waves have been proven to promote alertness, enhance mental clarity and increase mental consciousness. Each brain wave is directly correlated to a specific feeling. Alpha waves produce relaxation, delta waves are linked to deep sleep, and theta waves have been shown to help produce REM sleep.
Typically, binaural beats are experienced with the use of headphones in order to avoid other sounds interfering with the frequency waves, however binaural beats can also be experienced without the use of headphones.
When using speakers to listen to binaural sounds, apparent localized sounds may appear, which is why the preferred way to use this technique is with headphones rather than speakers.
Brainwave - A Theta Meditation Using Binaural Beats
Binaural Beats Have Been Found to Improve Deep REM Sleep

Were you aware of the power of binaural beats?
Aromatherapy is Another Great Way to Enhance Relaxation and Relieve Stress
The History Behind Binaural Sounds
Binaural beats were discovered in the 1830s by a man named Heinrich Wilhelm Dove. After reporting his studies to a scientific journal in Germany, significant research began in an attempt to analyze his findings and uncover more regarding these unusual sounds.
It wasn't until 1973 that scientists concluded the effectiveness of binaural beats. Gerald Oster, a scientist who researched sound waves for decades, was the first person since Dove to produce a scientific research article on the topic. "Auditory Beats in the Brain", which was published in the Scientific American Journal in 1973, identified the power of binaural beats when it comes to cognitive and neurological processes in the brain.
Oster expanded on Dove's research and even studied the effects of binaural beats on the brains of animals. Out of this study came the "cocktail party effect", which referes to how animals can pick out and focus on particular noises in their three dimensional environment.
After the studies Oster conducted where published, research regarding brain waves and binaural sounds increased profusely. Binaural beats were experimented in the medical field as a diagnostic tool and as a way to measure estrogen levels.
After Oster, the next most ground-breaking research revolving around binaural beats were conducted by Thomas Campbell, a physicist, as well as Dennis Mennerich, an electrical engineer.
These two studied binaural beats and the effects they had on human consciousness. From their research came the founding of The Monroe Institute, a charitable binaural research and education organization that is still in existence today.
Binaural Technology
Binaural Beats and Lullabies: Delta Waves and Theta Waves to Help Induce Deep Sleep
Enhance Your Meditation Experience with Binaural Beat Meditation Music

Understanding the Different Brain Waves
Binaural beats are beneficial in many ways. They can improve sleep, as well as quality of sleep, they can enhance concentration and foucs, they can help stimulate the body, and more.
By stimulating various parts of the brain depending on the frequency of the beat, these sounds can influence brain functions and stimulate particular brain waves.
In order to understand binaural beats and their effect on the brain however, the various brain waves must be understood. The five brain waves most commonly influenced by binaural beats include theta, beta, alpha, gamma, and delta.
Beta waves have a low amplitude, and typically are emitted from the brain when a person is aroused or excited. They can also be found in high quantities when the brain is engaged in intense mental activities. Actions like talking, teaching and working create high levels of beta waves.
Alpha waves appear right after beta waves on the chart of brain wave frequencies. Although they are slower than beta waves, they have much higher amplitude levels. Alpha waves help a person relax and meditate.
Gamma waves are often lumped together with beta waves, however these two types of brain waves are distinct in their own ways. Gamma waves can aid in perception and help promote mental clarity. This type of brain wave is associated with REM sleep.
Delta waves are correlated with deep sleep. Deep sleep is one step beyond REM sleep, and doesn't involve dreams. These waves are extremely slow and have the highest amplitude of all of the brain waves. Delta waves reach such a low frequency that they get close to the brain wave levels of a person who is brain dead.
Theta waves are slower than alpha waves and have higher amplitude levels. This type of brain wave is the most difficult to accomplish because they create a higher level of concsiousness that can take us away from the world that surrounds us. Daydreaming is often associated with high levels of theta waves. Those who can produce this type of brain wave in high levels can utilize theta waves to conceive creative ideas and reach a higher consciousness.
Binaural beat stimulation has been used fairly extensively in attempts to induce a variety of states of consciousness, and there has been some work done in regards to the effects of these stimuli on relaxation, focus, attention, and states of consciousness.
The Different States of Brain Waves
Frequency Range
| Name
| Usually Associated With:
|
|---|---|---|
> 40 Hz
| Gamma Waves
| High mental activity, problem solving, fear, higher consciousness
|
13 - 39 Hz
| Beta Waves
| Active, busy, working, anxious thinking, paranoia, active consciousness
|
7 - 13 Hz
| Alpha Waves
| Relaxation while Awake, Pre-Sleep and Pre-Wake Drowsiness, REM sleep, Dreaming, Day-dreaming
|
8 - 12 Hz
| Mu Waves
| Mu Rhythm and Sensorimotor rhythm
|
4 - 7 Hz
| Theta Waves
| Deep meditation
|
< 4 Hz
| Delta Waves
| A deep dreamless sleep or a loss of body
|
At Certain Frequencies, Binaural Beats can Reduce Stress and Increase Relaxation

The Healing Power of Sound: Recovery from Illness Through Sound, Voice and Music
Would you use binaural beats to help improve your sleep, relaxation and/or restfulness?
Other Uses for Binaural Beats
Besides meditation, relaxation and sleep, binaural beats have other uses which have yet to be scientificaly proven.
Some of these claims include improved memory and concentration, decreased cravings (especially when it comes to smoking and dieting), as well as improved athletic abilities and athletic performance.
Although it is unsure whether or not participants where just experiencing the placebo effect, several studies using binaural beats have shown that at certain frequencies these sounds can enhance relaxation and reduce stress.
Those who conducted the various studies were able to determine the ideal frequency level for enhanced meditative focus, which ended up ranging between 7 Hz and 15 Hz.
One of the most intriguing studies involving binaural beats involves their use when it comes to pain management. Although no studies have concluded that binaural beats can reduce pain, musicians overall have been found to be better at coping with pain and report instances of pain less frequently than non-musicians.
It is un-conclusive whether or not this is due to the music overall or because of the binaural beats involved in music and music production.
Some people claim that binaural beats used at specific frequencies can stimulate certain glands to produce desired hormones. Binaural beats have also been used in studies attempting to increase dopamine levels and stimulate lucid dreaming.
Therapists and psychiatrists working with patients with PTSD or other illnesses that interfere with their ability to recall memories have used binaural beats to help recover repressed memories.
Although studies are unconclusive still, it is theorized that binaural beats at certain frequencies can improve cognition and may even be able to improve a person's IQ.
© 2014 Kathleen Odenthal

![Deep Theta : High Coherence Soundscapes for Meditation and Healing [Clean]](https://m.media-amazon.com/images/I/51q5y5w++yL._SL160_.jpg)