Quantity Theory of Money in Economics : A Brief Note

Quantity theory of money is one of the important part of macro economics. Since money matters has more important. The theory has long age as money. Actually the initial feeds of the theory was introduced by dawan zatti an Italian economist in 1588. Later the theory was modified by different economists like Irvin fisher, ac pique and j.m Keynes till the 20th century. Any how, now Quantity theory of money has two versions
1 – cash transaction approach
2 – cash balance approach
Each of them are described briefly as below
1 – cash transaction approach
Cash transaction approach of quantity theory of money was developed by Professor: Irvin Fisher. He also introduced a equation to explain the theory. So, it is also known as Fisher’s equation of exchange. Simply the theory dealing with the relationship between supply of money and price level. In short, the theory states ‘ any changes in the supply of the money will be resulted in the same proportional change in the price level. Which means when quantity of the supply of money increases the price level also increase’. That is a positive relation between quantity of money supply and price level. Further the theory also states that ‘ any changes in the quantity of the supply of money will inversely affect the value of money’. Which means when the money supply increases the value of money will decrease. So there is a negative relationship between quantity of money supply and the value of money.
Equation of the theory by Professor: Irvin Fisher
To explain the theory, Professor: Irvin Fisher introduced a equation popularly known as the ‘equation of exchange’, the equation is algebraically showing below.
MV = PT
In the equation M = quantity of money
V = velocity of money
P = general price level
T = total volume of transaction
Velocity of money : - velocity of money refers to the total number of times the money is circulated in an economy or the number of times, the money is changes from hands to hands
In the left hand side of the equation (MV), is the supply of money and the right hand side of the equation (PT), is the demand for money.
To explain the theory we assume that, V and T in the equation are constant. Then quantity of money (M) is vary directly with price level (P). Any way in summary the theory suggest two major facts occurring in an economy due to changes in the quantity of money supply. They are
A – when money supply increases the price level also in increases ( will doubled)
B – when money supply increases the value of money will decrease ( will become half )
Diagrammatic representation of the theory
The transaction approach of the theory can be represented as showing in the graph below.
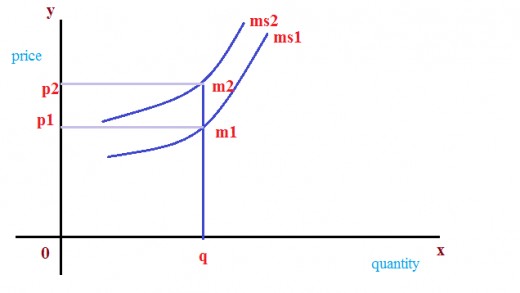
In figure 1, the total quantity of output is represented on the ‘x’ axis and the price level on the ‘y’ axis. And consider the quantity of output is constant at the level of ‘Q’. And MS1 is the initial supply curve of money M1 is the quantity of supply of money. Where the price level is P1. then suppose, an increase in the supply of money from M1 to M2, then the price level also increased by P2 from P1. It showing a direct relationship between quantity of money supply and the price level.
2 – Cash balance approach
This is the second version of the quantity theory of money. Actually the major contribution to the development of the cash balance approach labelled in the name of famous economist A.C. Pique. The cash balance approach is explained with the help of the Cambridge equation. So, the cash balance approach is also called as Cambridge version. The significance of the Cambridge version is it is not only considered on the supply of money but also focuses on the demand for money.
The Cambridge equation derived from the same equation of exchange, that is MV=PT. Then the equation is solving for M, then we will get
M = PT/V
The equation can be rewrite as given below.
M = 1/V * PT
For simplicity we can take ‘k’ in the place of 1/V. So, the equation become
M = KPT
In the equation M = money supply
P = price level
T = total volume of transaction
K= the demand for money the people want to held in hand
Since, K is equal to 1/V the velocity of money and the demand for money as a store of value is inversely related. In simple words the people demand money to held in hand is inversely related with the velocity of money.
Conclusion
Quantity theory of money is one of the most important theory in Economics dealing with the relationship between supply of money and price level, value of money etc. the theory stating that there is a direct and proportionate relation can be see between supply of money and price level, and a indirect relationship between supply of money and the value of money.
In short, now, quantity theory of money has two versions, namely cash transaction approach and the cash balance approach. The cash transaction approach emphasizes on the supply of money while the cash balance approach highlights the demand for money.
Keynesian View on Quantity Theory of Money
Keynes reformulated the quantity theory of money introduced by classical economists which was based on the assumption of full employment. According to quantity theory of money money supply and price level are vary in a direct way in a certain proportion. But later, J.M Keynes reformulated the same quantity theory of money by adding the theory of interest.
Keynesian's view was based on many assumptions as showing below.
a) the factors of productions are perfectly elastic and there exist unemployment in the economy.
b) All unemployed factors of production are homogenous in nature, that is one factor can use instead of other factor.
c) And all these factors are based on the Constant Return to Scale. When a certain percentage of factor input increased, it will give same proportionate increase in the output.
Based on this assumptions, Keynes argue that, the increasing of money supply resulted in the reduction of interest. Once the interest rate is declined, people invest their money (capital formation) instead of depositing with bank. Gradually the increasing of investment reduce the unemployment and increase the income. Since the factors of production are based on Constant Return to Scale, there is no possibility to increase the price of the commodity. And there is no any chance for raising the price proportionate to raising money supply. In short, after the full employment is attained (all resources are utilized) the increasing money supply varies directly with price level.