Causes Of Deafness and Hearing Impairment
How sound is your Hearing?

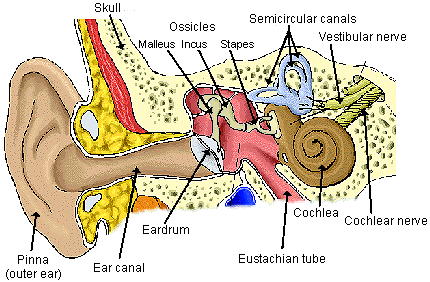
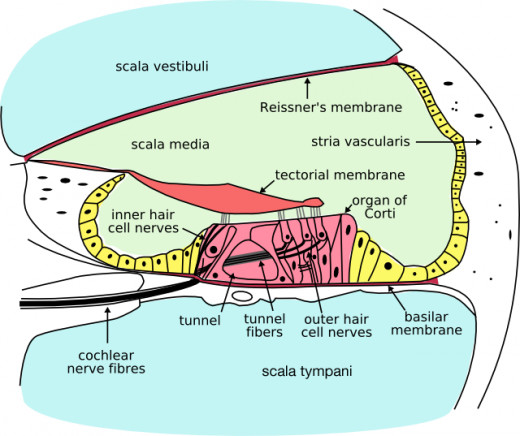
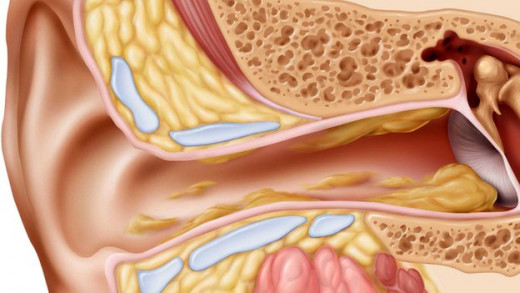
Anatomy of the ear
Hair Cells Within the Cochlea of the Inner Ear
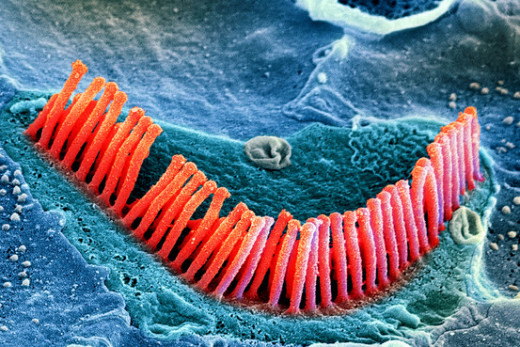

Parts of the Inner Ear, showing the Cochlea
Symptoms and early signs of Hearing impairment
You may have early signs of hearing loss when:
- You have difficulty in understanding what people are saying
- Your family complains that TV or radio are too loud
- You find that sounds are muffled, often need to ask people to repeat their sentences
- You avoiding social situations, because of inability to communicate properly
- You have trouble using the telephone
- You have whistling, buzzing, ringing or humming in the ears
Deafness Facts
Deafness is the complete loss of hearing in one or both ears, hearing loss is both complete and partial loss of the ability to hear.
- One in three people suffers from hearing loss by the age of 65.
- 60% of people with hearing loss are in the work force or in educational settings.
- An estimated 30 children per 1000 have some degree of hearing loss.
- The most common causes of hearing loss in adult is due to noise and aging.
- Changes in the inner ear due to presbycusis or age-relating hearing loss happen slowly, it may be mild or severe but always permanent.
- Sudden noise induced hearing loss such as gunfire and explosions is the highest cause of disability in recent wars.
- Most people with moderate to profound hearing loss live in low or moderate income countries.
- There are 360 million people world wide with disabling hearing loss.
- Chronic ear infections are major causes of hearing loss. Chronic otitis media range from 1% to 46% in both developed and developing countries.
- Noise is a leading cause of avoidable hearing loss. The risk of social noise is increasing globally among young people.
- Some frequently used medication such as aminoglycosides and anti-malarial drugs can cause irreversibly hearing loss.
- Around 0.5 to 5 of every 1000 children are born with or develop disabling hearing loss in early childhood.
- With public health actions, 50% of hearing loss is preventable through immunization, healthy ear, hearing care habits and effective treatment for acute and chronic ear conditions.
- An estimated 56 million people world wide uses hearing aid, the current hearing aid production meet only 3% of the need in developing countries.
- Generally, severe tinnitus or (ringing in the ears) will accompany hearing loss and can be just as debilitating as the hearing loss. about 1:10 adults in the UK have mild tinnitus, up to 1% have tinnitus that affects their quality of life.
- Causes of hearing loss include a build-up of earwax, foreign object in the ear, injury to the head or ear, infection, ruptured eardrum and conditions that affect the inner or middle ear.
Hearing loss, UK's Statistics

Protect hearing from noise at work
Noise in the work place

Hearing Impairment may be caused by a build up of ear wax
Causes of Deafness and Hearing Impairment
We are living in a noisy world, the incidence of deafness and hearing impairment is growing. The ability to hear and distinguish sound is said to be one of the most important of our five senses.
However, if I were to ask the blind man, which of his senses are more important to him, he will answer my sight, the masseuse will say touch, for the florist and perfumer it may be the ability to smell, for the gourmet chef it's all about the taste.
All five senses are important to us, but the lack of some senses can be more disabling than others. Partial or complete loss of hearing is referred to as deafness, hearing loss or hearing impairment.
Some people have an acute hearing; they are said to be able to hear a pin drop, while others who are profoundly deaf, exists in a world without sound.
Voltaire referred to the ear as " the road to the heart." Sound can have a profound effect on our emotions. Most people find it near impossible to turn a deaf ear to an infant's cry; this particular sound can trigger emotional responses in the brain like no other sound can, even in people who are not parents.
Listening to romantic music can indeed stir the emotions, while persistently loud, unpleasant noises have been known to drive people to the brink of insanity. Sound can also have an adverse impact on our health. A loud bang close to the ear, such as an explosion, gunshot, or long-term exposure to noises like loud music and machinery, can damage the delicate organs of the inner ear to cause irreversible hearing loss and deafness.
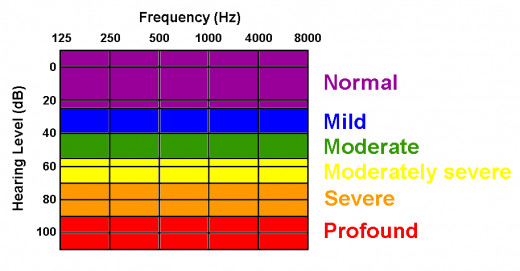
Hearing impairment or hearing loss is defined by the quietest level of sound an individual can hear and is known as the hearing threshold measured in decibels (dB).
The hearing threshold is used to categorise an individual's ability to hear. Normal hearing is classified as no impairment. Hearing impairment may be mild, moderate, severe or profound.
Individuals with mild hearing loss may find it difficult to follow speech in a noisy situation. For people with moderate hearing loss, following speech without the use of a hearing aid can be a real challenge.
An average of 40dB to 69dB would be the quietest sound someone with moderate hearing loss will be able to hear.
Where there is a severe hearing loss, the individual relies a great deal on lipreading even when a hearing aid is used, the quietest sound this person can hear average around 70dB and 94dB.
Someone with a Profound hearing impairment has an average threshold level of 80dB or worse and may not be able to hear any sound at all.
One of the very first sense we develop while still safely cocooned within our mother's womb is sound, the most powerful sound to the growing fetus is the sound of its mother's voice.
Research shows that a five seconds stimulation can cause changes in the fetal heart rate and movement that can last up to an hour. It is widely believe that the last sense we lose before we die is our ability to hear.
Personally, I find it hard to imagine a world without sound. sweet, soothing music that helps us relax, the natural sound of a babbling brook, the wind in the trees, birds singing, raindrops on windows. For many of us, certain types of music can move us to tears. Conversely; research has suggested that the body can react negatively to loud noises such as aeroplane sounds, even as we sleep.
New research has shown that the human body respond to some noise by producing stress hormones, hormones that are usually produced when we perceive a threat, they prepare us for fight or flight.
The exposure to loud noises can also trigger a surge of stress hormones that causes a rise in blood pressure, heart rate and disturbances in the hormonal balance, with certain health implications. All these conditions can be precursors to cardiovascular disease. The adverse effects of noise on our physiology are also seen in children.
A 1990s study of children in Munich, during a period before and after the city airport was closed, found that stress hormone levels were higher in these children and memory and reading comprehension were lower. There were a marked improvement in the scores once the airport was moved to a different location. However, children who were newly exposed to the sonic noise, displayed the same detrimental effects.
Disabling Hearing Loss as Defined By The World Health Organisation (WHO)
“Disabling hearing loss refers to hearing loss greater than 40dB in the better hearing ear in adults (15 years or older) and greater than 30dB in the better hearing ear in children (0 to 14 years)”
The UK charity organisation, Action on Hearing Loss, have estimated that over 10 million, or 1 in 6 people in the UK have some degree of deafness or hearing impairment.
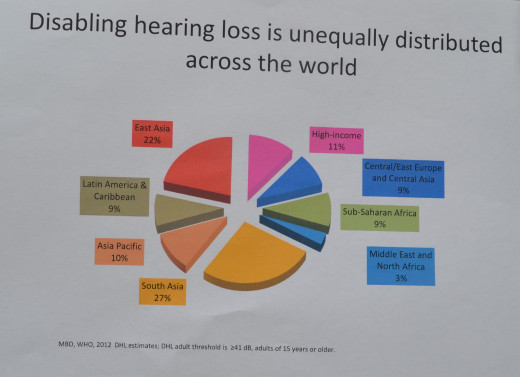
According to the WHO, 5.3% of the world's population, that is 360 million people worldwide, are affected by disabling hearing loss:
-
328 million or 91% are adults
-
183 million are male
-
145 million are female
- 32 million or 9% are children
Approximately 1/3 of people over the age of 65 years are affected by disabling hearing loss
Loss of hearing can happen suddenly, but more often, it develops gradually over a period. Many of us are living and working in environments where the noise levels are above that which is safe, although there are health and safety laws in place to prevent this.
I began to experience mild deafness and intermittent buzzing in the ear (tinnitus) a few years ago; I'm pretty sure that I sustained a degree of hearing impairment from years of working in close proximity to a lot of extremely loud intensive care equipment.
For critical care nurses, it is impossible to avoid the daily assault of noise on the eardrums. ICU nurses must, at times work in enclosed cubicles where they are constantly bombarded by noise from monitor alarms, infusion pump alarms, dialysis machine alarms and the constant rhythmic humming of ventilators on a daily basis.
Thankfully; while Critical Care Units will always be far too noisy, most of the old equipment are now updated with next generation quietier models, with a positive impact on noise levels. Unfortunately, for those of us who soldiered on through the 70s, 80s and 90s the damage is already done.
We've known for a long time that regular prolonged exposure to noise is a risk factor for hearing loss. More than 30 million American are exposed to hazardous levels of sound on a regular basis. Noise Induced Hearing Loss or (NIH), may be caused by a single exposure to an intense impulse sound, or by continuous exposure to loud sounds over an extended period.
What is Tinnitus
Tinnitus is typically described as ringing, buzzing, humming, singing, whistling or whooshing in the ears. Research has shown that if left in complete silence in a sound reduction chamber, tinnitus would become apparent in the majority of people. In a silence environment, 90% to 95% of people have reportedly experienced the odd incidence of tinnitus.
Ringing in the ear, deafness and hearing loss affects a large section of the population. the incidence of people with hearing loss have doubled in the past 30 years.
A study led by researchers at Johns Hopkins show that almost 20% of Americans aged 12 and older have hearing loss sufficiently severe to make communication difficult.
Around 30 million people in the US were found to have hearing loss in both ears, 48 million had hearing loss in one ear.
Hearing loss is divided into two main types, conductive and sensorineural. When the two kinds of hearing loss are present at the same time, this is referred to as “mixed” hearing loss.
Conductive hearing loss
Conductive hearing loss occurs when sound is unable to pass freely to the inner ear. This type of hearing loss can be due to a build up of ear wax in the ears, or as commonly occurs in children, an infection resulting in the build up and accumulation of fluid in the inner ear.
Abnormalities in the structure of the outer ear, middle ear or ear canal can also result in a conductive hearing loss, as do ruptured eardrum.
Otosclerosis is a condition that causes abnormal growth of bone in the middle ear, resulting in a severe conductive hearing loss, when the ossicles in the middle ear are unable to move freely. This type of hearing loss causes the sound to become quieter, while not necessarily distorted.
Conductive hearing loss can be temporary or permanent based on the cause and may be corrected by minor surgery or medical management.
Sensorineural Hearing Loss
The majority of sensorineural hearing loss is caused by abnormalities in the hair cells found in the organ of Corti in the cochlea. Sensorineural hearing loss is usually referred to as sensory, cochlea, neural or inner ear hearing loss or impairment, and can also involve the auditory portions of the brain. This type of hearing loss changes the ability to hear quiet sounds and reduces the quality of the sound heard.
An individual with sensorineural hearing impairment will find it difficult to understand speech. Once the hair cells of the cochlea are damaged, they remain damaged, sensorineural hearing loss is irreversible.
The cochlea can become damaged naturally as a result of the ageing process; this is referred to as age-related hearing loss or presbycusis.
© J. Alexis-Hagues 23/05/2014
Tinnitus is likened to an angry bee buzzing inside the head

Exposure to prolonged noise can cause hearing impairment

Causes of Sensorineural Hearing Loss
Sensorineural hearing loss
| Causes
| Treatment
|
|---|---|---|
Age
| Gradual damage to the hair cells
| Sensorineural hearing loss is irreversible and permanent. Once the sensitive hair cells in the cochlea are damaged, they remain damaged and cannot be repaired. However, where hearing is impaired, the condition may be improved with certain treatment such as hearing aids, cochlear implants and auditory brainstem implants
|
Noise
| Noise induced hearing loss are caused by exposure to extremely loud noises, acoustic trauma may result from exposure to high decibel noise like an explosion.
| Early intervention may have a role in the medical treatment of acoustic trauma. Animal studies have shown that hyperbaric oxygenation and corticoid therapy can result in significant improvement in recovery.
|
Ototoxic drugs
| Drugs that are toxic to the ear, more spicifically, the cochlea or auditory nerve. Drugs include antibiotics in the aminoglycosides group, diuretics such as frusemide and platinum based chemotherapy agents and some nonsteroidal anti-inflamatory drugs (NSAIDS).
| |
Viral infections of the inner ears
| Measles and Mumps
| |
Viral infections of the auditory nerve
| Mumps and Rubella
| |
Meniere's disease
| Increased pressure in the inner ear due to a build up of fluid.
| |
Acoustic neuroma
| Benign growth on or near the auditory nerve
| |
Meningitis
| An Infection of the protective membrane surrounding the brain and spinal cord
| |
Encephalitis
| Inflammation of the brain
| |
Multiple sclerosis
| neurological condition affecting the central nervous system
| |
Cerebral vascular accident or stroke
| blood supply to the brain is interrupted or cut off
| |
Vasculitis
| Inflammation and swelling within the ear.
| Inflammatory conditions such as vasculitis and acute sensorineural loss are treated with steriods
|
Autoimmune inner ear disease
| Damage to the inner ear by antibodies or immune cells.
| Hearing impairment may respond to steriod treatment.
|
Genetic predisposition
| ||
Certain birth complication
| ||
Injuries to ears or head
| The structure of the inner ear can be injured by trauma to cause bleeding, fluid imbalance, ruptured ear drum or damage to the cochlea causing temporary or permanent hearing loss.
|
Always see your doctor if you are concern about hearing loss.
Ototoxic Drugs that can cause hearing impairment
The Cochlea, Construction of a Computational model
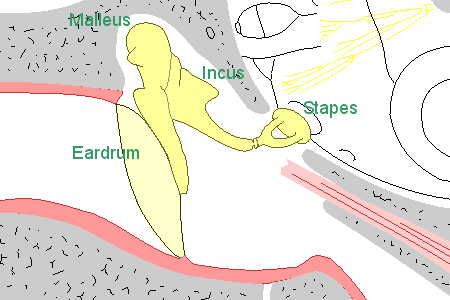
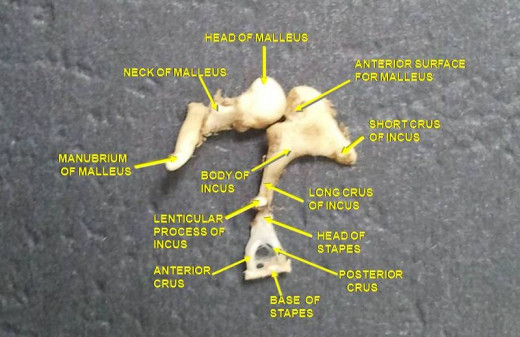
The Ossicles
Causes of hearing loss
Do you suffer from hearing loss, if yes, what do you believe caused it?
How we hear
The ear is divided into three parts:-
The Outer ear
The outer ear is known as the 'pinna' with ridged cartilage covered by the skin. Sound travels through the air in waves that enter the outer ear and moves through short tunnels approximately 25 millimetres long. When the sound waves reach the thin layer of skin known as the tympanic membrane or eardrum, it vibrates.
The Middle ear
The pressurised space behind the eardrum is the middle ear whose job is to transmit sound from air to fluid efficiently.
Sound travels from the outer ear causing movements of the eardrum and the three small bones, known collectively as the ossicles and conduct sound vibrations from the eardrum to the inner ear.
The fluid-filled inner ear converts sound into nerve impulses which it sends to the brain.
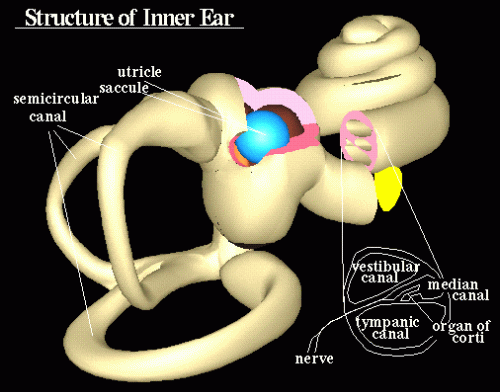
The Inner ear
The semicircular canals in the inner ear, also known as the bony labyrinth serve as the balance organ. The cochlea acts as the body's microphone filled with a watery liquid that moves to vibrations from the middle ear.
As the fluid moves, thousands of 'hair cells' also moves causing a motion that converts into electric signals. The signals communicate through neurotransmitters to the large numbers of nerve cells that are subsequently interpreted by the brain as sound.
Structure of the middle ear