Liver Protection - A Natural Approach
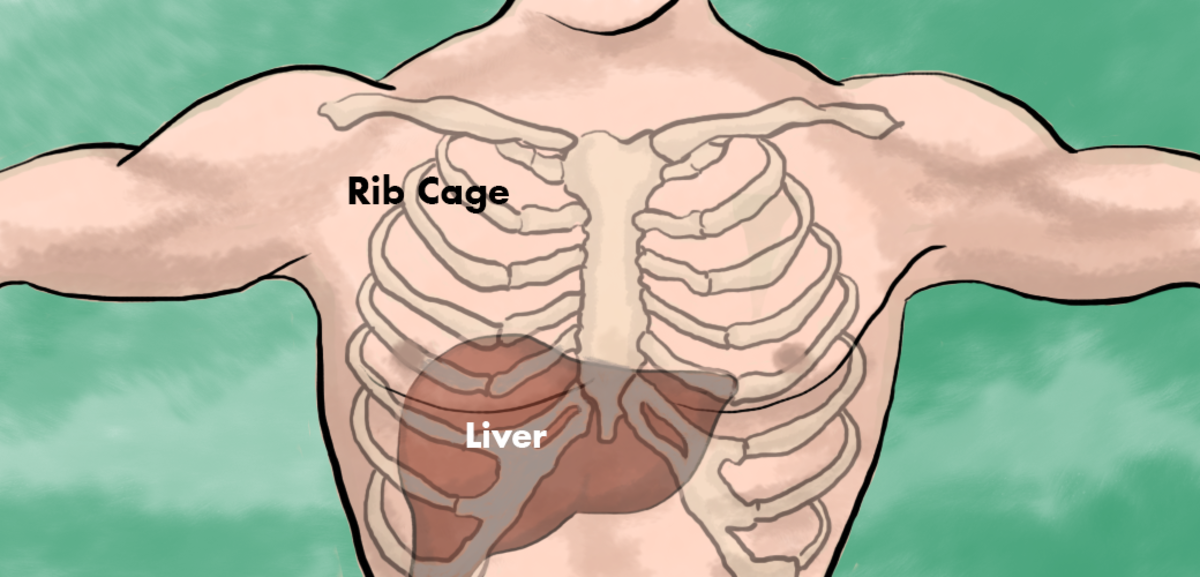
Liver Position
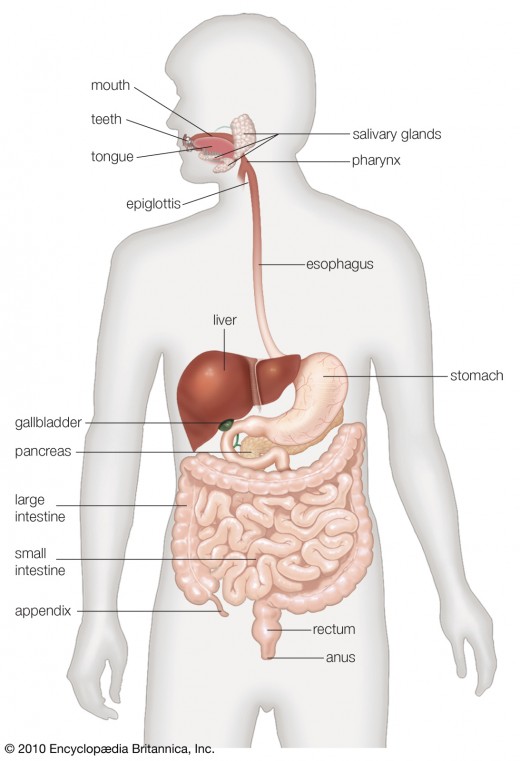
Discussion of the Liver
The liver is a very large organ (it goes almost all the way across the top of the abdomen in humans) with a great number of functions, all of them vital. Partly because almost all substances absorbed by the gastrointestinal tract (one exception being the small amount of alcohol absorbed in the stomach) go through the liver first, it is also quite easily damaged. Fortunately, the liver is also quite good at healing such damage, but there are limits which are sometimes reached.
The liver’s functions can be split into four categories; storage of nutrients, detoxification and filtering, production of bile, and metabolic processing.
Storage of Nutrients
The liver is capable of storing various nutrients, both obtained from outside the body and internally produced. The main internally produced nutrient stored in the liver is glucose, which is stored in the form of glycogen. Glycogen is similar in structure to starch, and is quite readily broken down into glucose when glucose is required as in exercise or after a period of fasting. Other nutrients stored in the liver include fat-soluble vitamins such as vitamins A and D (which is why cod liver oil is so useful as a supplement), fats, some minerals such as chromium and iron, and a few vitamins; the vitamin with the most storage in relation to requirements is probably vitamin B12.
Detoxification and Filtering
The liver filters out many toxins from the bloodstream, both from the hepatic portal vein (the specialised blood vessel that runs from the intestines to the liver) and the general circulation. It then detoxifies these toxins and gets rid of the breakdown products into the bile. The liver is also largely responsible for breaking down old, worn-out red blood cells and recycling what is recyclable; the remainder is also secreted into the bile in the form of bilirubin. Incidentally, bilirubin is the main pigment responsible for the normal colour of faeces. Another function of the liver is to get rid of hormones no longer needed by the body.
Production of Bile
Bile has two functions; to carry away toxins and metabolic breakdown products, and as part of the digestion. Specifically, bile has an emulsifying action, which means that dietary fat is broken down into very small globules so that the fat-digesting enzymes (lipases) can more easily break them down into useful fatty acids. The action of bile in this process is very similar to the action of detergents in removing greasy dirt from clothes and dishes.
Metabolic Processing
The liver is responsible for processing many nutrients obtained from the digestive system into forms that are actually usable; examples are pyridoxine (vitamin B6) being converted into pyridoxal 5-phosphate and beta-carotene being converted into retinol, the active form of vitamin A. The liver is also responsible for the formation of cholesterol for use elsewhere, and the formation of various non-essential amino acids and virtually all the proteins found in blood plasma. (Despite its bad reputation, cholesterol is actually an essential compound in the metabolism of all animals including humans.)
It ought to be seen, then, that a damaged liver is going to affect the health of the entire body.
Agents That Damage the Liver
As earlier noted, the liver can quite easily be damaged in various ways.
Physical Injury
The liver is quite well protected, as for the most part it lies under the bottom part of the ribs. However, damaging the liver is far from impossible; accident or deliberate physical assault can either make a hole in the liver or sometimes cause a blunt-trauma injury that causes bruising or even fracture of the liver. I won’t dwell on this anymore, because injury to the liver is a serious acute medical condition and even possibly a life-threatening surgical emergency. Vehicle accidents are probably the most common cause of this sort of injury. If you have that sort of injury - you should be in an ambulance or a hospital, not reading this! (And probably are in one.)
Chemical Poisoning
Many chemical substances, including some commonly consumed ones, have the potential for causing damage to the liver. The most common of these are probably alcohol in large amounts over a prolonged period, and paracetamol (acetaminophen) in excess or too frequently taken. Less common problem substances are amanita mushroom toxins (sometimes from eating such mushrooms in error) and chlorinated solvents commonly used in dry cleaning. The worst of the chlorinated solvents, carbon tetrachloride, is nowadays banned in most countries but the solvents in paint stripper (mostly dichloromethane) are fairly commonly consumed in the form of vapour absorbed into the lungs.
Disease
The various forms of hepatitis are probably the most obvious of these. Less common are the liver flukes that may be introduced into the liver by eating such foods as undercooked pork. There are also quite a lot of inherited metabolic disorders capable of damaging the liver. As might be expected, there are also various types of liver cancer.
All these diseases require medical treatment, although some forms of infectious hepatitis are sometimes self-limiting. However, it is possible to help the liver to recover from the damage caused by infectious disease.
Fatty Infiltration
Fatty infiltration, sometimes leading to cirrhosis of the liver, is a feature of liver damage caused by alcohol. Other possible causes of fatty infiltration are gallbladder disease (which causes bile to “back up” into the liver and therefore makes cholesterol excretion less efficient) and consumption of large quantities of heavily processed or heated fats, such as the hydrogenated and trans fats found in some margarines, processed foods and fried food.
Consumption of large amounts of processed starches and sugar can also lead eventually to fatty accumulations in the liver, in addition to the more obvious consequence of eating these foods; obesity.
Natural Aids to Liver Function
Diet
The usual remarks about helping your medical problems with dietary changes apply here. Eat as little processed food as possible. Eat less fried, particularly deep-fried, food. Eat less easily absorbed carbohydrate such as white rice and sugar. Eat less red meat. Eat more fresh, preferably organic, fruit and vegetables; eat more seeds, nuts and oily fish (if you are not a vegetarian, for the last item).
Foods that help particularly with liver problems include onions and garlic, which contain exotic sulphur amino acids that help liver detoxification. More semi-soluble fibres in the form of oat bran and fruit pectin also help, by preventing re-absorption of cholesterol and various hormone breakdown products.
Alcoholic drinks, particularly wines, are often seen as a dietary item rather than a drug. However, if your liver is already under stress or damaged then reduction or elimination of alcohol is a very good idea indeed.
Avoid Drugs
All drugs have to be detoxified by the liver; some cause more damage than others, a very common example being paracetamol (acetaminophen). The damaging potential of this drug is the reason why cold remedies containing it have a declaration on the label telling you not to use the product with other products containing paracetamol. This drug is probably the legal drug with the worst effects on the liver, and the fact that it is available in all sorts of outlets without prescription makes it worse. Prescription drugs have damaging effects on the liver too, but your doctor should be taking this into account.
Many illegal drugs have toxic effects on the liver, which is yet another reason not to use them.
The general rule about drugs is to use them as little as possible consistent with controlling any other health problems you might have.
Avoid Infection
Various forms of parasitic infestation (for example liver flukes) and infection can affect the liver. The simple solution to food-borne infection is to eat food that should be cooked only when it is thoroughly cooked, and to be careful about the source of uncooked foods. Some forms of hepatitis are blood-borne and also spread via sexual contact. This reinforces the advice above about illegal drugs, of course.
In some areas of the world, water can also be suspect. However, since water also potentially carries many other varieties of infection most people know not to drink suspect water. One point worth making is that freezing water generally doesn’t kill microbes - so be careful about ice cubes in some areas.
Generally, to protect the liver avoid infection of it.
Supplements
The nutrients needed to protect the liver fall into three categories; antioxidants, metabolic intermediaries and lipotropics. Antioxidants include vitamins C and E and also selenium; zinc is also important because it is needed for the production of various detoxifying and antioxidant liver enzymes. Sulphur amino acids including L-methionine, L-cysteine and N-acetyl cysteine (NAC) also help by boosting production of the tripeptide glutathione, which acts as an antioxidant in the form of the enzyme glutathione peroxidase. In fact, NAC in particular is so powerful as a detoxifying agent that it is used in conventional medicine as an aid against paracetamol poisoning.
Metabolic intermediaries are basically the B vitamins, particularly thiamine (vitamin B1). In fact, vitamin B1 is used in conventional medicine in very high doses for the treatment of people who have abused alcohol, including alcoholics. This is because thiamine forms part of alcohol dehydrogenase, and is used up in much greater amounts in people consuming large amounts of alcohol. This in turn leads to various deficiency diseases, but the liver’s being put under stress by having to get rid of large amounts of alcohol eventually damages the liver itself as well.
To get all these nutrients, high-strength multivitamin/mineral supplements are probably the best option.
Lipotropic agents are those involved in fat transport in the body. The main nutrients involved here are choline, inositol and carnitine (which is actually a dipeptide containing lysine and methionine). Lack of these nutrients can make worse any tendency to fatty infiltration of the liver. All three of these nutrients are available as supplements, often together.
Herbals and Botanicals
Dandelion root increases bile production, and also improves the action of the gallbladder in contracting when such is needed. This helps excretion of toxins in the bile.
Artichoke is protective of the liver and also helps bile flow.
By far the best botanical aid for the liver is the herb Milk Thistle, whose active constituent is silymarin. Silymarin is a mixture of compounds which not only have powerful direct antioxidant effects but also boost the production of glutathione peroxidase in the liver. It also helps synthesis of liver proteins and thus helps regeneration of the liver.
Silymarin is such a powerful agent that it has been successfully used as an aid for the liver poisoning caused by carbon tetrachloride and amanita (death’s cap) mushrooms.
Supplements of all these botanicals are readily available.