Peripheral Vascular Disease and Surgery
Future Career
What are you in school to be?
Outlined Resource for Educational Purposes
I. Vocabulary
A. Peripheral Vascular Surgery Terminology
Angioplasty- remodeling the lumen of a blood vessel.
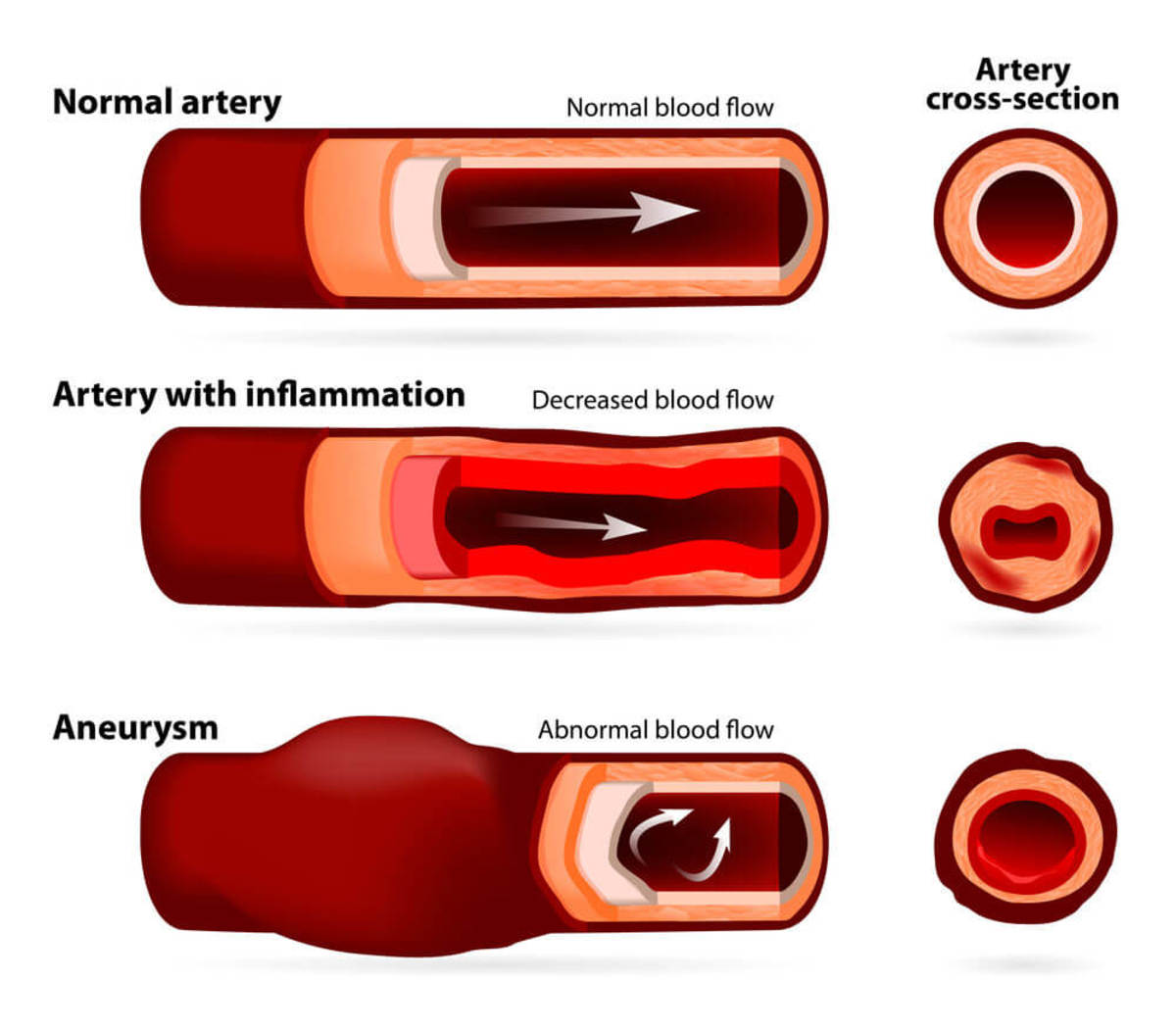
Arteriosclerosis- disease characterized by thickening, hardening, and loss of elasticity of the walls of arteries.
-
a) Atherocsclerosis- Most common form of arteriosclerosis. It is the formation of plaque.
-
b) Destroys intima layer in an artery by infiltrating the layer w/ lipids.
Arteriovenous fistula- AV Fistula, is a naturally occurring or surgically created connection between an artery and vein.
Bifurcation- a "Y"shap.
Diastolic pressure- Is the relaxing and lowest pressure, in a cardiac cycle.
Doppler Duplex Ultrasonography- Doppler ultrasonograpy amplifies sounds that pass through a vessel.
EEG, Electroencephalogram- A diagnostic tool measuring the electrical activity of the brain.
Embolus- A clot of blood, air, or organic material.
Endarterectomy- The surgical removal of plaque from inside an artery.
Hemodialysis- A process in which blood is shunted out of the body and through filters.
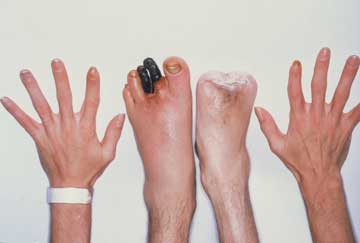
Infarction- A blockage in an artery
In situ- In natural positioning or normal place.
Intravascular ultrasound- A diagnostic tool in which a transducer is introduced into an artery, used to translate the physical characteristics of the lumen into a visible image.
Ischemia- Lack of blood flow to tissue.
Lumen- Hollow structure
Percutaneous- Through the skin
Stent- A tubular device placed inside an artery to hold it open. To treat and prevent strictures
Systolic pressure- Greatest amount of pressure, contraction phase of the Cardiac cycle.
Thrombus- Any organic or nonorganic material blocking an artery. ie: Blood clot.
Tunica Adventitia- The outermost layer of an artery.
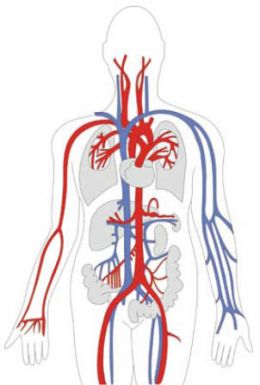
II. Anatomy of the Peripheral Vascular System-
A. Definition of PVS- The flowing of blood throughout the body.
-
1. Peripheral- The complex network of vessels whose function is to carry blood to all parts of the body.
-
2. Pulmonary- Begins with heart, through the lungs, interchanges de02 blood w/O2blood and returns to the heart via the pulmonary veins.
-
3.Systemic- Begins with the greater arteries of the heart. It involves the systematic interchange of de02 blood w/ O2blood. Arteries from the heart to all arterioles, capillaries, venules and then to the veins leading back to the heart.
B. Structures- Blood vessel tissue layers, except for capillaries. Which are the only blood vessels w/out layers. They are too tiny.
1. Tunica Adventitia- Outer layer, protective connective tissue layer.
2. Tunica Media- Middle layer, smooth muscle layer.
3. Tunica Intima- Inner layer, squamous epithelium which keeps blood cells from sticking to the inner walls of a vessel.
- (1) Differences between arteries and veins is that arteries carry blood away from the heart and O2 blood to the rest of the body. Veins are de O2, and carries blood back to the heart.
- (2) Blood Pressure is the force that is exerted on the arterial wall from the pumping action of the heart. (a) Systole- Contraction of heart muscle (b) Diastole- Relaxation
III. Equipment used in vascular surgery
A. Instruments Sets; are usually vascular and general surgery trays. Comprised of delicate fine tips, rt angels, Sarots, Collars, Bridges, Kellys, Aortic clamps, Bulldogs, Dietrich and Potts scissors, Cooley instrument and Debakey instrument
B. Suture; PTFE, Goretex, Prolene, Silk, Vicryl, Nylon. Double armed, CT-1’s Ur-5’s, FS-1,Sh 1 needles. Lots of times, suture is tagged w/ snaps or criles. Leave alone and expect to use shods.
C. Vascular Grafts; Used to replace a blood vessel or to make a patch.
C1. Synthetic grafts are made up of Dacron, polyester, or gore-tex.
-
a) Graft Tunneling- The tunneling through of subcutaneous tissue to connect one vessel to another.
C2. Patch grafts are autographs or bovine graphs sutured into place usually using Prolene stitches.
- (i) In tunneling surgeons like to use their finger to separate tissue that will est.an opening for tunneler, after a small incision is made. T Another instrument that plays an important in tunneling short distances, or to establish an opening is the Peon. Which is a big clamp that looks like an overgrown and heavier Kelly, with its blunt rounded nose, and long jaws.
IV. Various Vascular Tests used in surgery
A. Doppler scanning intensifies the sounds made by blood flowing through a vessel. The pitch, rhythm, and quality of the sound reflect pressure, vol., and flow rate.
- (i) Doppler Duplex Ultrasonography, combines Doppler scanning w/an ultrasound. This tool measures strictures, thrombi, and venous abnormalities.
B. Intravascular ultrasound- used in both peripheral and coronary surgeries.
-
a) It maps the lumen of a vessel. A transducer is introduced into a vessel to retrieve a visual image. It can be rotated 360 degrees.
C. Arterial Plethysmography- is a pulse volume recorder.
-
a) To perform the test 3 blood press.cuffs are placed around a leg, and inflated to 65mm Hg. The cuff readings produce a waveform reading which is compare to ea. other. A reduced wave is an indication of reduced blood flow at that point.
V. Surgical Procedures and Operations
A. Procedures
1. Retraction- is where a vessel is retracted by the aid of umbilical tape, vessel loops, feeding tube, or red rubber. They manipulate w/out trauma. Always pass with a snap. A tell-tell sign; Mixter or Gelpis are usually passed and used first.
2. Closures and Anastomosis-
- (a) Longitudinal & Circumferential incisions in blood vessels are closed with double-armed suture.
3. Hemostatis-
- (a) Suction- Poole and Yankuer suction tips are often used. (b) Meds and aids- Avitene, gelfoam, surgaseal, thrombin
4. Anticoagulation- Heparin
5. Vasospasms- Doctors sometimes like to use papaverine in the cases I have seen. However, in some operations expect your surgeon to use Lidocaine as an option.
VI. Surgical procedures-
A. Operations and Procedures
1. Intraoperative Angiography- Is to determine exact locations of strictures, occlusions or malformations contrast media is injected into an artery.
- (a) Often used in conjunction with Angioplasty for stent placement and embolectomy. This allows the surgeon to see the position of the stricture and place the catheter in the correct location.
2. Angioplasty- To reestablish the patency and circulation of arterial blood. Often performed on femoral iliac and carotid arteries.
- (a) It used to treat atherosclerosis or stricture of the blood vessel. (b) Performed during angiography w/ C-arm.
3. Stent- Is an implant that fits against the wall of an artery. Implant is a permanent fixture.
Two types Stents
- a) Balloon Expandable Stent- is a fine catheter with a balloon tip. The stent is fixed over the balloon, and when the balloon is expanded, the stent is pushed into position against the vessel wall. Most common type of expandable balloon stent is the Palmaz Stent. (i) A syringe called a tuberculin is used to expand the balloon.
-
b) Self-Expanding Stent- is a pre-loaded in a device and is passed over a guide wire. When the stent is discharged from the device, it opens up and adheres to the lumen wall. Most common type is the Wallstent.
4. Thrombectomy- Is an open procedure, to surgically remove a clot. Usually done with a Fogarty-type of catheter called of all things, embolectomy catheter.
- (i) Pulmonary emboli originate in the venous system of the lower extremities.
5. AV Fistula- Creates a larger venous access area for patients in need of renal hemodialysis.
6. Vena Cava Filter- Is the placement of a metal umbrella shaped filter to prevent emboli from entering the pulmonary system. The filter can be temporary or permanent. It is inserted via a needle.
-
a) Needle insertions are percutaneous approaches. Which means through the skin.
7. Carotid Endarterectomy- Obstruction of the carotid artery commonly forms at the bifurcation of the the artery at the internal and external branches. It is the remove of plaque that is temporarily occluding the artery. Critical phase is when the blood supply to the brain is interrupted. This period of occlusion is timed.
- (i) Internal Shunt Device is often employed to provide continuous blood flow to the cerebrum while plaque is removed. The internal shunt device is called a JAVID shunt. Must flush out w/NaCl before passing it to surgeon. If the shunt is used, a ring clamp called a Javid clamp and vessel tourniquets are used to maneuver and hold the shunt in place.
8. Saphenous Vein Harvesting- Harvesting of the vein from the leg for a CABG. This autograph is most commonly used as the bypassing graft.
9. Axillofemoral bypass- a way to create circulation betwn femoral arteries and the axillary artery to restore circulation. Indications for this is when lower extremities are deprived blood supply.
-
a) The shunt the blood directly from the femoral arteries through a femoro-femoral bypass to the axillary artery. Another indication is an infected aortic graft.
10. Femoral popliteal bypass- in situ grafting uses the saphenous vein as a shunt. Performed for atherocsclerosis of the femoral artery.
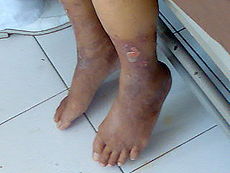
11. Varicose Vein Excision- Is where dilated and tortuous veins and their tributaries are surgically removed to prevent symptoms such as pain, swelling, and venous stasis which is the pooling of blood in the vessels.
-
a) They generally originate from the saphenous vein and its branches. Tributaries of the vein are often visible through the skin. Note this is surgical procedure is often performed for cosmic reasons.
12. A Triple A; Abdominal Aortic Aneurysmectomy with Graft Insertion- Is the bulging of the aorta in the abdominal cavity. However, they can occur at any location in the artery.
- (i) Dissecting aneurysm is one in which blood seeps between the layers of the vessel causing it to tear and split.
-
a) Vessel loops should be passed with a tag, such as a crile or snap.
-
b) Angiograms and ultrasounds are used to verify patency of the vessels.
-
c) Pedal pulses are monitored.
-
d) Hemostatic agents are applied to the suture lines until all bleeding has been controlled.
-
e) If there is a risk of excessive bleeding, despite cross clamping technique being used, a fogarty catheter w/ a 30ml is prepared to be used as an intraluminal tamponade in the aorta.
13. Aortofemoral bypass is performed to treat aortoiliac occlusive disease- Usually performed in patients with extensive calcification of the arteries.
14. Above the Knee Amputation- surgical removal of a leg. Usually performed because of a vascular insufficiency caused by arteriosclerotic or thromboembolic disease, that causes necrosis in lower limbs. Dexon and absorbable sutures are used.
- (i) In this procedure the end of the sciatic nerve is crushed using a heavy Kocher clamp. This is done to prevent the formation of a neuroma. A tumor at the end of a nerve.