Vitamin A - the vitamin of the eyes and skin!

Vitamin A is the generic descriptor for compounds with vitamin A activity, namely all-trans retinol and its derivatives, retinal and retinoic acid, which are the naturally occurring vitamins. Carotenoids are precursors which has the activity as vitamin A; a class of nearly 400 known naturally occurring pigments found in certain fruits, vegetables, oils and animal foods like egg yolk, milk and shrimp, of which approximately 50 are known to be biologically active as vitamin A. Of them β-carotene has the highest vitamin activity. Some carotenoids are absorbed intact and then deposited in various tissues, including fat depots, skin, shell, milk and eggs. Vitamin A molecules are extremely hydrophobic so they tend to dissolve in fat.
How is Vitamin A taken into the body?
In food the vitamin exists as esters, which are hydrolyzed in the duodenum, a process that is assisted by bile salts. Absorption of the retinol and carotenes is facilitated by fat in diet being associated with micelles formed during fat digestion. Dietary protein and zinc help utilization of both retinol and beta-carotene.
Absorption is aided by cellular retinal-binding protein type II situated on the epithelial cells of the small intestine. About 90% of dietary retinol is absorbed however β-carotene forms micelles less readily so only 60-70% is absorbed. In the absorptive cell, carotene is converted into retinal, which is reduced to retinol as the next step. Retinol is esterified with long chain saturated fatty acids and the esters are transported in to chylomicrones(molecule which transport fat from liver to peripheral tissues . They are remained in chylomicrone remnants when triglycerides are removed by lipoprotein lipase(enzyme on endothelial surface to remove triglycerides) and they are taken up by liver and stored there.
Where are they stored in the body?
Ninety percent of the body reserves of the vitamin stored in the liver. However plasma level remains constant. Retinol is mobilized from liver and transported in plasma to target cells as a complex with retinol binging protein (RBP). By that plasma concentration of retinol is maintained reasonably constant.
What are the functions of Vitamin A?
There are three active forms of the vitamin, retinol, retinal and retinoic acid and it has three main functions i.e. function in vision, a systemic function and a reproductive function. Only retinal can function in vision and retinol and retinal are equally effective in reproductive function. All three forms are effective on other target tissues, promoting growth and maintenance of tissues and resistance to infection.
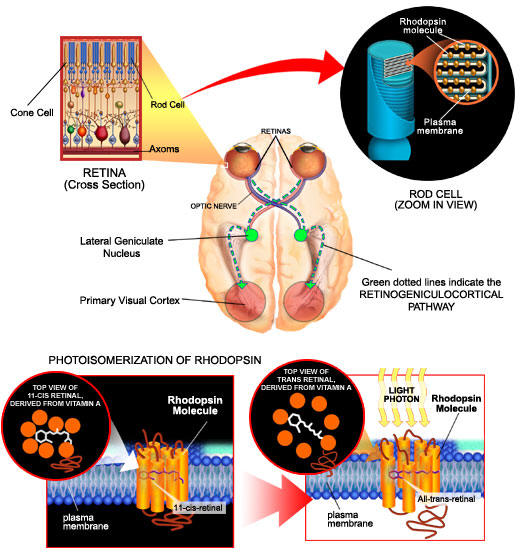
The visual function is the first to be deranged in a deficiency state although less than 1%of the vitamin in the body is involved in. Rhodopsin and iodopsin are photosensitive pigments contain in rod shaped and cone shaped nerve endings in the retina. Each pigment consists of a protein, an opsin, and an isomer of retinal which is 11-cis-retinal. When light falls on these end-organs, the 11-cis retinal is converted all-trans-retinal which separates from the opsin. This isomerization triggers off a series of chromophoric changes in the complex, affecting ion transport and membrane potentials, which is responsible for the nerve impulse. Rhodopsin is essential in photoreception in dim light, while bleaching of iodopsin is the basis of perception of high intensity and of color. Rod vision is the first to be affected in a deficiency, resulting night blindness.
The systemic function is also not very well defined like vision but it is shown by the effect of deficiency on bone and epithelium. In deficient state osteoblasts(cells which form bone) and osteoclasts(cells which dissolve away the bone) are distributed in areas different from those in which they are usually found; resulting osteoblasts to continue lay down bone while osteoclasts are not there to remove the excess bone. This causes lying of bone around foramina and on the inner side of long bones causing pressure on cranial nerves.
Epithelial tissue depends on vitamin A for their function. Epithelial tissue needs the vitamin for proper morphology and function. Retinoids powerfully affect the differentiation of a variety of cell lines in culture including neoplastic and non-neoplastic cells. They suppress the process of malignant transformation of non-neoplastic cells induced by various factors and epidemiological studies have linked diets rich in carotenoids significantly reduces the risk of many cancers. But it is important to appreciate that there is a teratogenic effect (causes deformities in fetus) with excessive use of retinol during early weeks of gestation.
The reproductive function of the vitamin is less well defined. In experimental animals the reproductive cycle is interfered with vitamin A deficiency.
There is a role of vitamin A in the immune process and in deficiency of vitamin increase infection rate. It is postulated that mucus producing cells are replaced by keratin producing cells in respiratory, gastro-intestinal and genitor-urinary tracts and in the corneal-conjunctival epithelium which results in invasion of organisms causing infections. Also vitamin A deficiency reduces the activity of macrophages. Lysozyme which is an antiviral substance depends on vitamin A for its synthesis. Deficiency also reduces T lymphocyte activity to viral infections and levels of immmunoglobulins in blood particularly immunoglobulin A.
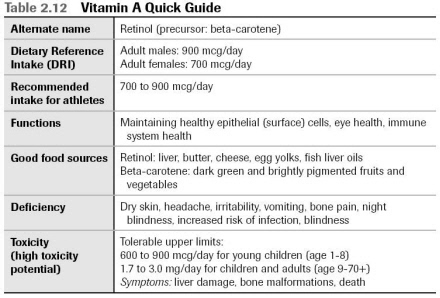
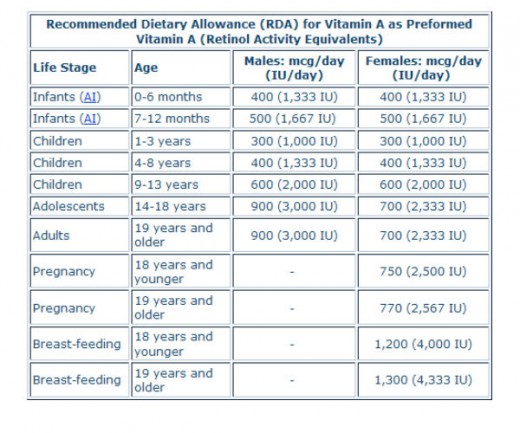
Daily Requirements of Vitamin A


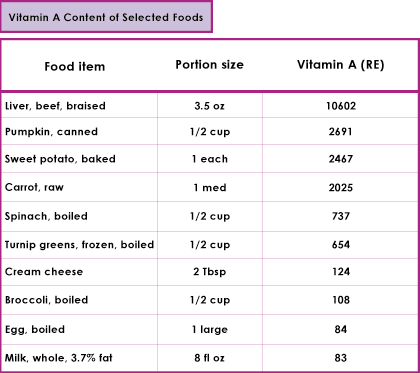
What are the sources of Vitamin A?
The dietary sources of vitamin A fall into two categories; vitamin A or all-trans retinol, also referred to as preformed vitamin A, and provitamin A which refers to those carotenoid precursors which are biologically active as retinol.
Provitamin A contained in dark green leafy vegetables, algae, red and yellow vegetables, red and orange fruits, flowers and juices.
Preformed vitamin A is in milk and milk products, eggs, shell fish, liver and organ meats, chicken, fish livers and fish oils.
What happens in excess - Hypervitaminosis A
Unlike most other vitamins, vitamin A has toxic effects with high doses since there is no way of elimination of the vitamin as it is fat soluble. Acute toxicity will give rise to sudden rise in intracranial pressure but it will resolve once it is withdrawn. Chronic toxicity will cause anorexia (loss of appetite), painful extremities, dry skin, sparse hair, enlargement of liver and spleen, anemia and periosteal thickening of bone.