- HubPages»
- Technology»
- Internet & the Web»
- Search Engines
Google :: Search Google :: Web Search Google :: Advanced Search Google :: Tips & Tricks Google

Google Search :: Google Web Search
Google searches can be conducted using Google Web Search from a number of different locations:
-
Google Homepage
- Google Results Page
- Google Chrome Address Bar
- Google Custom Search
Your Google Homepage is really your Google Web Search Homepageas can be seen by the 'Web' link at the top left of your Google Homepagewhere the link is not highlighted in blue. The Google Results Page not only shows results but also supports a couple of Google Search boxes. A Google Custom Search is conducted from website owners web content pages. You can also initiate a Google Search from your Google Chrome address bar (See Google :: Homepage Google :: Home Page Google :: Home Google Page :: Classic Home Page Google for more details).
Google Web Search searches through Google word indexesfrom web-sites with written content (see Google :: Search Engine Google by Humagaia).

Google Search From The Classic Google Homepage

Google Web Search :: Searching the Web By Accessing Google Word Indexes
The Google Search box is the place where you enter search word-strings to try to give the Google Search Engine enough information for it to access the Google word indexes and return results that are as relevant as possible to the search word-string that you have entered. The Google Search box is available from your Google Homepage, Google Results Page or from innumerable third-party web-sites that host Google Custom Search boxes.
Technically, matching the parsed search-string words with the parsed web-content words that have been indexed, is reasonably simple. Semantically, though, this is much more difficult. Each of us may use different words to try to access the same information. Web content providers should analyse the possible search queries that may be entered in the Google Web Search box to access the information that they are providing. They need to predict what search terms will be entered and insert those search terms into their web content. Only by doing this can Google word indexes be matched with search terms entered with words contained in web content. If the two don't match then the person searching for particular information will not be presented with a link to a website that supplies that information – both sides miss out.
It is not only the web content provider that needs to ensure that most search strings that would relate to their content are actually in their web content. It is also incumbent on the searcher for particular information to consider what relevant words might be in the web content they are looking for, that will have been indexed by Google. Only by both sides undertaking these tasks can the most relevant information be presented to the correct audience.
To make things easier, Google Web Search does give some assistance to the searcher in order for them to have a better chance of accessing the information for which they are searching. The Google Search Engine processes enormous numbers of searches. It has, since it's inception, undertaken to save, index, analyse and utilise these search strings to educate web content providers and to assist web searchers. For this article we are only interested in the latter.
When entering search queries Google Web Search gives a drop-down query-completed list of most-searched queries for the search-string entry to date. This is called Google Search Assist. You can utilise this Google Search assistance or not, as the case may be. The options available to you when entering a Google Search are to either:
-
click on one of the Google Search Assist options (which could also be versions of what you have entered, for instance some punctuation may be inserted such as “What's” from “Whats” - remember these could give different search list results on the Google Search Results Page) or
-
complete your Google Web Search query and click on [Google Search]. Your query is processed and the Google Search Results Page is presented, with results, or
-
complete your Google Web Search query and click on [I'm Feeling Lucky]. You are then taken direct to a web-page that Google thinks best matches your search query, bypassing the Google Search Results Page. This option can be utilised to access some specialised Google Web Search features such as Klingon, Pig-Latin, Elmer Fudd and various other Google Homepage variations. This option is only available on your Classic Google Homepage.
Each of the three Google Search locations: Google Homepage, Google Results Page and Custom Google Search pages will show a different maximum number of options for you to choose from. Your Google Homepage and Google Results Page will give a maximum of 10 options. Google Custom Search pages may be a lot less. This assistance can be switched on and off.
Google Search Assist
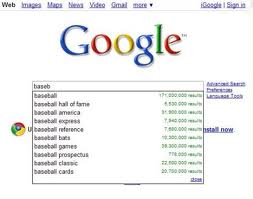
Google Search Assist :: How Does Google Search Assistance Assist?
Google Search Assist (Google predictive queries) assists by giving you, the surfer, options that expand and extend the search word-string that you have entered up to a point in time. So, if you have entered “Google Search”, the options you are presented with by Google Search Assist would be something like:
-
Google Search Engine
-
Google Search
-
Google Search History
-
Google Search Bar
-
Google Search Tips
-
Google Search API
-
Google Search Stories
-
Google Search Appliance
-
Google Search Tricks
-
Google Search Story
I say “something like” as the options change with the vagaries of the number of searches that have been made worldwide for the search string entered.
Another innovation supported by the new Google Search Assist function shows that Google finally understands that some searches are actually asking for a specific website. They have introduced an additional entry onto the Google SeachAssist drop-down list in the form of a blue direct link (with the website address below) to certain of Google's own (and rivals) major websites. For instance, if you type 'google maps' then the Google Search Assist box will show a blue link to Google Maps, as the first entry, with 'maps.google.com/' shown below; if you type in 'yahoo m' Google Search Assist will show a blue link to "Yahoo! Mail. The best web-based email!" as the first entry, with 'mail.yahoo.com/ shown below
Google Search Assist assists the web content provider by showing the current highest ranking search queries for the search word string that they have entered into the Google Search box. This can be invaluable in determining what words they should use in their web content to attract the highest audience numbers for that web content. As explained above, if their content does not match what surfers are typing in to access such web content, then surfer will never meet provider.
What Google Search Assist does not do and what would assist still further is to use Google's Semantic Lexicon to give you word alternatives for your search word-strings. This could be presented in the same way as Google Search Assist and be toggled between the two – just a suggestion! It could be called Google Search Synonyms. The Google Search Engine does use synonyms in its search process but does not give you the options.

Lawrence Page & Sergey Brin

Google Search :: Google Search Facts
Google Search can be as simple as you want it to be. The majority of surfers utilise Google Search in its very basic form: enter some search terms in the Google Search box and press 'Enter' or click the [Search] button. That's it!
But are we getting the most relevant results for our efforts? Probably not!
Here are some things you should know which will assist you in getting those most relevant results from your Google Web Search efforts:
-
Every word you enter in the Google Search box will be used. The more you enter the less results you will get. This may mean you lose some results that would be of use. The exception to this is that prepositions and conjunctions are not normally used (unless within a phase contained between quotation marks -see below). Thus words like 'the,' 'a,' and 'for,' will be superfluous from a Google Search point of view.
-
It does not matter if you capitalize any words, they will be used as if they had not been capitalized. Google searches are case insensitive.
-
There is no need to punctuate your searches: punctuation is pretty much ignored.
-
Apply the KISS (Keep It Simple Stupid) principle to your searches. If one word will do, don't use any more. Think before you type.
-
Think what words might be used by the web content provider to describe things. These are the words that the Google Search Engine uses in it's index – it has no other words to use! You will be accessing the Google word indexes not the web pages themselves. Your words will be matched with the words recorded in the Google word indexes for websites.
-
Start your Google Search with as few descriptive words as possible. If you get too many irrelevant results you can always add some additional words later to limit the number of results returned.

How To Use Quotation Marks In Google Search Terms
Google Search :: Additional Search Parameters
Most of the time the basic Google Search process is sufficient for you to obtain the Google Search Results you need. There are a few situations, though, where you might find some additional Google Search functions useful. Google Search supports the following additional search functions:
-
Phrase search ("…......") - by typing double quotes at either end of a phrase, the Google Search Engine will search it's word indexes for those exact words being next to each other in the order you have entered within the double quotes. You may inadvertently miss some results though.
-
Term exclusions (-) - if you place a minus sign before a word you are telling the Google Search Engine that you do not want results with this word in them. This can be done for words and also before a 'site:' operator (no space) to exclude a specific website from your Google Search results.
-
Wildcard (*) - if you include this very powerful, but little used, parameter in a Google Search query, you are telling the Google Search Engine to 'insert one or more unknown words' into your query and to find the best matches. Play with this parameter to find out how powerful it is.
-
Exact match (+) - if you want to turn off the Google synonym matching function (which is the standard, and undertaken automatically), then attach a + to the beginning of a word (without a space between them). If you place the + before a word you are telling the Google Search Engine to match precisely the word as typed. You could, of course, alternatively, put double quotes around a single word which will achieve the same result.
-
Allowed alternatives (OR) - if you want to allow one or more of several words, use the OR (in all caps) parameter.

Google Search Operators: Define
Google Search Operators: Link
Google Search Operators : Site
Google Search Operators: Filetype
Google Search Operators: Inurl
Google Search Operators: Allinurl
Google Search Operators: Intitle
Google Search Operators: Allintitle
Google Search Operators
Google has many additional search operations beyond just the normal way that you utilise Google Web Search. One set of additional Google Web Search facilities is the Google Search Operators. This group of operators can be very powerful when you want to make very specific searches on subsets of information that are contained in web content pages for which you may be searching. The Google Search Operators are:
- Define:
- Link:
- Site:
- Filetype:
- Inurl:
- Allinurl:
- Intitle:
- Allintitle:
- Intext:
- Allintext:
- Inanchor:
- Allinanchor:
If you want to define a term that you are unfamiliar with, all you need to do is type 'Define:' [Term] into the Google Search box (where [Term] is the term you want defined e.g. PDSA), hit return and a definition of the term you want to define is returned in the Google Results Page.
If you want to find out what web-sites are linking to another web-site all you need to do is type 'Link:' [Web Address] into the Google Search box (where [Web Address] is the web address of the site you are interested in), hit return and links to all the web-sites that link to the web-site you are interested in are returned in the Google Results Page.
If you want to search a specific site or specific types of site all you need to do is type 'Site:' [Web Address] for a specific website or 'Site:' [.tld] (where [tld] is a top level domain such as com or edu or co.uk or gov.uk etc.), hit return and your Google Search will be conducted against the specific site or the specified TLD and results returned in the Google Results Page.
If you want to search specific filetypes like Adobe Acrobat (.pdf), Microsoft Excel (.xls) or Shockwave Flash (.swf) then all you need to do is type 'Filetype:' [filetype] (where [filetype] is the filetype extension{without the full stop}), hit return and the Google Search Engine will search for your search words that are in that filetype. You can also use 'Ext:' [filetype extension] to obtain the same results. A full list of supported filetypes is available in the advanced search section of this article.
If you want the search word you have entered in the Google Search box to occur in the URL of a webpage then all you need do is type 'Inurl:' [word], hit return and you will have website links returned where that search word occurs in the URL of each returned website.
If you want more than one search word to occur in the URL of a webpage then all you need do is type 'Allinurl:' [words], hit return and you will have website links returned where those search words occurs in the URL of each returned website.
If you want the search word you have entered in the Google Search box to occur in the title of a webpage then all you need do is type 'Intitle:' [word], hit return and you will have website links returned where that search word occurs in the title of each returned website
If you want more than one search word to occur in the title of a webpage then all you need do is type 'Allintitle:' [words], hit return and you will have website links returned where those search words occurs in the title of each returned website.
If you want the search word you have entered in the Google Search box to occur in the text of a webpage then all you need do is type 'Intext:' [word], hit return and you will have website links returned where that search word occurs in the text of each returned website
If you want more than one search word to occur in the text of a webpage then all you need do is type 'Allintext:' [words], hit return and you will have website links returned where those search words occurs in the text of each returned website.
If you want the search word you have entered in the Google Search box to occur in the anchor text of a webpage then all you need do is type 'Inanchor:' [word], hit return and you will have website links returned where that search word occurs in the anchor text of each returned website
If you want more than one search word to occur in the anchor text of a webpage then all you need do is type 'Allinanchor:' [words], hit return and you will have website links returned where those search words occurs in the anchor text of each returned website.
Google ~ (tilda) Search Operator
Google Search: Tips & Tricks
Google Search :: Google Search Tips and Tricks
In addition to the Google Search operators above, there are a number of methods for getting specific information returned for non-standard Google searches. The first dozen tips / tricks are further Google Search operators:
- Define: [word] - this is a look-up for a word definition.
- Cache:[website URL] - if you want to use Google as a proxy and use the cached version of a website. This could be utilised to access blocked sites.
- Movie: [Name of Movie] - to get movie reviews etc.
- Stocks: [stock ticker symbol] - to obtain information about that stock.
- Phonebook: [name] - to get all phonebook listings.
- Rphonebook: [name] - to show residential phonebook listings.
- Author: [name] - to find Google Groups messages from a particular author.
- Group: [group name] - to find messages from a particular newsgroup.
- Insubject: [words] - to find Google Groups messages containing the words in the subject line.
- Location: [location] - to find News articles from that location.
- Source: [source] - to find News articles from that source.
- Store: [store] - to find Froogle articles from the specified store.
The next four use 'in' as an operator:
- Time in [place] - gives time wherever.
- Convert [number of measure] in [measure] - such as "convert 1 litre in gills'.
- Weather in [place] - self-explanatory I think.
- Currency [number of currency] in [currency] - such as 'Currency 1 dollar in pounds sterling'.
There are a number of very specific search functions:
- Math - just type in a mathematical problem.
- [#............#] - search within a range of numbers (these can be dates, years etc and combined with words specified outside the range operators. Play with this operator, you will be surprised how powerful it is, especially if used with a wildcard. Try 'kings * #1939 1945#' for instance.
- ~ (tilda) [word or words] - returns websites that have those keywords listed against them.
- Book or Books - gives the scanned version of the book if it is available.
- Flight details - [Flight name and number] - gives various flight details.
- [city1] [city2] - gives flight details for travel between the two cities.
- [number] - gives an area code lookup. Try it!
- [............] [ better than ........] - try this in your search query sometime.
- Image [search query] - brings back images links rather than website links.
Link To Google Advanced Search
Google Advanced Search :: Google Advanced Web Search
Google Web Search is very simplistic in it's basic form. This is to address one of Google's basic tenets: search for everyone. However, search terms can be expanded with Boolean search functions to make them more complex and therefore more specific in letting the Google Search Engine know what type of content you are searching for and which content you prefer not to see. There are a very limited number of people that utilise Boolean search terms to develop the searches they will use. However, to assist those that want to be more specific in their search criteria but do not utilise Boolean search, Google has produced Google Advanced Search.
Access to the Google Advanced Search facility is gained:
-
by clicking the [Advanced Search] link located to the right of the Google Search query box on your Classic Google Home Page, or
-
by clicking the [Advanced Search] link located underneath your Google Results Page Google Web Search box to the right hand side, or
-
by entering a web address in your browser address bar similar to:
http://www.google.com/advanced_search?q=search+results&hl=en&prmd=fd
where “q=search+results” can be substituted with the search word string that you want to search on (with q= at the start and + replacing any spaces), “hl=en” can be replaced by “hl=xx” where xx is a two character representation of a language (for example “es” for Spanish or “fr” for French). Changing the “hl” parameter will give you the Google Advanced Search Page in the language you have specified, if it is supported by Google.
Google Advanced Search is not available where Google Custom Search is presented.
Google Advanced Search allows you to:
-
Enter search limiting functions;
-
Increase the number of Google search results shown on the Google Search Results page;
-
Search in an alternative language;
-
Search within a site or in a different format, such as word or excel documents;
-
Place date, regional, usage rights and SafeSearch constraints on the Google results retrieved;
-
Find pages that are either similar to or link to the current web-page.
The options you enter will be reflected in the Google Search Query box at the top of the Google Advanced Search page.

Google Advanced Search :: Including And Excluding Search Words
The first set of options available on the Google Advanced Search page is for those that relate to inclusion and exclusion of words for a search. The options available are:
-
Find web pages that have ….......
-
all these words
-
this exact wording or phase
-
one or more of these words
-
But don't show pages that have …......
-
any of these unwanted words
An example using all these options would be:
-
All these words = pears peaches grapes
-
This exact wording or phrase = fruit salad
-
One or more of these words = cherries OR apple OR orange
-
Don't show any of these unwanted words = strawberries plums
Basically, I am searching for a recipe for fruit salad which definitely has pears, peaches and grapes in it, could have cherries, apples or oranges in it, but definitely does not have strawberries or plums in it.
The search query looks like this:
- pears peaches grapes "fruit salad" cherries OR apple OR orange –strawberries –plums
By knowing this you can construct Google Search queries that follow this format. Your Google Search results should more closely match those that you would otherwise expect.
By clicking [Advanced Search] at the bottom right hand side of the Google Advanced Search page your Google Search request will be processed using the search string created from your input criteria.

Google File Search
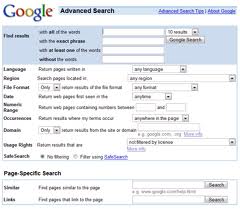
Google Advanced Search :: Additional Search Function Facilities
The second set of options available on the Google Advanced Search page is for additional tools. These are available below the heading: Need More Tools? There are four additional Google Advanced Search facilities:
-
Results per page – you are given a drop-down list with options for 10, 20, 30, 50 and 100 results per page. This relates to the number of results that you are presented with on the Google Results Page. The normal setting is 10. Just select and click the option you prefer. For checking where in the Google Results Page your website or web content page occurs, the 100 results per page assists no end.
-
Language – you are given a drop-down list of 46 languages plus the option for 'any language'. The chances are that the option already posted in the Google Advanced Search Language selection box is 'English'. You will receive some interesting results if you mix the search words with a search in a different language, although this can be of use if, for instance, you want to search for words that are not translated (names, products etc.) in the target language. For instance 'Mono sodium glutamate' from Chinese producer websites - this could be achieved by entering the search string in English and changing the 'Language' to 'Chinese (simplified)'.
-
File type – you are given a drop-down list with options for: Adobe Acrobat (.pdf); Adobe Postscript (.ps); Autodesk DWF (.dwf); Google Earth KML (.kml); Google Earth KMZ (.kmz); Microsoft Excel (.xls); Microsoft Powerpoint (.ppt); Microsoft Word (.doc); Rich Text Format (.rtf); and Shockwave Flash (swf). If you have a need to search through any of these formats then this is the place to let the Google Search Engine know.
-
Search within a site or domain – searching within a site is pretty much self-explanatory, just enter the web address of the site you want to search within. Searching within a domain means that you can limit your searches to websites that have a particular top level domain (TLD) extension, for example education establishment (.edu) websites, government websites (.gov.uk) or perhaps locally registered Australian (.com.au) websites.
Google Advanced Search Page
Google Search Tips by Google's Matt Cutts
Google Search Story : Ole
Google Advanced Search :: Google Search Results Constraints Parameters
With Google Advanced Search you can also place date, regional, usage rights and SafeSearch constraints on the Google results retrieved. You will need to open up the additional '…...and more' section. There are four extra additional Google Advanced Search facilities:
-
Date – the default setting is 'anytime' but you can change this to: past 24 hours; past week; past month; or, past year by clicking one of these options from a drop-down list.
-
Usage rights – the default setting is 'not filtered by license' but you can change this to: 'free to use or share'; 'free to use or share, even commercially'; 'free to use, share or modify'; or, 'free to use, share or modify, even commercially' by clicking one of these options from a drop-down list. So, if you want some copy for your web content pages you can search, with the last option selected and any content you find may be modified to your requirements – a note thanking the original content creator would be appropriate.
-
Where your keywords show up – the default setting is 'anywhere in the page' but you can change this to: 'in the title of the page'; 'in the text of the page'; 'in the URL of the page'; 'in links to this page' by clicking one of these options from a drop-down list. I think this one is self-explanatory.
-
Region - the default setting is 'any region' but you can change this to any one of the countries (full set of countries) that is presented on the drop-down list.
-
Numeric Range – you can enter a lower and upper figure in either a numeric or currency-based range.
-
SafeSearch – this can be switched on or off.

Google Advanced Search :: Page Specific Tools
The two options available for Google Advanced search specific tools are:
-
Find pages similar to the page – all you need to do is enter the web address for the web-page for which you want to find similar pages. How does this assist? Well, it saves you trawling through a load of irrelevant web links on the Google Search Results Page.
-
Find pages that link to the page - all you need to do is enter the web address for the web-page for which you want to find linking pages. How does this assist? Well, if you are looking to obtain backlinks or to find out what backlinks a competitor web-page has, then this is a good way to start that research.

See also:
How To Google - homepage of "Google How To".
How To Google in English - for the English version index to "Google How To" subjects.
Google Search :: Google Citations and Relevant Websites