- HubPages»
- Technology»
- Computers & Software»
- Computer Science & Programming»
- Programming Languages
A Server Side Web Tutorial #6 - PHP Sorting Arrays
Recap of the Last Tutorial & Goals for This One
In our last tutorial, A Server Side Web Tutorial #5 - Working with PHP Indexed, Associative, and Multidimensional Arrays we defined the three types of arrays PHP supports. We then demonstrated the use of looping construct to list the array contents.
In this tutorial we will be mainly concerned with sorting arrays. An array can be sorted in alphabetical or numerical order, descending or ascending.
The PHP sort() Function
- There are a number of flags which can be used with sort()::
- SORT_FLAG_CASE - can be combined (bitwise OR) with SORT_STRING or SORT_NATURAL to sort strings case-insensitively
- SORT_LOCALE_STRING - compare items as strings, based on the current locale.It uses the locale, which can be changed using setlocale()
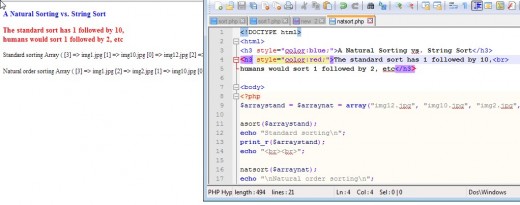
- SORT_NATURAL - compare items as strings using "natural ordering" like natsort(), see the example in the snapshots which follow. Basically, in will sort in an order that would be used by a human.
- SORT_NUMERIC - compare items numerically
- SORT_REGULAR - compare items normally
- SORT_STRING - compare items as strings
An important thing to recognize about sort(). It is a boolean function which will return true of false based on the sort being successful or not.
Performing a Simple Sort With sort()
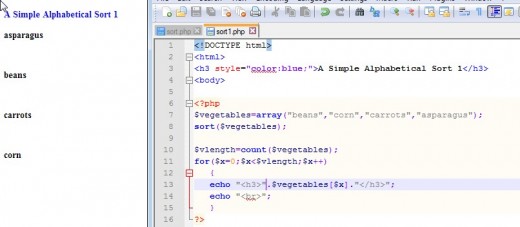
A Natural Order Sort Using natsort()
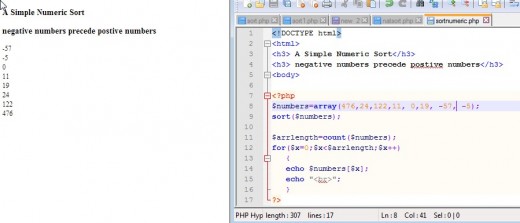
A Numeric Sort
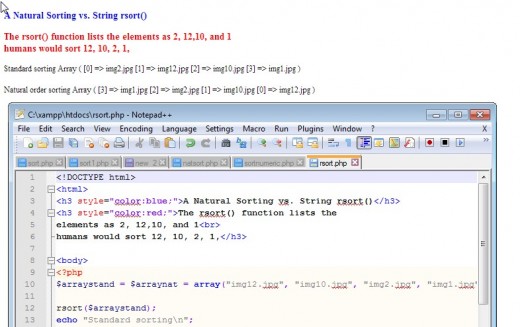
The PHP rsort() "Reverse" Sort Function
The rsort() function sorts strings or numeric values in reverse order. "rsort()" like sort() is a boolean function returning true or false based on whether the sort was successful or not. rsort(0 used the same flas as sort().
rsort() vs. natsort() For String Values
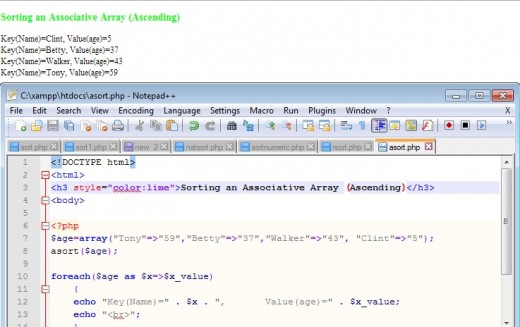
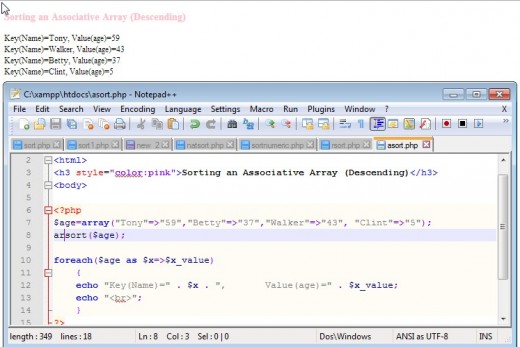
Sorting An Associative Array Using asort() and arsort()
asort() is used to sort an associative array in ascending values.while arsort() is used to sort the array in descending values. The functions are boolean returning true or false based on the success or failure of the sort. The sort preserves the association between key and value pair.
Examples of Associative Function asort() and arsort() Use
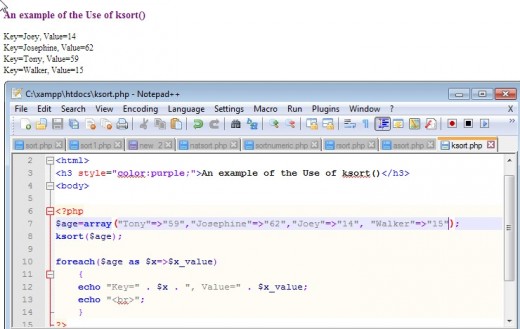
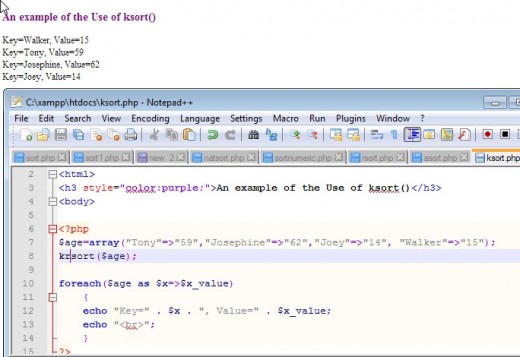
Sorting According to Key Values: ksort() and krsort()
Instead of sorting by the value in a key/value array. One can sort based on the key value with the PHP ksort() function.in ascending order or krsort() to sort in descending order. The same set of flags used by sort(0 can be used by these functions. Again, as with all the other functions we have seen up to now, ksort() and krsort(0 return a boolean value of true or false.
Examples of the Use of ksort() and krsort()
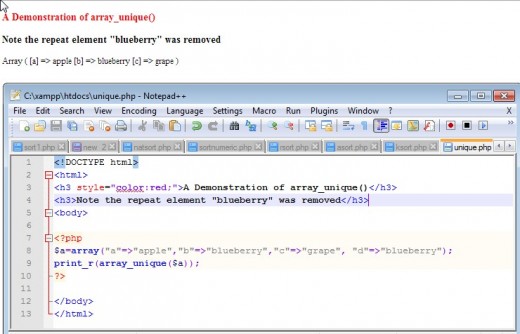
The array_unique() Function
At times it may be desirable to remove duplicate values from an array. The PHP function array_unigue() does this.
Example of the Use of array_unique()
Finding Differences Between Arrays
The array_diff() function compares two arrays. The result is the differences in values ONLY.
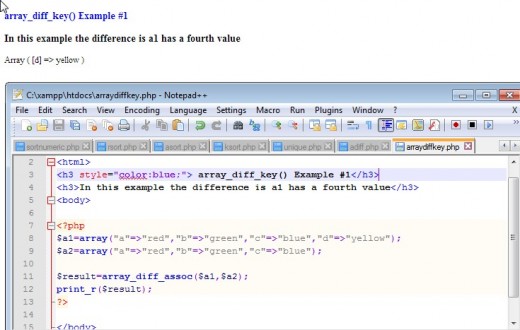
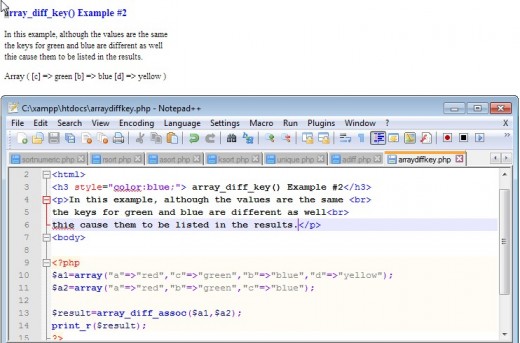
The array_diff_key() function compares not only the value but also the key. If the values are the same and the keys are different, the function will in this in reporting the differences.
The array_sum() Function
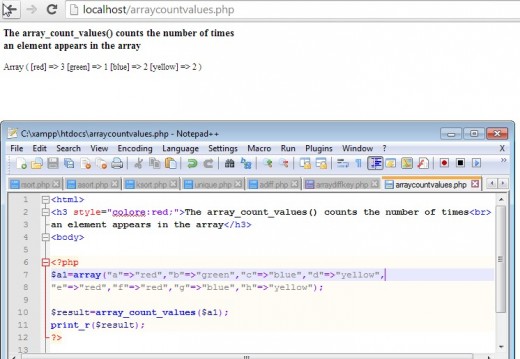
The array_sum(0 function counts the occurrences of the values in the array.
An Example of the Use of array_count_value()
Wrap Up and What's Next
In this tutorial we started looking at different ways of sort an array. The functions occur in pairs to indicated ordering ascending or descending keys or values. The functions are:
- sort() - sort arrays in ascending order
- rsort() - sort arrays in descending order
- asort() - sort associative arrays in ascending order by value
- ksort() - sort associative arrays in ascending order by key
- arsort() - sort associative arrays in descending order,by value
- krsort() - sort associative arrays in descending by key
We then covered a "sampling" of several useful built-in functions for working with arrays, We will see many more!
As far as the next tutorial we will turn our attention to how PHP interacts with HTML forms.