Learning Objectives for Science Six
Science Six

Breakdown of Contents
Here are the contents of this article.
▪ Overview of Science Six Lessons
▪ Scope of the Sample Learning Objectives
▪ Learning of Objectives for Unit One
▪ Learning of Objectives for Unit Two
▪ Learning of Objectives for Unit Three
▪ Learning of Objectives for Unit Four
▪ Learning of Objectives for Unit Five
▪ Learning of Objectives for Unit Six
▪ Author's Note
▪ Resources and Related Links
Overview of Science Six Lessons
Science VI confers the circulatory and nervous systems, health, ecosystems, matter and materials, structure of the earth and volcanoes, stars and galaxies.
The discussion on the human organ systems focuses on the structures and functions of these systems. The diseases associated with these systems and how to prevent them are given emphasis. Health is presented in a broad sense to include various environmental problems and solutions highlight the discussions on the ecosystem. These topics cover the study of the biological world.
The study of the physical world begins with matter and materials. It includes a wide range of concepts such as the particle model of matter, states of matter and their characteristics, commonly used materials and substances, and the effects of these materials on the environment. The lessons about energy include its forms, transformations, transfers, and conservation follow. Then discussions on motion, speed, velocity, and acceleration are presented together with simple but practical problems and calculations. The dynamic earth, its parts, formation of volcanoes, and concepts on weather climate, and seasons are then clarified. The last part deals with the solar system, star, and galaxies.
Scope of Science Six Lessons
The sample objectives in this article are based on the learning contents below.
I. PEOPLE AND THEIR HEALTH
A. The Circulatory System
B. The Nervous System
II. PEOPLE AND THEIR ENVIRONMENT
A. Interaction and Balance in an Ecosystem
B. The Endangered Ecosystem
C. Saving the Environment
III. MATTER AND MATERIALS
A. Matter
B. Materials
IV. ENERGY AND MOTION
A. Energy
B. Motion
V. THE DYNAMIC EARTH
A.The Structure of the Earth
B. Volcanoes
C. The Changing Atmosphere
VI. BEYOND THE SOLAR SYSTEM
A. Stars in the Universe
B. Galaxies and the Universe
Learning Objectives for Unit One
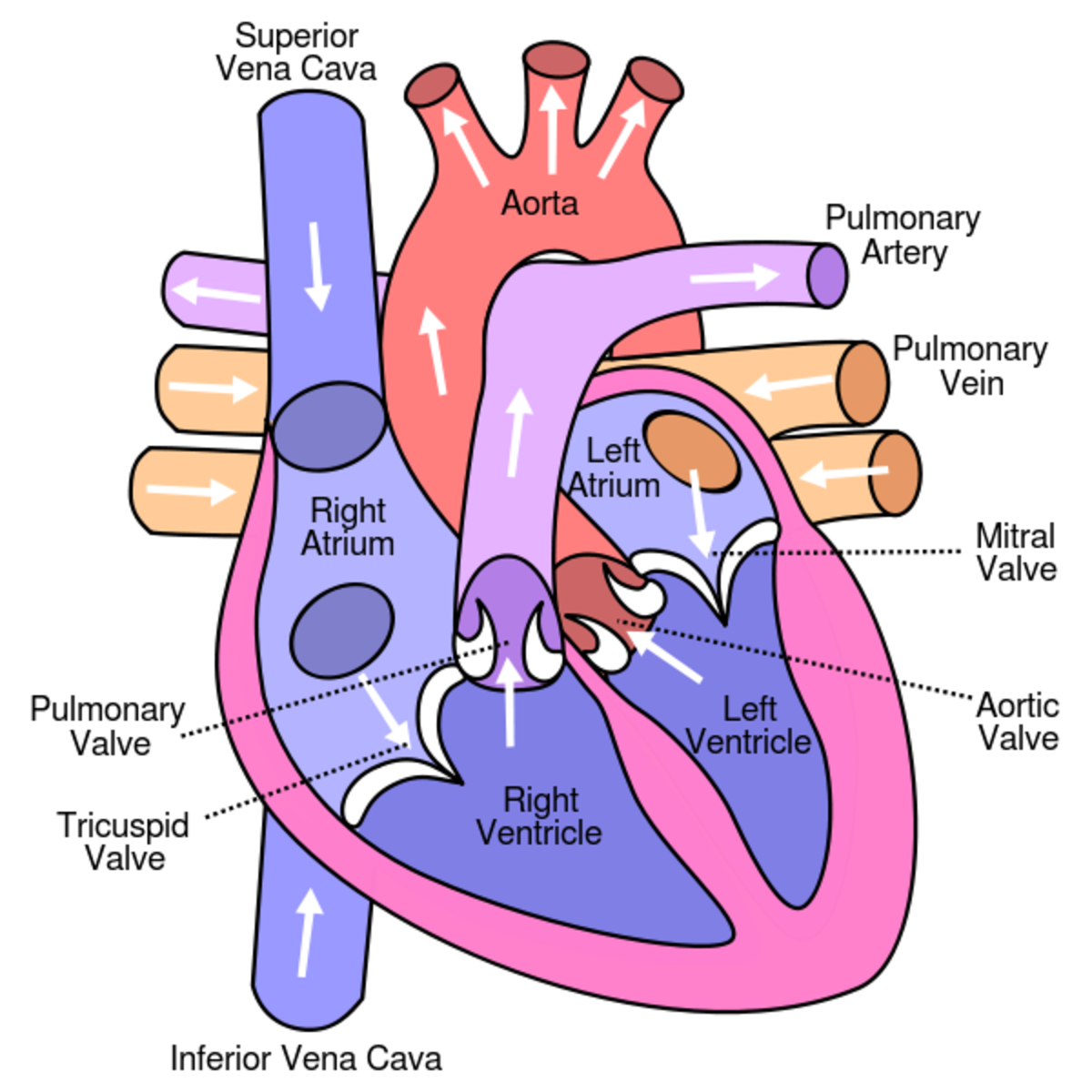
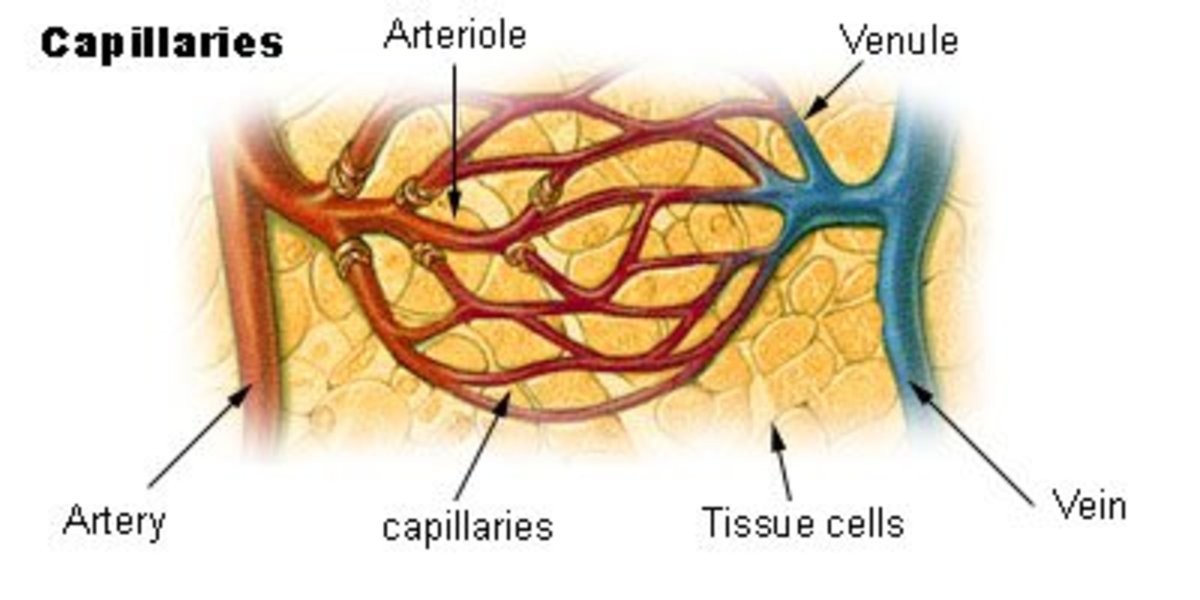
A. The Circulatory System
1. Describe the structure of the circulatory system.
2. Give the functions of the circulatory system.
3. Explain the circulation of blood throughout the body.
4. Name and describe common cardiovascular disorders.
5. Enumerate risk factors that may lead to cardiovascular disorders.
6. Name some desirable habits that will help keep the circulatory system healthy.
B. The Nervous System
1. State the functions of the nervous system.
2. Identify the parts and functions of the central and peripheral nervous systems.
3. Describe the structure of a neuron.
4. Identify the three types of neurons and give the functions of each.
5. Describe the flow of a nerve impulse within the nervous system.
6. Describe the structure of the brain and the spinal
cord.
7. Name and describe some common ailments of the nervous system.
8. Enumerate desirable habits that will help nervous system healthy.
9. Compose a poem about how the brain and the spinal cord keep the body parts functioning in harmony.
Lesson on Circulatory System
Learning Objectives for Unit Two
A. Interaction and Balance in the Ecosystem
1. Define ecosystem.
2. Name the biotic and abiotic components of an ecosystem.
3. Explain the role of producers, consumers, and decomposers in an ecosystem, and their relationships with one another.
4. Explain how abiotic components affect the organisms in an ecosystem.
5. Define and construct food chains.
6. Define and construct food web.
7. Explain the transfer of energy in a food chain and food web.
8. Explain how biological magnification occurs.
9. Construct and interpret a diagram of the oxygen-carbon dioxide cycle.
10. Construct and interpret a diagram of nitrogen cycle.
11. Name ways through which forests help maintain the balance in the earth’s ecosystem.
B. The Endangered Specie
1. Explain how the increasing population and people’s activities disrupt the balance in the ecosystem.
2. Discuss the causes of the destruction of the ecosystem.
3. Explain the causes of air, land, and water pollution.
4. Describe the effects of air, land, and water pollution.
C. Saving the Earth
1. Explain that a person’s attitude and lifestyle can help save the environment from destruction and improve its condition.
2. Discuss ways of conserving the natural resources.
3. Identify ways of conserving the natural resources.
4. Identify ways to save energy and water.
5. Identify ways to prevent pollution of air, land, and water.
6. Define organic farming.
7. Define sustainable development.
8. Conservation of natural resources.
Saving the Earth

Hazard Signs

Learning Objectives for Unit Three
A. Matter
1. Discuss the particle model of matter.
2. Define matter and describe its major properties.
3. Classify the kinds of matter based on their properties.
4. Explain how the arrangement of particles in a substance determines its properties.
5. Give examples of solids, liquids, and gases.
6. Relate the particle model of matter to solids, liquids, and gases.
7. Investigate the properties of matter through an experiment.
B. Materials
1. Cite some technological improvements made on materials and substances.
2. Name ways of lessening waste products from commonly used materials and substances.
3. Describe the proper ways of using and storing chemicals.
Learning Objectives for Unit Four
A. Energy
1. Define energy.
2. Name and describe the forms of energy.
3. Cite sources for each form of energy.
4. Describe examples of energy transformation.
5. State and explain the law of conservation of energy.
6. Describe how different forms of energy are transferred from one form to another.
7. State ways to conserve energy.
B. Motion
1. Define the terms speed, instantaneous speed, and average speed.
2. Calculate the average speed of a moving object.
3. Distinguish speed from velocity.
4. Define acceleration.
5. Calculate the acceleration of a moving object.
6. Define force using the concept of acceleration.
7. Relate the mass and the force acting on a moving object with its acceleration.
8. Describe the motion of a falling object.
9. State and explain Newton’s Law of Motion.
10. Describe the motion of an object moving in a circular path.
Learning Objectives for Unit Five
A. Structure of the Earth
1. Identify the layers of the earth.
2. Describe each layer of the earth.
3. Explain why the interior of the earth is hot.
4. Name the tectonic plates.
5. Explain why an earthquake occurs.
6. Describe the different scales used to measure the magnitude of an earthquake.
7. Infer the effects of the earthquakes on the environment.
8. State the precautionary measure before, during, and after an earthquake.
9. Perform an earthquake drill.
B. Volcanoes
1. Describe how a volcano is formed.
2. Explain how volcanic eruption occurs.
3. Differentiate active, inactive, and ancient volcanoes from one another.
4. Name the beneficial and harmful effects of volcanoes.
5. Cite precautionary measures before and after volcanic eruption.
6. Create a diagram that will show the formation of volcanoes.
C. Changing Atmosphere
1. Define climate.
2. Identify and explain the factors that affect climate of a place.
3. Describe the effects of the rotation of the earth on climate and wind system.
4. Identify and describe the seasons in the Philippines.
Learning Objectives for Unit Six
A. Stars
1. Name and describe some characteristics of stars.
2. Differentiate luminosity from apparent brightness.
3. Compare the temperature of stars base on their colors.
4. Identify instruments used in studying the stars.
5. Explain why some stars seem to twinkle.
6. Name the three classes of stars according to size.
7. Show how a light-year is equivalent to trillion kilometers.
8. Convert given distances to light-years.
B. Galaxies
1. State what a galaxy is.
2. Name the classes of galaxies and describe each class.
3. State that our solar system is part of the Milky Way Galaxy.
4. Describe the universe.
5. Explain some theories about the universe.
6. Cite some problems in space explorations and how these are overcome.
7. Identify some modern facilities used to study the universe.
8. Name some space probe and identify missions.
9. Create a picture of a galaxy.
Author's Note
This set of learning objectives for Science VI can be used as reference guide for young and experienced teachers. Revision could be done depending on the needs of the students, available facilities and school curriculum.
Related Links
- Predicting Weather, Weather Folklore for Kids
Teaching children how to read the natural weather by looking at reliable weather folklore. Reading mother nature along the hiking trail or when camping. - Weather Unit Plan
Katelynn Hamilton Unit Plan Weather in the Four Seasons The unit I will be teaching is weather. The main focus of the unit will be based on the seasons. From there the students will explore what type of weather is to... - Wind and Air Pressure Lesson
This is part 2 of a 4 part hands-on unit study on Meteorology and Weather. Make weather vanes and barometers, act out high and low pressure, blow up a balloon and collapse a can using hot water, make and eat prevailing winds, and more! My lessons are - Solar System Lesson
This is part 1 of a 4 part hands-on unit on Astronomy. Make planet pizzas, take a planet walk, and more in this exciting lesson on our fascinating solar system! Use these fun lessons with your classroom, family, or co-op! - Sun, Seasons, and Weather Lesson
This is part 1 of a 4 part hands-on unit study on Weather. Conduct experiments and demonstrations on how the sun, soil, and water affect the seasons and weather, dramatize the Earth's revolutions around the sun, and more! My lessons are geared toward - Erosion Lesson
This is part 6 of a 6 part hands-on unit study on Earth Science. Demonstrate various types of erosion as children carve gullies and valleys in sand using air, water, and ice. Re-create the Grand Canyon. Compare how soil resists erosion. My lessons ar - Study the Water Cycle with Terrariums: Lesson Plan ...
Terrariums are easy for students to set up in the classroom and make an excellent tool for observing the water cycle. Create these mini ecosystems with your class and have your students investigate this most important earth process. They will gain in