Space Facts - Volume 1 Looking at Space

Factoid 1 - Let me blow your mind
I find the size of the universe mind blowing. We already know Earth only makes a small percentage of our Solar System.
To get an idea of just how BIG space is, think of the Sun as a basketball. The Earth would be a pea 32 meters away, while the next star would be another basketball 9 kilometres away.
Our System is one of 200 Billion in our galaxy (The Milky Way). Galaxies are separated by huge empty voids of Space.
Our Galaxy is one of more than 100 Billion Galaxies spread throughout the Universe.
There are more stars in space than grains sand on Earth.
Factoid 2 - Eyecredable
Did you know on a clear night, the human eye can look to the heavens and see 3,000 stars several planets, some star clusters and nebulae and even some galaxies nearest to our own!

Factoid 3 - So how do we make it smaller and comprehend-able?
Due to the amazing distances we have to spread units called Astronomical Units (AU). With the Solar System, a basic unit of measurement from our Earth to Sun for example is 149.6 million or 1 AU.
Factoid 4 - Whats a Light Year?
To describe interstellar and intergalactic distance we use a light year. This is simply how far Light (the Fastest phenomenon in Space) travels in a year.
Light travels at an incredible 1,079 Million Kph or 670 Million Mph. A Light Year is equivalent to a distance of almost 9.5 Trillion Km or or 5.9 Trillion Miles.
Factoid 5 - Where's the Highest Telescope?
Since the 1600's Scientist have be using Telescopes to view the heavens. The best place for modern telescopes is high up on mountains away from adverse weather conditions, like clouds, that block the view. The highest Telescope is on Mount Graham, USA. Its 11.8 Miles above sea level and is called the Large Binocular Telescope.
Factoid 6 - Seeing is believing
Scientist observe the night sky using a variety of Telescopes. There have been evolving since 1600's in the 19th Century, (thanks to the discovery of light as an electromagnetic wave) our eyes use nerves to produce an image stimulated by patterns of electrical and magnetic distance.

Factoid 7- Radio Telescopes
Radio Telescopes dish shaped metal antenna pick up radio waves generated by astronomical objects and interstellar gas clouds.
The dish is designed to make images sharper as a a small amount of the Radio waves can distort as they penetrate the Earths atmosphere.
One of the worlds most advanced radio telescopes is in the Very Large Array (VLA). Located in the Socorro Desert, New Mexico, USA. It is made up of 27 Radio dishes, each measuring 25 meters in diameter. These are linked together to make a very sensitive radio telegraph. The VLA has made important discoveries in New Stars and black holes.
Factoid 8 - Microwave Telescopes
Microwave Telescopes pick up tiny microwaves emitted by objects such as stars in the process of being formed. The shortest of Radio Waves could also pick up Cosmic Background radiation- an echo of the Big Bang!
Did you also know there is a Microwave Transmitter on the South Pole! Brrrr
Factoid 9 - Why is Infrared not Infrablue?
Infrared Telescopes get their name from picking up waves closet to Red in the visible light spectrum.
Infrared (effectively heat radiation) is emitted by objects, that do not have enough energy to glow brightly at night or in visible light. They are used for detecting much colder regions of space, such as clouds of gas and dust surrounding new stars.

Factoid 10 - Optical Telescopes
Optical Telescopes rely on huge mirrors to counteract the blurriness from Turbulence to resolve an image. Today's, astronomers use giant telescopes with mirrors up to 10 metres wide. They are kept in dome shaped buildings called observations.
Telescopes collect the light from very far away stars and galaxies to make faint objects appear closer and brighter. Telescopes that use mirrors are called reflecting Telescopes. Sometimes a lenses is used to collect and focus the light-these telescopes are called refracting telescopes. The bigger the mirror (or lens) on the end the more light it can collect, which in turn makes the image brighter and sharper.
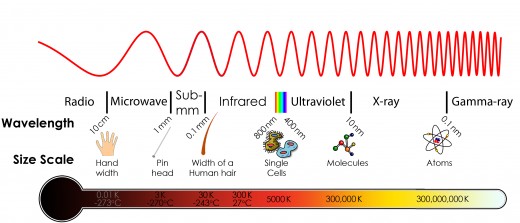
Factoid 11 - Ultraviolet, X-ray and Gamma Telescopes
Ultraviolet, X-ray and Gamma Ray or High Energy Telescopes which have shorter wavelengths and higher energy levels, pick up the most violent images in Space.
The light we see is called Optical or visible light, buts its just one type of light. Radio Waves, infrared, ultra violet, X-rays and gamma rays are also types of light, and together they make up the full range, which is your electromagnetic spectrum. This range goes from low-energy light (Radio Waves) to high-energy light (Xrays and Gamma rays). Most of the objects in our universe give off one of these types of light.
Fortunately, the Earth's atmosphere protects us from X-rays and gamma rays, which can be harmful. So this means in order to see past our natural defence we have to launch telescopes via satellite past it.

Factoid 12 - Launch Pads
Launching into space is no easy feat. There are 22 locations across the globe which allow us to travel into space. The most famous being Cape Canaveral located on Florida's Atlantic Coast.
This enormous site is also home to KSC or the Kennedy Space Centre, which is famous for launching the Apollo Missions to the moon.

Factoid 13 - Escaping the Gravitational Pull
Rocket Power to escape Earths gigantic gravitation pull. Spacecraft need to reach speeds of several kilometres per second to reach the Earth's orbit.
According to NASA website;
"The hot exhaust is passed through a nozzle which accelerates the flow. Thrust is produced according to Newton's third law of motion. The amount of thrust produced by the rocket depends on the mass flow rate through the engine, the exit velocity of the exhaust, and the pressure at the nozzle exit."

Factoid 14 - Space Shuttle
When most people think of space craft they think of NASA's Space Shuttle. Its first mission was in 1981. It was designed to reduce huge costs of space flight. It achieved this by being reusable and having reusable rocket booster tanks. The Plane like orbiter acted as a satellite delivery system, recovery and repair vehicle and also an orbital laboratory.
However the project was shelved in 2011 after 135 missions due to expensive running costs and a couple of publicly aired tragic accidents.

Factoid 15 - How far is Orbit?
Orbit is 60 miles above the Earths surface or 100 Km. That is the edge of space!
It takes 8.5 minutes to reach (via rocket) 340 Km or 210 miles Low Earth Orbit (LEO). When you reach this distance, you move at 17,000 mph or 28,000 kph in parallel with the Earth Surface. This distance keep the orbiter moving in a straight line and perfectly balanced against the Earth gravitational pull.
Or if we had some road we could drive it in under an hour!
© 2018 Leo J Wicks