useful mutations
Mutations as economically beneficial for men
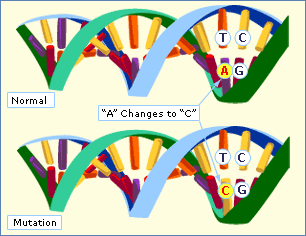
Mutation means any sudden qualitative or quantitative heritable change in the genome or genetic material of an organism. It excludes those heritable changes that results from the incorporation of genetic material from other organism during recombination. Mutations results in the modification of structural characteristics or enzymatic capabilities of an individual.
Mutations are of two types, chromosomal mutations involving changes in number of chromosomes (Euploidy and Aneuploidy); and changes in structure of chromosomes (Addition, Deletion, Translocation and Inversion).
Another type of mutation is gene mutation or point mutation which could by intergenic or intragenic. It is of two types namely spontaneous occurring naturally of its own; and induced mutation. Induced mutations can be modified to make them beneficial for human beings.
Some microorganisms are known to develop resistance to certain antibiotics because of mutations. Antibiotics originally effective for the control of a bacterial infection becomes less effective as antibiotic resistant mutants appear.
It is possible to isolate biochemical mutants capable of producing large yields of an end product. This process is important in industries. For example, the yield of penicillin antibiotic in commercial production has been dramatically increased through the selection of mutant strains of mold Penicillum crysogenum.
Microbial mutations are also extensively used in the investigation of various biochemical processes, particularly biosynthetic reactions. For example, mutation with impairment or blocks at different enzymatic steps has been used to unravel metabolic sequences.
Mutations are also extremely useful in determining the effect of particular gene on the structure and function of specific proteins in combination with genetic engineering techniques.
It is also useful in establishing that a certain protein is essential to a particular cellular function. Because, it is technically much simpler to produce and detect mutants in bacteria and yeast, these organisms have been favorite experimental targets for biochemical geneticists. Once the gene for a protein has been isolated it can often be inserted into a bacterial or yeast cell, which then acts as a biological factory, overproducing the protein.
The base analogue 5 BromoUracil is used in the chemotherapy of microbial infection. By pairing with Guanine, instead of Adenine, it disturbs the normal replication mechanism of microorganisms responsible for infections.
Mutations also has role in evolution. It can adapt a cell to survive in a new environment. A mutation can better equip an organism or cell to survive in its environment. The mutant enzyme can acquire a slightly different specificity so that it is now able to use some compound as a reactant that the cell was previously unable to metabolize. If a population of cells find itself in an environment where the compound was the only available source of fuels, the mutant cell would have an advantage over the other unmutated cells in the population. The mutant cells and its progeny would survive in the new environment, whereas the unmutated or wild type cells would starve and be eliminated.
Gradual accumulation of mutations over a large period of time results in creation of new biological species, each one having a unique DNA sequnence.
New desirable traits can be developed in plants through induced mutations. Plant breeders have reported induced mutations in barley, wheat, oats and fruit trees that may improve some cultivated strains. For example, Barley mutants have been obtained that provides increased yield resistance to smut and increased protein content.
Mutations can be effectively utilized for improving a specific property of an enzyme. For example, E.coli anthranilate synthetase enzyme is normally sensitive to tryp. inhibition due to feed inhibition. A mutation in E.coli was found to have an altered form of the enzyme which is insensitive to tryptophan inhibition. This may help in a continuous synthesis of tryptophan without any inhibition by tryptophan accumulated as a product.
This usefulness of mutations may suggest that these mutations could someday be used as a method for early detection of harmful and dangerous diseases.