Clinical Manifestation Of Dengue Fever As A Significantly Important Arbovirus Infection
The Aedes aegypti Mosquito Causing The Dengue Fever

Infectious Diseases
Dengue Fever (Break Bone Fever)
Dengue is an acute febrile illness characterized by high fever, severe pain of the bones and joints, lymphadenopathy and a characteristic rash.
Etiology: Dengue is caused by a group B arbovirus. It measures 50 nm and there are at least four distinct serotypes- 1 to 4. Viremia is present from the onset up to the first three days. Man is the usual reservoir of infection. The disease is common in India in particular. It is transmitted by female Aedes aegyi mosquitoe which becomes infective 8 to 14 days after taking an infective meal.
Pathology: The pathological processes are not clear due to scarcity of autopsy studies. The small blood vessels show endothelial swelling, perivascular edema and infiltration with mononuclear cells.
Clinical Presentations
The incubation period is 2 to 15 days. The patient is struck down with severe body aches and pains, high fever, rigor headache and prostration. There is relative bradycardia. The disease is noted for the severe pain in the joints, muscles, long bones and back and this feature is reflected in the synonyms break bone fever and Dandy fever. Orbital pain may develop and movements of the eyeball may be painful. Lymph nodes in the posterior cervical, epitrochlear and inguinal regions become mildly enlarged. They are discrete and nontender.
After 3 days of fever, the temperature drops, to remain so for 1 to 2 days. Then a second bout of fever occurs. This is milder than the first and it lasts for 2 to 3 days. This temperature patterns is described as the “saddle back”temperature. The second episode of fever comes down by lysis.
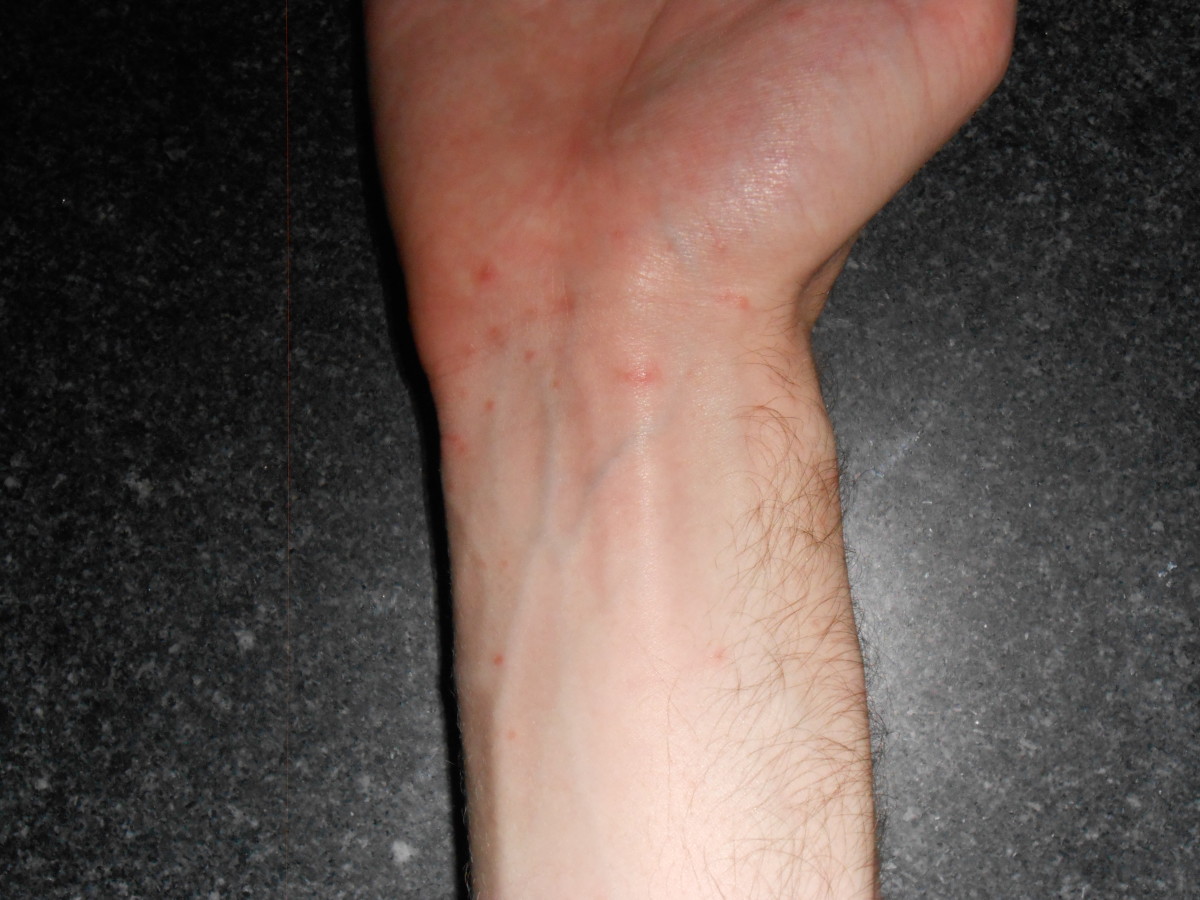
A maculopapular reddish rash occurs on the third to fifth day on the trunk, limbs and face. It disappears as the temperature falls.
Diagnosis: Dengue should be suspected when small outbreaks of short fever with severe pains and rash occur. It may be mistaken for influenza but the absence of respiratory symptoms in dengue is a point of difference. Other short fevers like sand fly fever has also to be kept in mind.
Laboratory Findings: Usually, there is lecucopenia with neutropenia. It is difficult to recover the virus. Serological diagnosis is possible by demonstrating hemagglutination inhibiting and complement fixing antibodies, 7 to 14 days after the onset.
The Dengue Fever Rash
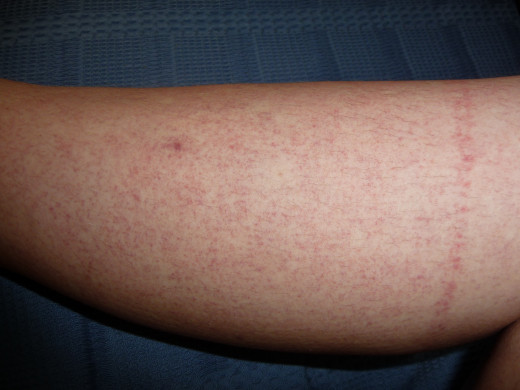
Treatment And Prevention Of Dengue Fever
Treatment: Analgesics to control pain and supportive measures are sufficient to tide over the illness. The course is benign and recovery is uneventful. Subsequent second attack is rare, but if it occurs, it may be associated with hemorrhagic manifestations. In these cases, the mortality is higher.
Prevention: General measures include anti-mosquito operations and personal protection using nets or mosquito repellants. Attenuated virus vaccines are under trial.
© 2014 Funom Theophilus Makama