- HubPages»
- Health»
- Diseases, Disorders & Conditions»
- Chronic Pain
Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome Treatments

What is EDS?
Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (EDS) is a group of disorders that affect connective tissues, such as: tissues that support the skin, bones, blood vessels, and other organs (2014, Genetics Home Reference). It is estimated that about 1 in 5,000 individuals worldwide suffer from EDS (Genetics Home Reference, 2014). There are four main types of EDS: hypermobile EDS, classical EDS, vascular EDS, and kyphoscoliotic EDS. Each type of EDS comes with a different set of symptoms, but all types of EDS share certain similarities in the ways they affect the skeletal, cardiovascular, integumentary, and/or digestive systems depending on which symptoms each individual experiences; currently all types of EDS are treated symptomatically.
EDS is an inherited condition that affects the connective tissues in the body; connective tissue is made up of cells, fibrous material, and a protein called collagen responsible for supporting and structuring the skin, blood vessels, bones, and organs (Kahn, 2012). EDS is triggered by a defect in collagen production; this defective gene is passed from parents to their offspring (Kahn, 2012). Defects in the genes which provide instructions for making the proteins that work with collagen and the genes that provide instructions on how to assemble collagen can cause EDS; collagen is the molecules that give structure to connective tissues in the body (Kahn, 2012). Defects in any genes known as: ADAMTS2, COL1A1, COL1A2, COL3A1, COL5A1, COL6A2, PLOD1, and TNXB weaken the process and formation of collagen which causes EDS (Kahn, 2012).

Four Main types of EDS
Hypermobile EDS, also known as hypermobility EDS, is the most common form of EDS, but also often remains undiagnosed due to its similarity to joint hypermobility syndrome (NHS Choices, 2014). There are currently no tests available to distinguish between hypermobile EDS and joint hypermobility syndrome; this causes the diagnosis to be made based on a physical examination and medical history (Mayo Clinic Staff, 2014). Hypermobile EDS has three main symptoms that separate it from the other forms of EDS; these symptoms are generalized joint hypermobility, stretchy skin, and smooth or velvety skin (Mayo Clinic Staff, 2014). Hypermobile EDS patients also tend to experience joint hypermobility, unstable joints, joint pain, fatigue, joints that are easily bruised, and/or gastrointestinal complications (NHS Choices, 2014).
Classical EDS was previously referred to as EDS types I and EDS II; classical EDS is a rare condition that many health professionals are unfamiliar with (Mayo Clinic Staff, 2014). Classical EDS has three main symptoms that make it different from other forms of EDS; these factors are: skin that can stretch beyond normal range (hyper-extensibility), widened scars, and hypermobility (NHS Choices, 2014). Patients with classical EDS often experience fluid effusions into the knees, ankles and elbows, loose joints that can lead to dislocations, hyper-extensible skin, fragile skin, slow healing with papery scars, and sometimes periodontal disease as a juvenile (NHS Choices, 2014).
Vascular EDS is one of the rarer kinds of EDS that is sometimes associated with life-threatening complications (NHS Choices, 2014). Female patients with EDS experience an increased risk of vascular complications and womb rupture during pregnancy (NHS Choices, 2014). Vascular EDS has four symptoms that mark it as vascular EDS instead of a different form of EDS; these symptoms include fragile arteries subject to sudden rupturing, thin, translucent skin, easy bruising, and characteristic facial features (Mayo Clinic Staff, 2014). Patients with vascular EDS can also experience: fragile blood vessels which can lead to blood vessels tearing and arterial aneurysms, fragile arteries and intestines, sudden rupture of the uterus, and a risk of damage to hollow organs (NHS Choices, 2014).
Kyphoscoliotic EDS previously known as EDS VI is a generalized connective tissue disorder characterized by friable, hyper-extensible skin, thin scars, and easy bruising (Yeowell, 2013). Kyphoscoliotic EDS is categorized based on joint looseness, severe muscle weakness (hypotonia), curvature of the spine (scoliosis), and fragile white part (sclera) of the eye (Mayo Clinic Staff, 2014). Children born with kyphoscoliotic EDS may experience severe muscular hypotonia at birth; progressive scoliosis, scleral fragility with increased risk of rupture of the globe, and fluid effusions into the knees, ankles and elbows (Yeowell, 2013).
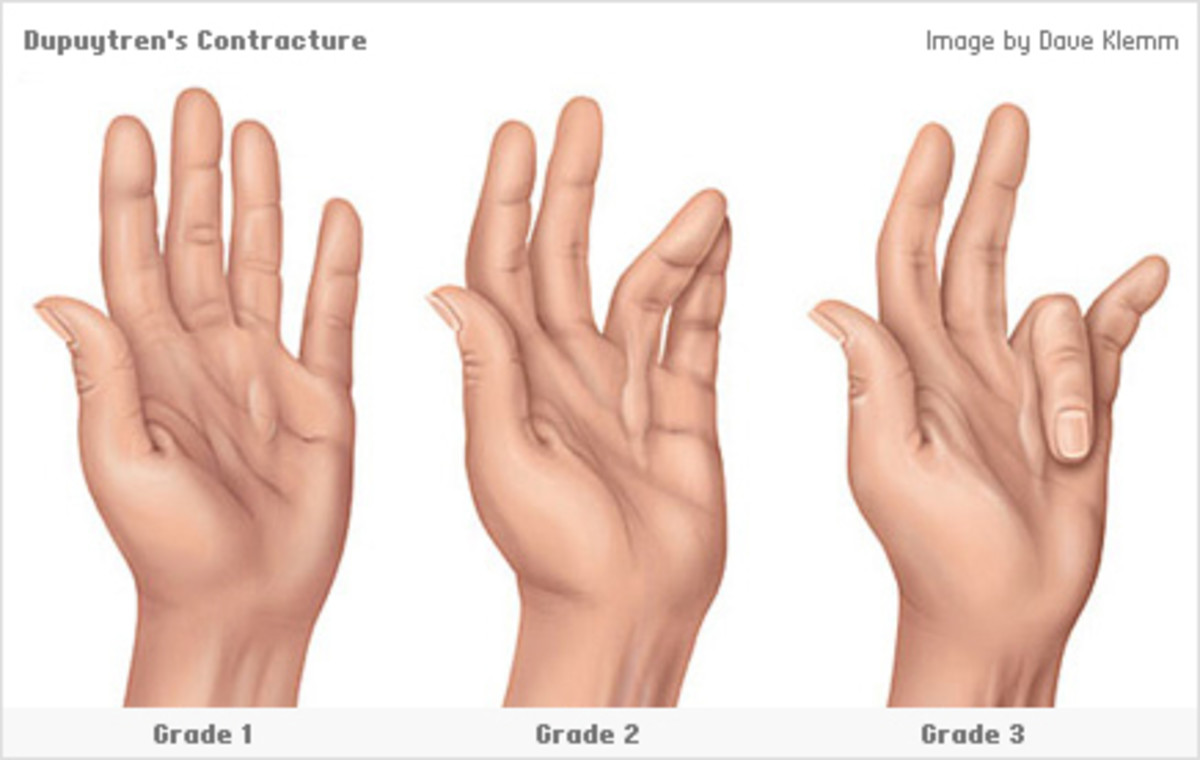
All of the types of EDS can have an effect on the skeletal, cardiovascular, integumentary, and/or digestive systems depending on which symptoms each individual experiences. EDS affects the skeletal system through: joint dislocations, subluxation, spontaneous reduction or replacement of the finger digits and shoulders, pain from hypermobile joints, the need to crack or pop joints to relieve pressure, difficulty or pain walking, clumsiness due to overextended joints, weak joint and bones in hands, and neck instability (Jenkins & Saul, 2009). The effect EDS has on the cardiovascular system is shown by: low body temperatures, difficulty controlling body temperatures when exposed to heat or cold, blood pressure problems, dilated aortic roots, incompetent heart valves, autonomic dystonia, difficulty finding pulse, severe bruising, and/or fragile arteries that can rupture (Jenkins & Saul, 2009). The integumentary system experiences the effect of EDS through skin traits such as: easy bruising, delayed wound healing, differing types of scarring, thin to translucent skin where the blood vessels are visible, velvety elastic skin, skin that splits open at slight pressure, and/or redundant folds of skin (Jenkins & Saul, 2009). The digestive system’s gastrointestinal tract is affected by EDS through: gastrointestinal complications reflux, GERD, incompetent esophageal sphincter allowing stomach acid to backflow, tissue extensibility and laxity causing lack of contraction of the stomach preventing food from moving into the intestines, mega-colon and rectal prolapse, and/or irritable bowel syndrome (Jenkins & Saul, 2009). EDS affects all of these systems because it is a connective tissue disorder, meaning that it can affect the joints from the skeletal system, the body temperature, blood pressure, and the heart from the cardiovascular system, the skin from the integumentary system, and the GI tract from the digestive system all at the same time or in any combination

Is there a CURE?
Currently, there is no cure for EDS and treatment involves the management of the manifested symptoms. Current treatment plans involve a combination of physical therapy, over the counter pain medicine, prescription medicine for pain and muscle spasms, stress reduction therapies and activities, and/or anti-depressants for depression. Holistic treatment of EDS offers a variety of non-prescription options for treatment. Vitamin C, MSM, aloe vera, gelatin, and hyaluronic acid help replenish collagen and can restore skin firmness (Earth Clinic, 2014). Furthermore apple cider vinegar, honey, and vitamin D can be used to restore the balance of nutrients in the body (Earth Clinic, 2014). A healthy diet of whole foods and a minimum consumption of sugar can assist in the alleviation of the general pain associated with EDS (Earth Clinic, 2014). Yoga and other stretching activities can be used in order to tighten and realign the body’s structure and relieve pain (Earth Clinic, 2014). Treatment plans differ from patient to patient based on medical history, type of EDS, and the symptoms the patient is experiencing.
Treatments
Unfortunately there is not one set treatment plan for EDS. I truly wish I could tell you one thing that you could do to make the pain go away, but I can't. I can tell you about some treatment options that MIGHT work for you or your loved one, but there is no cure all for everyone.
- 5-htp
- diet changes
- doctor prescribed pain pills
- exercise
- physical therapy
- yoga
- vitamins and supplements
- warm baths/showers
- chiropractor
- pain management doctors
- aroma therapy (essential oils)
- pressure points
- muscle relaxers