MDR-TB - a big monster
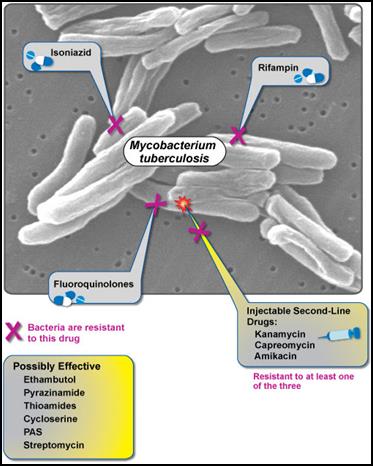
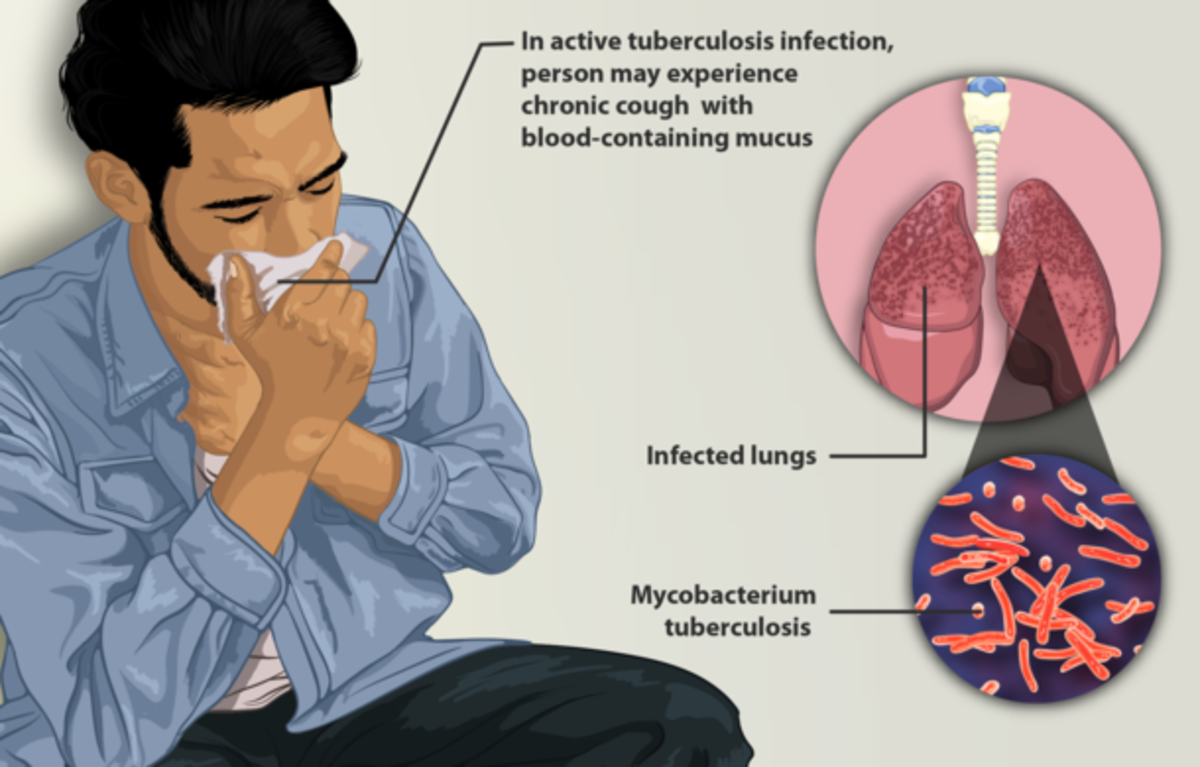
The bacteria that cause tuberculosis can develop resistance to the antimicrobial drugs that are used to treat it. So, tuberculosis that does not respond to the drugs like isoniazid and rifampicin that are used to treat it is called multi-drug resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB).
Extensively drug-resistant TB (XDR-TB) is a form of TB caused by organisms that are resistant to isoniazid and rifampicin (i.e. MDR-TB) as well as any fluoroquinolone and any of the second–line anti-TB injectable drugs (amikacin, kanamycin or capreomycin).
These forms of TB do not respond to the standard six month treatment with first-line anti-TB drugs and can take two years or more to treat with drugs that are less potent, more toxic and much more expensive.
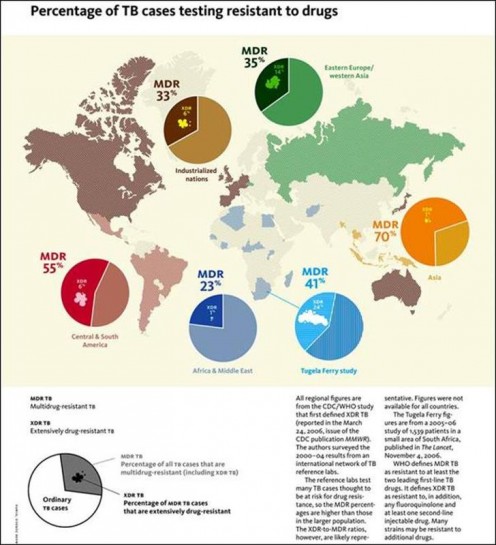
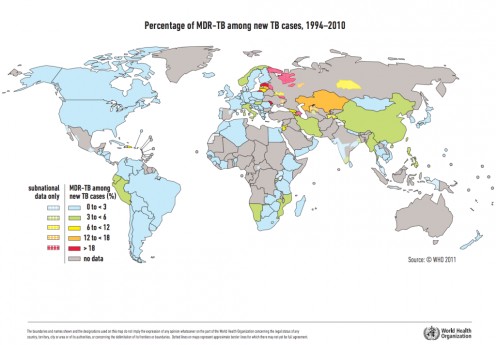
The following world wide statistics of MDR-TB deserve a serious attention of everyone -
- The total number of MDR-TB cases estimated to have occurred world wide in 2004 is 424,203. In the same year, 181,408 MDR-TB cases were estimated to have occurred among previously treated TB cases alone. Three countries—China, India, and the Russian Federation—accounted for 261,362 MDR-TB cases, or 62% of the estimated global burden.
- In 2010, the World Health Organization (WHO) estimated that there were globally 290,000 cases of MDR-TB among those cases of pulmonary TB that were reported to them. It was also estimated that in total there were 650,000 cases of MDR-TB among the world’s 12 million prevalent cases of TB.
- There are 27 "high burden" countries for MDR-TB. These are countries where there are at least 4,000 cases of MDR TB each year, and/or at least 10% of newly registered TB cases are of MDR TB. The high burden countries are – Armenia, Azerbaijan, Bangladesh, Belarus, Bulgaria, China, DR Congo, Estonia, Ethiopia, Georgia, India, Indonesia, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Latvia, Lithuania, Myanmar, Nigeria, Pakistan, Philippines, Republic of Moldova, Russian Federation, South Africa, Tajikistan, Ukraine, Uzbekistan, and Viet Nam.
- About 3.7% of new tuberculosis patients have multidrug-resistant strains (MDR-TB). Levels are much higher in those previously treated – about 20%. The frequency of MDR-TB varies substantially between countries. About 9% of MDR-TB cases also have resistance to two other classes of drugs, or extensively drug-resistant TB (XDR-TB). By March 2013, 84 countries had reported at least one XDR-TB case.
- WHO estimates that there were about 0.5 million new MDR-TB cases in the world in 2011. About 60% of these cases occurred in Brazil, China, India, the Russian Federation and South Africa alone (BRICS countries).
- 48% of patient with MDR-TB enrolled on treatment in 2009 were reported to have been successfully treated.
Cause of MDR-TB –
A strain of MDR-TB originally develops, when a case of drug-susceptible tuberculosis is improperly or incompletely treated. This occurs –
- When a physician does not prescribe proper treatment regimens or
- When a patient is unable to adhere to therapy.
Improper treatment allows individual TB bacilli that have natural resistance to a drug to multiply. Eventually, the majority of bacilli in the body are resistant. Once a strain of MDR-TB develops, it can be transmitted to others just like a normal drug-susceptible strain.
Factors contributing to its development –
The following factors contribute to the development of MDR-TB -
- Noncompliance or inadequate compliance with anti-tuberculosis drug therapy
- Delayed diagnosis and delayed determination of drug susceptibility, which may take several weeks
- Susceptibility of immune-suppressed individuals for rapid disease progression, which may result in rapid transmission of the disease to other immune-suppressed patients
- Inadequate isolation arrangements and other environmental safety conditions, especially in confined areas like prisons
The success of treatment depends upon how quickly a case of TB is identified as drug resistant and whether an effective drug therapy is available. The second-line drugs used in cases of MDR-TB are often less effective and more likely to cause side effects.
DOTS Program –
DOTS stands for Directly Observed Treatment Sort Course. It is a strategy used to reduce the number of tuberculosis cases. In DOTS, the health workers observe patients as they take their medicine because many patients fail to take their medication when left alone. This contributes to the spread of MDR-TB. DOTS remains at the heart of the Stop TB Strategy.
A DOTS program should incorporate the following five elements as per recommendations of WHO -
- Political commitment with sufficient financing – It includes legislation, planning, human resources, management, and training.
- Case detection through strengthened laboratory network – It requires strengthening TB laboratories, and drug resistance surveillance.
- Standard treatment under supervision and with patient support – It includes TB treatment and program management guidelines, International Standards of TB Care (ISTC), Practical Approach to Lung Health (PAL), and community-patient involvement.
- An effective drug supply and management system – It includes availability of TB drugs, TB drug management, global drug facility (GDF), and green light committee (GLC).
- Monitoring and evaluation system and impact assessment – It includes TB recording and reporting systems, global TB control report, data and country profiles, TB planning and budgeting tool, WHO epidemiology and surveillance online training.
MDR-TB is a major public health problem that threatens progress made in TB care and control worldwide. Drug resistance arises due to improper use of antibiotics in chemotherapy of drug-susceptible TB patients. This improper use is a result of a number of actions including administration of improper treatment regimens and failure to ensure that patients complete the whole course of treatment. Essentially, drug resistance arises in areas with weak TB control programs. A patient, who develops active MDR-TB strain, can transmit this form of TB to other individuals. The frightening monster of MDR-TB is to be stopped in its tracts before it becomes unmanageable.