- HubPages»
- Health»
- Personal Health Information & Self-Help»
- Self-Help for Sleep Issues & Sleeplessness
NREM sleep vs. REM sleep

It is a fact that most adults are moderately to severely sleep deprived. Most healthy adults need between seven and a half to nine hours of sleep per night to function at their best. So, a good sleep isn’t a luxury but is a necessity.
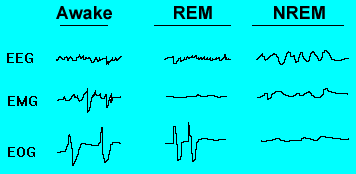
Typically, sleep falls into two categories – NREM sleep and REM sleep. A sleep cycle, consisting of NREM sleep and REM sleep, typically lasts for 90 minutes and repeats itself 4 to 6 times over the course of the night. During the first 2-3 sleep cycles, we spend most of our time in deep NREM sleep (stages 3-4), whereas during the final 2-3 sleep cycles, we spend much more time in REM sleep accompanied by lighter NREM sleep. Regardless of when we fall asleep, people tend to experience more NREM sleep in the earlier hours of the night and more REM sleep in the later hours of the night.
In the first half of the night, mostly deep sleep of stages 3 and 4 occur and later in the night, REM stages become longer, alternating with light sleep of stage 2. That is why the persons sensitive to waking up in sleep do so in the early morning hours and not immediately after going to bed.
NREM sleep –
NREM sleep consists of four stages viz. stage 1, stage 2, stage 3 and stage 4. Stages 1 and 2 are characterized by theta waves which are slower in frequency and higher in amplitude than alpha waves. These two stages last for 5 to 10 minutes each and sleep normally is light during these stages. During stage 1, it is not uncommon to experience strange and extremely vivid sensations by an individual. In the stage 2, there are primarily theta waves interspersed with sleep spindles periodically every minute or so. Sleep spindles indicate sudden increase in wave frequencies.
Stage 3 and 4 are characterized by delta waves that are slower than theta waves. Stage 3 is a transitional period between light and deep sleep. This stage usually lasts for 10 to 15 minutes. Stage 4 represents deep sleep and usually lasts for about 30 minutes. Bed wetting and sleepwalking typically happen at the end of the stage 4 sleep. If aroused from stage 3 and 4 sleep, an individual feels drowsiness and disorientation for some time.
During deep stages 3 and 4, the body repairs and regenerates itself. Our muscles and bones are built and immune system is strengthened.
It has been found that NREM sleep improves declarative memory which include memories of fact based information and personal events. It doesn’t enhance procedural memory. Daytime naps represent NREM sleep, so that is why they are also quite energizing and improve our declarative memory.
The first half of the sleep period primarily contains increased amounts of slow wave sleep (SWS) but it still contains substantial amount of REM sleep. It has been suggested that SWS and REM sleep play complementary roles in memory processing. As one ages, one sleeps more lightly and gets less deep sleep. Aging is also associated with shorter time spans of sleep, although studies show the amount of sleep needed doesn't appear to diminish with age.
REM sleep –
REM sleep is characterized by the production of alpha waves operating at 8 to 13 cycles per second. This is also called paradoxical sleep since alpha waves also occur when we are awake. The brain neural patterns in REM sleep resemble those in an awakened state. It is also characterized by rapid eye movements and paralysis of muscles. It normally makes up to 20% to 25% of the total time spent in sleep in adults. The persons with depression tend to be in a stage of REM sleep shorter than normal adults. The persons who are deprived of sleep enter into REM sleep faster than those who aren’t.
During REM sleep, blood flow decreases to the brain as it is redirected to the muscles with the result that body and mind are more rested and refreshed. In REM sleep, the brain absorbs and stores new information as long term memory. Sleep spindles – brain waves rapidly waxing and waning at strong frequencies - occur predominantly in REM sleep though less frequently in stages 3 and 4 of NREM sleep.
REM sleep phase takes place near the end of the night between 6 to 8 hours of sleep when people have dreams. In this stage, the brain replenishes neurotransmitters which organize neural networks for remembering, learning and problem solving. In REM sleep the brain transfers short term memories in the motor cortex to the temporal lobe to become long term memories. The sleep spindles fire to stimulate the temporal lobe to make sense of new information and store it in long term memory. Therefore, sleeping fewer than six hours may block spindles, thus preventing new information from entering into long term memory.
The brain stimulation is critical for proper brain development. When we were still a fetus or a small child, we hadn’t yet developed the senses; REM sleep is the only proper stimulation the brain would get. Infants spend 50% of their total sleep in REM and 50% in NREM phases. But when we’re older we can get this stimulation from the outside world.
Differences between NREM and REM sleep –
The following table enumerates main differences between NREM sleep and REM sleep -
NREM sleep
| REM sleep
|
|---|---|
It mainly generates theta waves.
| It mainly generates alpha waves.
|
Its first two stages produce light sleep and last for 5 to 10 minutes.
| During REM sleep, brain is awake but the body is asleep. Rapid eye movements take place but the muscles are paralysed in this sleep. It is characterized by dreams.
|
Its second two stages produce deep sleep. Stage 3 sleep lasts for 10 to 15 minutes whereas stage 4 sleep lasts for 30 minutes.
| REM sleep forms 20 to 25% of the sleep cycle.
|
During NREM sleep, the body repairs and regenerates itself. Muscles and bones are built. The immune system is strenghtened. NREM sleep enhances declarative memory.
| During REM sleep, brain aborbs and stores new information received during the day as long term memory.
|
Conclusion –
The brain stimulation is very critical for the development of the brain in a fetus or a small child. Since they cannot receive adequate brain stimulation through their senses, which are not fully developed, REM sleep provides the proper stimulation to their brain. It has been found that if an adult is deprived of REM sleep due to any reason, he or she may not have serious health problems apart from some long term memory defects.
The typical adult sleeps about 8 hours per night with lots of individual variability. Teenagers tend to need 9 or more hours of sleep a night to be optimally alert the next day. So, it can be concluded that an adult should take an adequate amount of sleep in order to function optimally and stay healthy.