- HubPages»
- Health»
- Mental Health»
- Addiction»
- Drug Addiction
The Effects of Smoking Weed

Is Marijuana Bad for Your Health?
When you smoke weed, it effects your brain. And when your brain is affected, your body is affected. Obviously, mucking around with your brain isn't recommended unless you're using marijuana for a seriously legit medical reason. Yes, marijuana is natural, but so are lots of things that you wouldn't want to put in your body, like seeds from the fruit of a strychnine tree. Another thing is the difference in potency between natural marijuana that grows in the wild and the stuff you buy from your dealer. You can't really even compare the two anymore. What you're smoking is a mutant GMO THC bomb compared to the stuff growing peacefully on the mountainside, untouched by humans.
Are you addicted to weed?
- I am addicted to weed.
Are you addicted to weed? Only you can answer that question. If you feel that weed's taken over too much of your life, this site can help you gain that control back. Admitting that there's a problem is the first step to eliminating it.
Marijuana and Dopamine
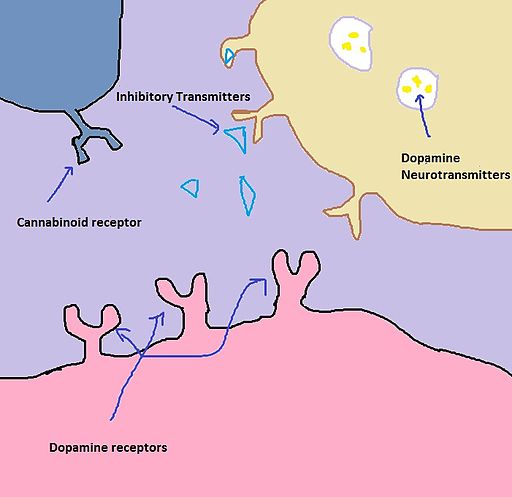
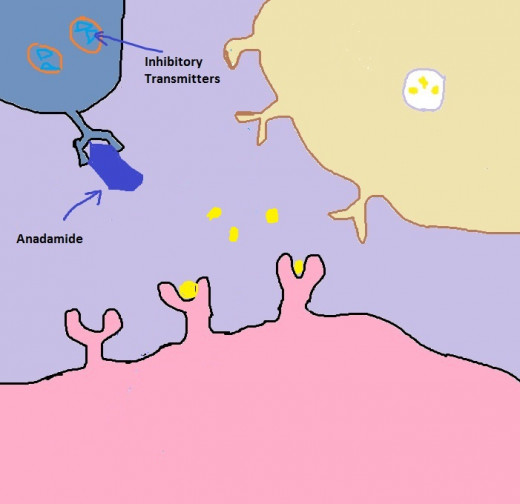
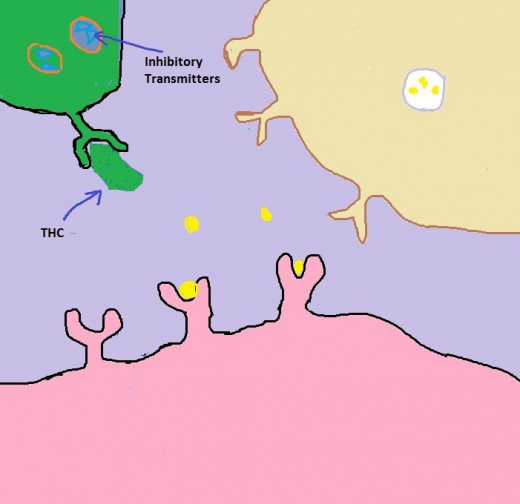
What exactly does THC do when it makes its way to your brain? In a nutshell, it alters the normal flow of neurotransmitters. Brain cells (a/k/a neurons) talk to each other by releasing and receiving chemicals. These chemicals are called neurotransmitters. Think of neurotransmitters as keys and receivers as locks. Only certain keys will fit into certain locks, and THC just happens to be an exact copy of the key that lets dopamine flow unobstructed. (The scientific community, by the way, is boggled by this exact copy of the key thing.) So here's how THC works: It binds to an opiate receptor. That's it. This binding blocks the release of inhibitory neurotransmitters. The job of inhibitory transmitters is to head on over to neurons with dopamine gateways and plug those gateways up. THC has therefore prevented inhibitory neurotransmitters from plugging up dopamine gateways by plugging up the gateways of the inhibitory neurotransmitter. The dopamine now flows unobstructed. Of course, this bungles the delicately balanced soup of neurotransmitters swimming around in the brain. Altering one's brain chemistry in this particular fashion results in higher than normal amounts of dopamine being released, and that makes a body feel really good.
Marijuana (THC) and Dopamine 1
Click thumbnail to view full-size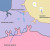
Marijuana (THC) and Dopamine 2
Click thumbnail to view full-size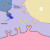
Marijuana (THC) and Dopamine 3
Click thumbnail to view full-size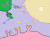
Is Weed Addictive?
Ok, the next thing you need to know is that there are certain areas in your brain that have an especially high number of cannabinoid receptors. And guess what? Those are the parts of the brain that are most affected when you use weed.
So let's get down to brass tacks: Which parts of the brain are we talking about and what's the effect THC has on them? Ok, let's start with the brain stem. It's the go-between for your brain and your spinal cord and controls a lot of basic functions like heart rate, and when it's impaired by THC, it speeds up your heart rate, lowers blood pressure, and blocks your ability to feel pain. Your neocortex, which performs higher functions like conscious thought and language, when impaired by THC, alters thought and judgment. Your hypothalamus, which is in charge of your metabolic processes, when impaired by THC, increases your appetite for sex and food. The nucleu accumbens, your brain's reward center, when impaired by THC, makes you feel euphoric and strongly reinforces whatever you're doing at that moment (using marijuana) so that you'll want to do it again and again.
How Does Weed Affect Your Brain?
Currently, it is believed that these effects are only temporary. And marijuana doesn't seem to cause permanent structural changes in these areas of the brain either. Other areas of the brain, however, are a different story. Research has located structural differences in two areas of the brains of long-term marijuana smokers when compared to the brains of subjects who do not use marijuana. These structural changes are located in the brain's hippocampus and amygdala. The hippocampus is a part of our brain that comes into play every time we either learn something or recall something we've learned. And the amygdala helps us process emotions, both positive and negative. So it can be said that long-term marijuana use makes permanent structural changes in the brain in the areas of learning, memory, and emotion processing. There are, however, limitations to these findings: The studies were short-term and done only on males, they all had small numbers of subjects, and they weren't consistent in how they made structural measurements. Needless to say, more studies need to be conducted in this area of research.