Shea Butter Benefits, Uses, and Recipes
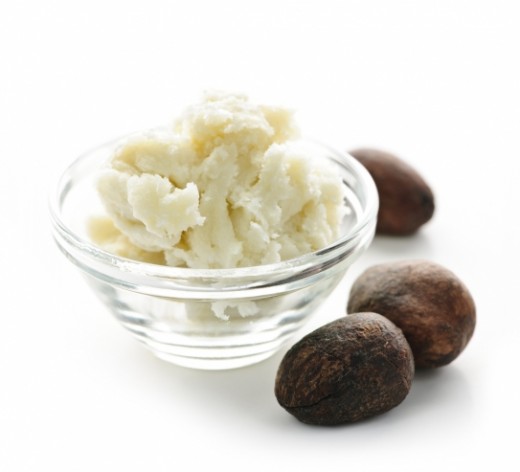

What Is Shea Butter?
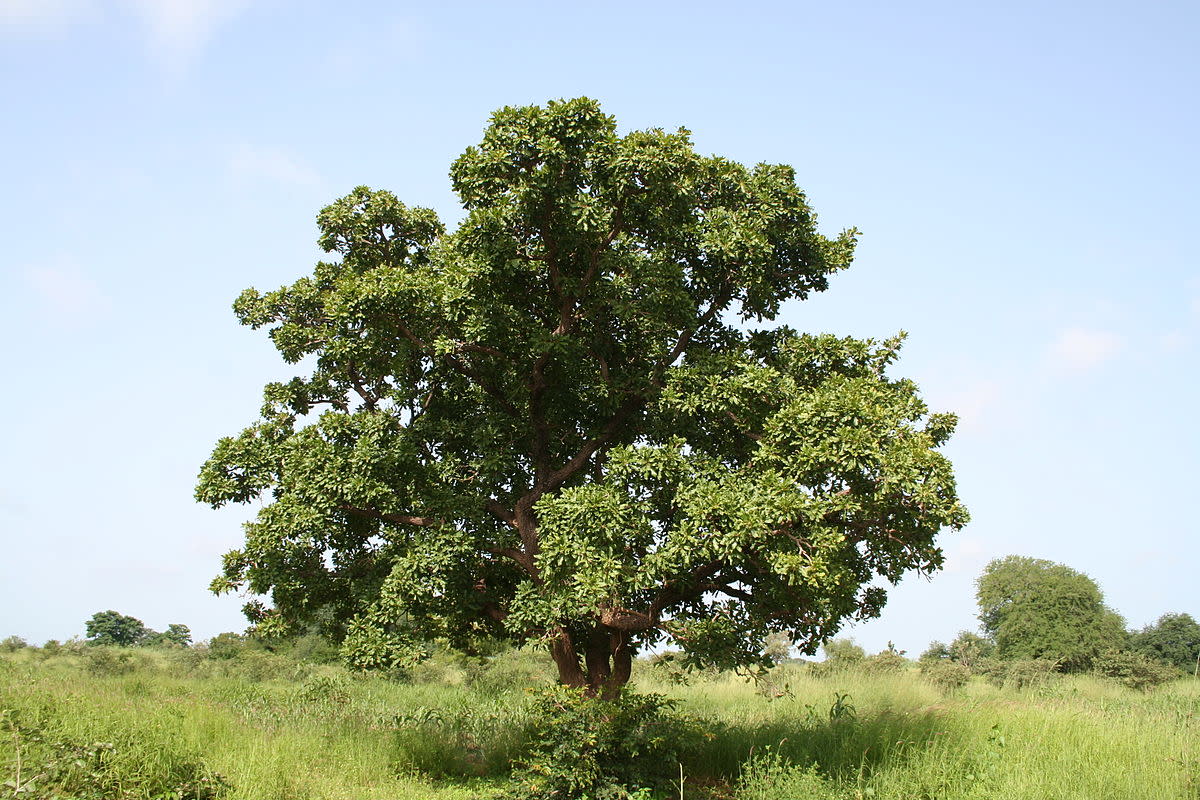
Shea butter is a highly fatty substance that is extracted from the African karite tree. It is a triglyceride ranging from bright yellow to ivory in color. Shea butter is derived mainly form oleic acid and stearic acid. The english word "shea" (pronounced shay) comes from the word s’í in the language of Mali known as Bamana.


Shea butter is a complex fat that is made up of approximately 40-60% oleic acid, 20-50% stearic acid, 3-11% linoleic acid, 2-9% palmitic acid, less than 1% linolenic acid, and less than 1% arachidic acid. It is an extremely rich, natural source of vitamins A and E.
The moisturizing properties of the butter are similar to those produced by the sebaceous glands in the skin, making shea butter highly beneficial in skin care. In addition, the healing fraction of shea butter ranges from 5-17%. it is this high healing fraction that makes shea butter superior to other nut oils. Shea butter has been shown to be improve a number of skin conditions. These include:
- Eczema
- insect bites
- frostbite
- sunburns
- skin allergies
- small wounds
- wrinkles
- psoriasis
- arthritis
- stretch marks
- And more...
Shea Butter Classifications
Grade
| Meaning
|
|---|---|
Grade A
| Raw or unrefined, extracted using water
|
Grade B
| Refined
|
Grade C
| Highly refined and extracted with solvents such as Hexane
|
Grade D
| Lowest uncontaminated grade
|
Grade E
| With contaminants
|
Grade A shea butter retains the most natural vitamins, especially vitamins A and E. These vitamins are partially lost in the other grades.
The Traditional Refining Process
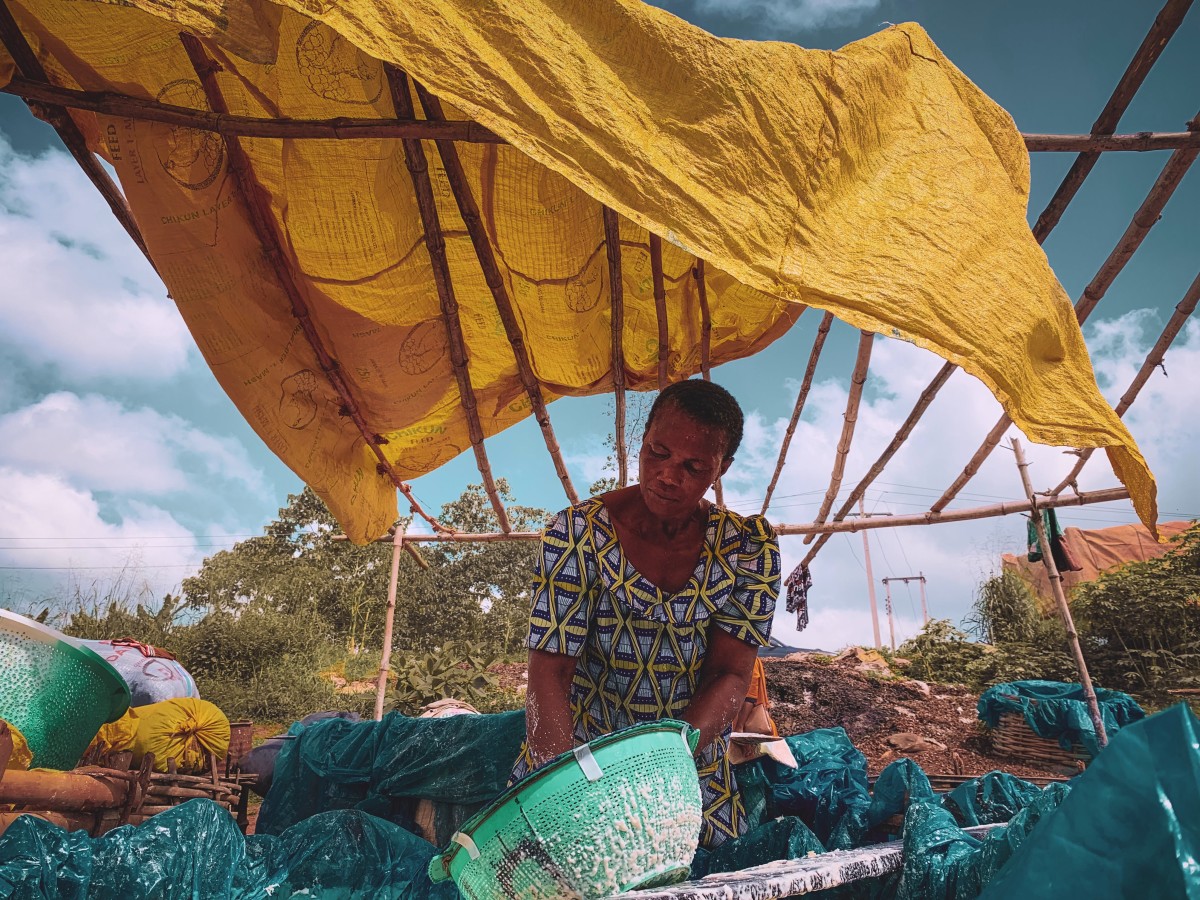
1. Cracking/Separating: This consists of separating the outer shell from the nut and is traditionally completed by the female elders and young girls in Africa.
2. Crushing: The shea nuts are then crushed, traditionally with mortars and pestles.
3. Roasting: Huge pot are then placed over wood fires and the crushed nuts roasted inside. This requires constant stirring with wooden paddles to prevent the butter from burning.
4. Grinding: Once roasted, water is gradually added to the shea nut as it is ground into a smoother paste.
5. Oil Separation: The paste is then kneaded by hand as water is gradually added in order to separate the butter oils. These butter oils are in a curd state and easily float to the top where they are removed and excess water is squeezed out. The curds are then slowly melted and the remaining water removed by evaporation.
6. Collecting and Shaping: The resulting shea butter is then ladled from the top of the pots and placed in a cool place to harden. Finally, they are formed into balls.
Refined Versus Unrefined Shea Butter
It is important to understand that all shea butter is not created equal. One of the many factors to consider when making a shea butter purchase, is to decide if you would prefer refined or unrefined butter. In general, the difference between the two are as follows:
Refined Shea Butter - cleaned, bleached, and deodorized. This shea butter cannot be used in cold process soap but can usually be added to cosmetics such as lotions and creams. The refining process typically leaves the butter a snow white color with no odor. It also reduces the bioactive nutrients found in unrefined shea butter by as much as 75% or more.
Unrefined Shea Butter - smells nutty and can be used in cosmetics and cold process soap. Unrefined shea butter has not passed through any filtering or meshing system using chemicals, clays or other methods. The vitamin content of unrefined shea butter, therefore, remains intact.
What Color is REAL Shea Butter?
There has been much debate over the color of real, unrefined shea butter. The fact is unrefined shea butter can vary in color from ivory, beige, greyish-white, pale yellow, and any other shade of yellow to off-white. Most sources report that the color is indicative of the region in which the shea butter was made. Others suggest that fresh shea butter turns yellow when it is old and has lost some of its quality (while others report that yellow shea butter is fresh and the butter turns white as it ages). To even further complicate matters, there is also the suggestions that yellow shea butter is actually African butter from a completely different tree. Unfortunately, the quality and authenticity of shea butter cannot be determined by color alone.
ASBI Testing Services
If you are uncertain about the quality and authenticity of your shea butter, the American Shea Butter Institute provides a analytical testing and grading service that may help. For more information and to submit a sample of your shea butter for analysis, visit;
http://www.sheainstitute.com/grading-services/grade-analysis-submission/
Instead of relying solely on color, here are some tips for purchasing a quality shea butter:
1. Sample a small amount of he product prior to buying a bulk supply.
2. Check the shea buttter for visible debris and mold
3. Smell the butter. If no frangrances have been added it should have a nutty aroma.
4. Is the butter smooth or grainy? If grainy, the shea butter may have been heated at some point. This is sometimes done to add fillers and additives
5. Lastly, shea butter absorbs quickly and easily into the skin. If the butter remains waxy or greasy on your skin is is not real, unrefined, pure shea butter.
Shea Butter Recipes
Creating your very own shea butter cream for use in your hair or on you skin is simple. In general, shea butter recipes include shea butter and whatever carrier and/or essential oils desires. For best results, it is recommended that shea butter be heated carefully using a double broiler until fully melted. This will help eliminate crystallization and/or graininess later. Be careful not to overheat your butter as this will reduce its healing properties. Also, shea butter should be packaged into the desired container and frozen or refrigerated immediately following completion of your recipe. The rapid cool down also aids in avoiding the formation of crystals.
Though melting shea butter is probably the most common method, there are those who choose not to use heat. It is possible to obtain a creamy butter and even to create your own recipe using other desire oils without heat. Simply whip your butter as is, adding your desired carrier oil or essential oil as you go. With this technique you can obtain a smooth texture and ensure all nutrients are preserved.
Lastly, when deciding what carrier and essential oils to use in your shea butter mix, there are a few factors you should consider. These are:
1. purpose of the cream (stretch marks, wrinkles, dry skin, ect.)
2. Desired scent of your cream
3. Any other personal preferences
Do your research to determine which other oils and/or butters may be beneficial to your mixture. For example, wheat germ oil, almond oil, cocoa butter, coconut oil, lavender, emu oil, bergamot, and birch are all great for eczema. An anti wrinkle cream may benefit from additions such as jojoba oil, sage, extra virgin olive oil, etc. Research is the key to creating the perfect shea butter mix for you. Be creative and have fun.