How Incandescent light bulbs work

An explanation on how an incandescent light bulb works
The incandescent light bulb is probably one of the most important inventions that inaugurated the age of electricity. There were many who already have invented or created a light bulb before Thomas Edison. It was Thomas Edison’s creation that was more efficient. It was also Thomas Edison’s light bulb that created a huge impact in the industry and started the age of electricity.
In cartoons, any bright idea thought of by the character is represented by a light bulb appearing above his head. It is associated with the light bulb because of Thomas Edison. It took him thousands of attempts to create a functional and efficient light bulb. And when he did, his invention was great enough to change the world.
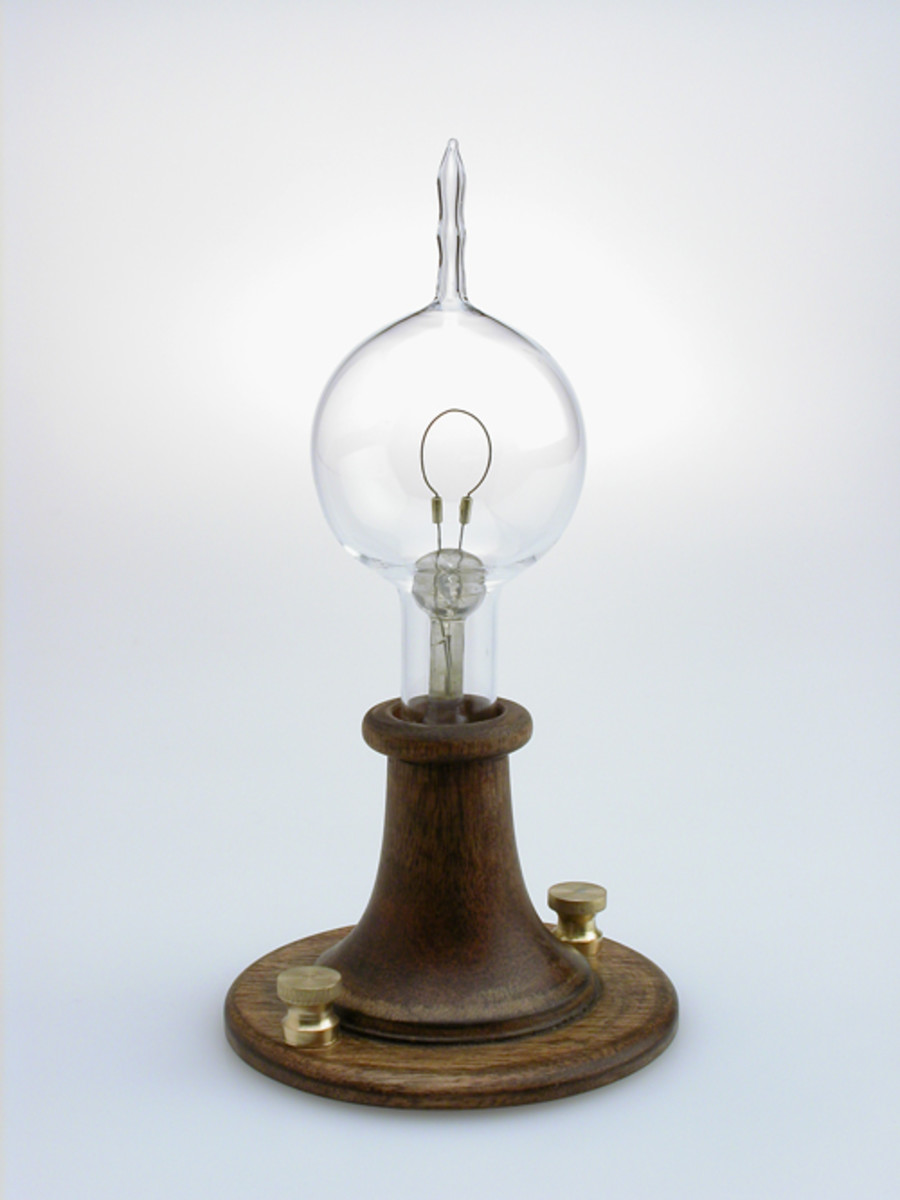
The Incandescent light bulb is composed of a base, tube and a filament. The base is where the filament is connected. The base is then connected to a light bulb receptacle then to a power source. The tube is either a vacuum or is partly filled with an inert gas. The filament is a metal that has high resistance and has high photon output when heated. Examples are tungsten and magnesium.
Electric current is allowed to pass through the filament. The filament is composed of a very, very thin wire – about 10 times or smaller than a hair strand. It is then coiled then coiled again and again so that a very long wire can fit in a short filament. This design allows for a very high resistance filament. Resistance is directly proportional to the length and inversely proportional to the cross-section area of any conductor. That’s why the filament is made that way.
The reason why the filament should have very high resistance is that the goal is to heat the filament until it glows bright enough. The temperature increase is directly proportional to the current and resistance. The reason it heats up is because the flowing electrons are “interfered” or “bump” or are “resisted.” They counter this obstacle and like a man running at sprinting speeds through a very busy street, it causes excitement. By excitement I mean that the other people are “bumped off” in the process. The same thing happens in the molecular level. Atoms get “bumped” then it creates small vibrations which is the cause of heat.
When any metal is heated to a certain temperature, it glows. It glows because of what we call electron excitement. When metal is heated, the electrons in it are excited. The word excited here is used differently than that of the previous paragraph. By excitement, we mean that the electrons enter a higher unstable energy level. They don’t stay in that energy level for long. They drop back eventually to a lower, stable energy level and as they do, they release a photon in the process.
The vacuum and inert gas is used so that the filament will not react with anything. The temperature the filament reaches is very high and we know that higher temperatures cause chemical reactions to take place. To prevent the filament from burning up, a vacuum or an inert gas at a very low pressure is placed inside the tube.
Simply put, the incandescent light bulb works by heating a high resistance filament using electric current until it glows bright enough to illuminate its surroundings.