Why Insurance Companies Embrace Thermography
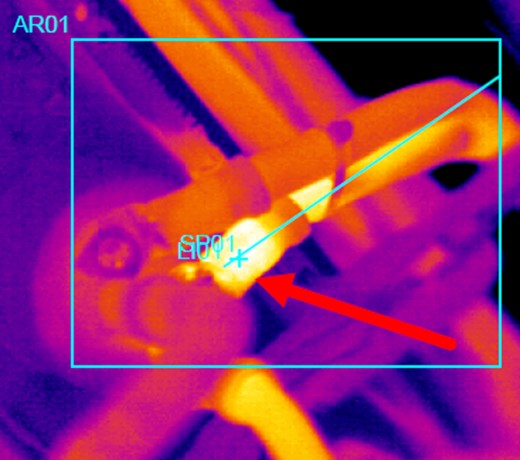
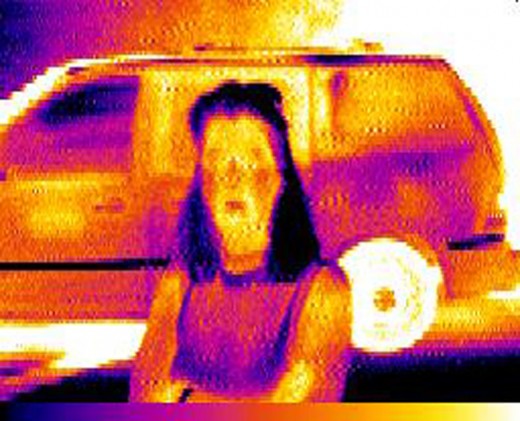
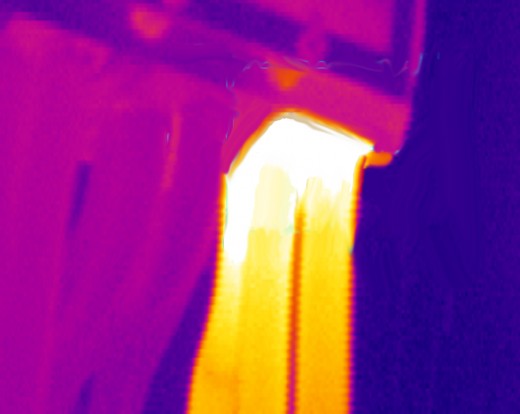
Infrared Images





The Risk Averse Philosophy
Insurance companies are experiencing increases saving in the tens of millions of dollars by employing trained thermographers to inspect facilities insures by the company. In actuality this has been the case throughout the forty years thermographers have been active in land and marine operations.
It is not surprising then that more companies and ships are turning to thermography to save money, that the US Congress is considering legislation to increase the operational safety of ships at sea which may well include biannual ship inspections by qualified thermographers, or that insurance companies are increasingly suggesting or requiring the insured to perform regular inspections.
For those few of us, long in the marine thermography business it is no surprise then that the UK’s Maritime and Coastguard Agency issued MGN 132 (M+F) in 1999 stating in part:
It is apparent from the number of reported incidents that ships personnel have, at times, been placed in unnecessary danger. In order to identify potential overheating situations in electrical equipment, owners are advised to consider the use of ‘thermal-imaging techniques as a means of verifying the security of electrical connections and pinpoint problem areas at an early stage.
It is not surprising then to find insurance companies hiring thermographers directly and requiring the insured to allow inspections to ensure the adequate maintenance and safe operating conditions exist on the assets insured.
Most people think of insurance companies as merely those contracted to be financially responsible when something goes wrong. If an incident requires a payment, the company simply raises your insurance, however, some feel a moral responsibility to keep others safe, keep their rates down, provide excellent service, and see greater profitability for their companies. Those with such a philosophy require or provide these services, those people with other insurance companies ought to have regular thermographic inspections if only to prevent those incidences which insurance covers and which destroy businesses and from time to time take human life.
Cost Savings
Some thermographic inspection companies calculate the dollars saved by comparing and contrasting the cost of a Run-To-Failure model again a Repair-As-Found model showing the clients the dollars saved not in a worst case scenario, rather in a typical scenario where equipment regularly fails.
Inspections that compare these costs are most helpful because they not only give the crew action points and identify the condition of the equipment but also allow for profit justification with the C-Level management so they can show their companies how much money is being saved, what costs are being avoided by this inspection.
While a land based electrical fault may cause between $400 and $5000 in damage, on a ship, a small fire in the Motor Control Center may cost a million dollars when all costs are calculated. In both locations small fires have a way of turning into large conflagrations which periodically cost human lives and total loss of the facility or ship.
Insurance is all about risk and risk avoidance. Thermographic analysis is the best way to ensure you are not regularly filing insurance claims and receiving insurance premium increases. For insurance companies it is the most cost effective cost savings mechanism they have found and a great cost reduction service to their clients.
The Most Useful and Critical Nondestructive Test Modality
Infrared (IR) imaging, thermographic inspection, or thermography is one of the most common nondestructive testing (NDT) methods worldwide, and its use continues to grow as the technology improves and users begin to realize the true potential of this testing method.
Thermography uses thermal and infrared sensors to compare or measure temperature variations (respectively qualitative and quantitative analysis) in a broad variety of test objects.
It is important to consider a variety of thermal laws and properties to determine how the surface of a subject absorbs or emits thermal energy for thermographic NDT.
Emissivity
First, emissivity, the ratio of the infrared energy radiated by an object at a given temperature to the energy emitted by a blackbody radiator at the same temperature, is critical to understand and compensate for. Without emissivity adjustment, indicated temperatures can be significantly in error.
Emissivity is a surface condition or property and is immediately modified when the surface material changes, say, is painted or coated, touched, or cleaned.
The author recently suggested to another scientist that he coat his printed circuit board with a thin spray of foot power which has an emissivity of 0.98 to equalize the emissivity across various elements to improve his imaging of the device.
In the past we have suggested to engineers that they paint valves which could not be insulated with sliver paint to lower heat losses from the valve body. Or consider the case of the overheating hydraulic system where merely painting the pipes black lowered the heat sufficiently to maintain operations without further alteration.
Diffusivity
Second, diffusivity (sometimes called thermal conductivity) is critical to understanding various thermal patterns encountered. Diffusivity is the property of a mass that describes thermal energy traveling through the mass. Some materials have high diffusivity rates such as copper and aluminum, the heat transmits rapidly through them according to Fourier’s Law, which must be understood to understand some thermal patterns.
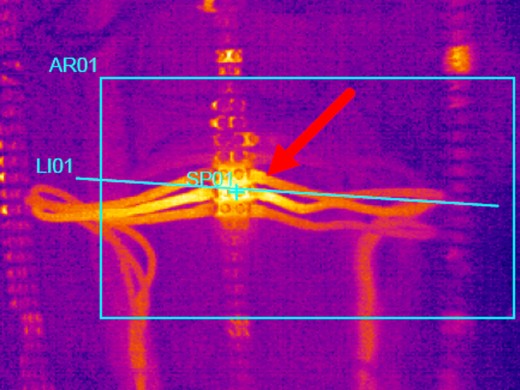
Inspecting a petroleum product storage tank is a classic example where the tank is often banded when imaged by a thermographic radiometer. The banding results from different masses in the tank with different specific energy and different rates of energy diffusion; sediment, if any, the petroleum product itself, say oils from gasoline, separations within the product, water contamination, and gasses at the top all have different diffusive properties. In NDT, understanding these diffusive properties is important to properly analyzing the conditions being observed.

Thermal Advantage
Thermography has many distinct advantages in a complex environment over the other NDT modalities. Thermography as the primary NDA is a flexible method that can be applied to a broad variety of materials in nearly all environments; it is a noncontact, noninvasive NDA method. It is used to inspect nearly all objects and equipment in service at inspection time, and therefore, not only prevents lost operational time but helps prevent downtime by accurately determining root causes and malfunctioning conditions prior to failure and avoiding both noncritical and critical failures.
Equipment Failure Risk Reduction Methodology
Equipment failure risk is one variable that companies can control when proper and effective measures are implemented including thermographic inspections and the resulting corrective maintenance measures. This will extend equipment life toward the manufacturer’s projected life expectancy. Reducing risk has a strong tendency to increase profitability, reduce loss, and protect lives. Thermography is the most productive of all predictive maintenance techniques available.
Industrial equipment failures are more frequent than expected for their design or their specified failure limits, and this can be caused by wrong installation, harsh operating environments, poor operations, and inadequate maintenance practices.
Fortunately, the identified failure rates of machines can be beneficially impacted by predictive and preventative practices such as regular thermographic inspections and analysis, corrective maintenance practices as well as by precision installation techniques.
When you reduce the risk of excessive stress, you reduce equipment failures. No single analytical modality is better at this than thermography which, when properly performed by qualified thermographers yields strong indicators of stresses which can be corrected and failure modes enabling corrective or restorative measures before failures occur.
The risk of equipment failure is comprised of the change of failure expressed as a decimal, multiplied by the consequence of failure, also expressed as a decimal.
Chance of failure reduction strategies reduce the opportunity that failure modes will be entered. These are comprised of:
- Reliability engineering, and purchasing equipment which has undergone reliability engineering studies and design practices,
- Supply Chain Management techniques,
- Utilizing only properly sized equipment
- Total Quality Control and Continuous Improvement models
- Predictive and preventative maintenance (thermography, vibration, oil analysis)
- Precision Maintenance practices
- Root Cause Failure Analysis
- Engineering and Maintenance Standards
The Consequence of failure reduction strategy is a bit harder because it is less defined and more difficult to control, but incorporates:
- Condition based monitoring and corrective maintenance (thermography, oil analysis, power quality, other prognostics)
- Emergency Management
- Operator Watch Keeping
- Improved Critical Response
Stated differently, if you reduce the risk, you reduce the negative consequences on your operations and the company itself. The number of independent variables is high in any operating environment. However, thermography by itself, represents the single most effective analytical technique for reducing that risk because, it alone can identify stress on the largest array of equipment and induce through proper analytics the most accurate corrective measures.
Thermography cannot guarantee equipment will experience expected operational lifetimes, there are simply too many variables. Conditions change from moment to moment, however, no nondestructive test modality, no predictive test modality has such a broad range of applications nor is capable of identifying such a large range of failures, faults, or conditions, recommending such a broad range of potential restorative measures to the maintenance personnel by allowing them to control equipment stresses, fatigue and wear thus enhancing reliability and reducing risk.
Thermography as a condition monitoring tool with application of corrective measures reduces equipment failures across a broad range of industries from petroleum to shipping, from manufacturing to transportation.
Thermography is used to gather operative condition information on the failure modes, active wear, and other adverse conditions. Thermography is a highly reliable tool used to optimize equipment reliability ensuring correction of adverse circumstances allowing outcomes you want and expect from a preventative maintenance program.