Artificial Disc - Anatomy of Human Spine - Role of Intervertebral Discs
Buy Lumbar Support Online - Angel Sales PosturePro lumbar support to help your low back pain
In order to understand the importance of Artificial Disc Replacement Surgery - An Alternative to Lumbar Fusion, one must know the anatomy of human spine and importance and role of intervertebral discs because these two things are most important if you are having degenerative disc disease of the spine and would like to select a procedure or select a treatment or get a second opinion before undergoing lumbar spine fusion for health of your spine. So here is a simple and brief guide through which you can learn and understand what your spine consists of and what is it’s role in your body. Read on..
Anatomy of human spine: The spine is a column or supporting pillar of human skeleton, which consists of discs and bones. Vertebrae or blocks of bone provide anterior support and structure to this supporting pillar. In the posterior level, the 2 facet joints, one on each side of the spine, provide movement and stability of this mobile segment.
Role of intervertebral discs:
Intervertebral discs are situated between bones and act as a buffer, cushion, or shock absorber between the vertebrae. The spinal discs also make a contribution to the movement and flexibility of the human spine. The spinal discs are made up of 2 parts:
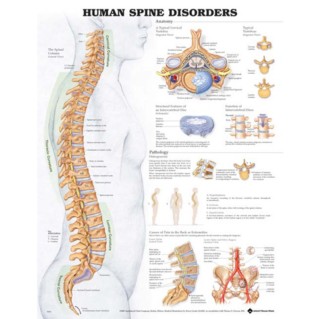
- First one is the inner portion of the disc, which is known as nucleus pulposus, which is a viscous or gelatin-like material.
- The second one is the outer portion of the disc, which is much more stronger than first one known as annulus fibrosus. The annulus fibrosus supports and surrounds the inner gel-like portion of the disc. The annulus fibrosus, outer ring of collagen, is also in contact with pain receptors known as nociceptors and nerve fibers, which stem from the anterior column of the human spine.
The human spine is primarily composed of proteins and water. Due to aging of the human body, the water content starts to decrease gradually, which causes the disc to become flat and cause some fissures or tears via the fibrous ring. These diseased discs are frequently called as degenerative discs and sometimes can convert into painful conditions.
Degenerative disc disease at a glance
In patients having degenerative discs, the inner portion of the disc, which is known as nucleus pulposus may bulge out and put pressure onto the fibrous ring (outer portion of the disc). This degenerative bulging process of the inner portions stimulates the pain receptors, which causes pain of the spine. Tears, fissures, and cracks developed within the outer portion (annulus fibrosus) can also cause severe pain.
Pain caused by intervertebral discs is frequently called as discogenic back pain or in simple words low back pain. Now due to the disadvantages of lumbar fusion mentioned in my previous article, Artificial Disc Replacement Surgery - An Alternative to Lumbar Fusion, orthopaedic surgeons are considering placement of artificial discs or artificial disc replacement surgery as an alternative to lumbar fusion to provide relief from constant severe back pain and discomfort.