A Simple Way to Help Kids Understand and Retain Knowledge of the Times Table

A teacher’s role includes careful observation of each student to quickly identify students who show sign of lack of engagement in school and provide needed intervention before frustration sets in. Most students who struggle will benefit from early intervention depending on their level of lack of engagement. This intervention should be aimed at improving their perception abilities and critical thinking skills to arrest the slide into frustration.
If students will perform well in math, interest in the task at hand is a factor that propels them to reach their full potentials. Math tutors should generate and sustain interest at every point in the learning process and help struggling students uncover and understand math procedures. This strategy of helping struggling students uncover and understand math procedures, generating and sustaining interest , will remove the dull misery and disengagement struggling students face and promote challenging, engaging fun sessions.
Uncovering the Times Table
The times table is a table every student needs to comprehend to be able to do very well in Math. Kids need to have a good knowledge of the times table early in life to be able to make good progress in math. Memorizing the times table is only a temporary way to make progress and sooner than later, the child forgets the table.
Helping the student uncover how 5 x 6 equals 30 or how multiplication is repeated addition can go a long way in helping the student retain this knowledge for a lifetime and derive proof for themselves. It is the role of a math tutor or educator is to carefully explain the process of formation of the Times table to the student so as to build a good pedestal and help the student imbibe the spirit of different solution strategies when dealing with multiplication facts.
Let us take a look at the 12 X 12 Times table grid below.
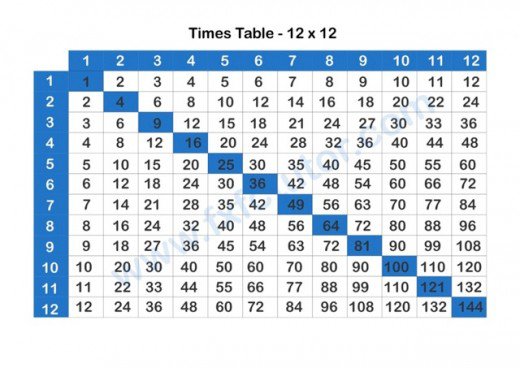
Students will learn how to derive their times table to 12 and beyond, they will learn how to derive square numbers and why multiplication of repeated addition from the grid above.
Let us begin to uncover the times table.
First, as a math tutor, I present the student with the 12 X 12 completed Times table grid shown above and allowed them study it for some time. I then ask the student to look at the times table grid with a view to spotting as many patterns as necessary. Since math is built upon rules, patterns and procedures, every student should explore each math question by asking themselves if there is a pattern that can be observed, a rule to be kept, and a procedure that needs to be followed in arriving at the solution. Next, I notify the student to tell me what patterns they spotted from the Times table grid. If the students cannot find any pattern, I give them a heads-up by asking student to look at each row and each column to find a pattern in each. If student cannot make out anything from each row and column, I begin by asking the student to look at Row 1 and I point out the pattern in each square box in Row 1. I start by informing the student that in Row 1, each square box is increasing by adding 1 consecutively in each preceding square box to arrive at the value of the succeeding square box. Row number 2 shows a similar pattern of each square box increasing by adding 2 consecutively in each preceding square box to arrive at the value of the succeeding square box. This pattern also plays out for Row 3 where each square box in Row 3 is increasing by adding 3 consecutively in each preceding square box to arrive at the value of the succeeding square box. This pattern is the same for all the Rows. Row 4 increases by adding 4 consecutively to each preceding square box to arrive at the value of the succeeding square box going to the right and it continues for all the rows in the Times table to Row 12.
The idea is to look at the square boxes in each Row as increasing consecutively by adding the row number been considered to each preceding square box to arrive at each succeeding square box going forward in the Row. This means if the student were to construct this Grid on their own and to fill the Rows, Row 1 will be completed by adding 1 consecutively to each preceding square box to arrive at the value of the succeeding square box going forward; Row 2 will be completed by adding 2 consecutively to each preceding square box to arrive at the value of the succeeding square box going forward, Row 3 will be completed by adding 3 consecutively to each preceding square box to arrive at the value of the succeeding square box.
This means Row (x) will be completed by adding (x) consecutively to each preceding square box to arrive at the value of the succeeding square box going forward.
Next, I point to Column 1 to the student and ask if they find a similar pattern as in the Rows. If the student can find such similar pattern, I acknowledge there alertness and awareness and continue uncovering the Times table grid.
I inform the student that the same pattern in the Rows plays out in the column, where column 1 increases by adding 1 consecutively in each preceding square box to arrive at the value of the succeeding square box going down the column. Column 2 increases by the addition of 2 consecutively in each preceding square box to arrive at the value of the succeeding square box going down the column, the same pattern plays out in column 3 where each square box increases by adding 3 consecutively in each preceding square box to arrive at the value of the succeeding square box going down the column. This pattern is the same for all the columns.
The idea is to look at the square boxes in each column as increasing consecutively by adding the column number been considered to each preceding square box to arrive at each succeeding square box going down the column. This means if the student were to construct this Grid on their own and to fill the columns, column 1 will be completed by adding 1 consecutively to each preceding square box to arrive at the value of the succeeding square box going down the column; column 2 will be completed by adding 2 consecutively to each preceding square box to arrive at the value of the succeeding square box going down the column, column 3 will be completed by adding 3 consecutively to each preceding square box to arrive at the value of the succeeding square box going down the column.
This means column (x) will be completed by adding (x) consecutively to each preceding square box to arrive at the value of the succeeding square box going down the column.
To further understand and uncover this grid, I point out to the student to view 3 X 5 from the standpoint of Row 3 multiplied by Column 5. Using the grid, the student will discover the product of 3 X 5. To discover the product of 3 X 5, the student simply needs to draw a straight horizontal line with a pencil through row 3 and a straight vertical line through column 5. The intersection of both lines is the product of 3 X 5 which is 15 from the grid. To uncover this for themselves, I encourage the student to try 5 X 4 using the principle outlined above to find the intersection which is the product of both factors.
Multiplication is repeated addition
Saying multiplication is repeated addition without going through the process to make the student understand it and uncover proof for themselves will amount to no teaching, since the actions of learning and teaching cannot be separated.
3 X 5 is equal to 3 + 3 + 3 + 3 + 3 which is equal to 15. The student should be made to uncover this for themselves by looking at row 3. Since we stated that each row increases consecutively by adding 3 in each preceding square box to arrive at the value of the succeeding square box going forward, 3 X 5 simply means begin by adding 3 to the first square box of row 3. To get the numeral in the second square box, add 3 to the first square box, this means the second square box will equal 6 (3 + 3 = 6). To get the numeral in the third square box, add 3 to the numeral in the second square box, this means the third square box will equal 9 (3 + 6 = 9). To get the numeral in the fourth square box, add 3 to the numeral in the third square box, this means the fourth square box will equal 12 (3 + 9 = 12). Finally, to get the numeral in the fifth square box, add 3 to the numeral in the fourth square box, this means the fifth square box will equal 15 (3 + 12 = 15).
Square Numbers
Since square numbers are the product of a number multiplied by itself, the student can see from the grid that the numbers highlighted in the diagonal are square numbers. I have marked them for clarity.
The square numbers in the diagonal are 1, 4, 9, 16, 25, 36, 49, 64, 81, 100, 121 and 144.
The hallmark of good teaching and online tutoring help session is to assist the student learn different ways of solving problems and build confidence. Knowing that they have the right problem solving skills in their arsenal will boost confidence and generate interest to confront problems. The ability to apply different solution strategies to a problem shows mastery of the topic.
© 2016 Charles Onwugbene