What Good is Gallium?

Many are introduced to gallium in school, where they learn about it in books or maybe through firsthand experience. What makes gallium so unique is that it has a melting point of 30 degrees Celsius, which means that human body heat is enough to make it melt.

Many might be left wondering what gallium can be used for seeing as its melting point is so low. Gallium is mainly used as a semiconductor or in alloys, but there is something it can do that very few, if any, other elements can do. It can detect neutrinos.
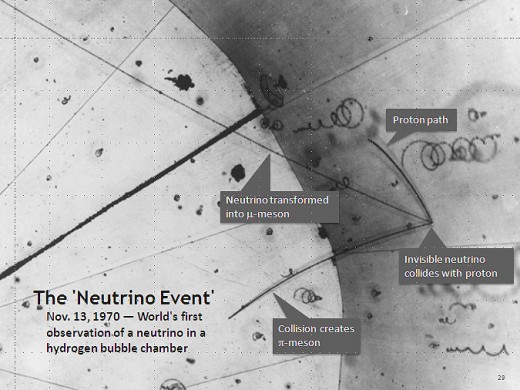
What is a Neutrino?
A neutrino, if it can be explained simply, has no electrical charge and almost no mass. It can pass through material without interaction. Because of this, neutrinos are very hard to detect and understand. They are one of the fundamental particles of the universe and the smart people know very little about them.
Where Does Gallium Fit into This?
In the GALLEX Experiment in the 90's, scientists studying these neutrinos had 30 tons of gallium, and they performed a neutrino-induced nuclear reaction. The 30 tons of gallium was the target of the reaction, and it was transmuted into germanium.
This germanium was then taken to be studied. The half life of germanium is around 11 days, so the scientists kept track of the decay with a counter. What they then found out was that for each neutrino that was released, there was a corresponding decay recorded. In other words, there was a recorded decay for each neutrino.
What Does This Mean?
If you are not a physicist or an astronomer, then you have no reason to care about gallium and neutrinos. However if you are an astronomer or even kind of inclined in science, then you should know that this bodes well for the study of neutrinos. Now that scientists can detect these particles, they have a better chance of studying and understanding them. They are one of the oldest particles in the universe, and we have not even scratched the surface when it comes to them, but we might be a bit closer.