Integumentary System (Skin)
Integumentary System
Skin is the largest organ of the human body which performs many essential functions. Perspiration is give, off through the skin; the skin helps regulate body temperature.
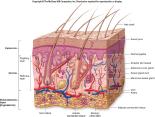
The epidermis (comeum or cuticle) and dermis (corium) constitute the two basic parts of the skin.
Epidermis is the top layer of the skin. The cells of the epidermis grow from the bottom and upward. In the lowest row, cells are shaped like columns. Above these rows are round cells. Cells grow flatter and becomes drier towards the surface. When they reach the surface, they are shed as thin flakes. These flakes are the dead skin a person often rubs off with a towel after taking a bath.30 Some nerves are located in the epidermis but there is no blood vessel. Epidermis is responsible for the color of the skin. Hairs and nails are parts of the epidermis with special functions.
Dermis. This layer is composed of closely woven network of connective tissue. It contains blood vessels, glands, nerves and hair follicles. On the outer surface of the epidermis are tiny elevations called papillae that fit into tiny pits on the undersurface of the epidermis and help connect the two layers of the skin.
Functions of the Skin
Sweat glands. These are glands that give off small amount of liquid waste matter.
Oil glands or sebaceous glands. These glands give off oily substances that make the hairs smooth and glossy. They also keep the skin from becoming too dry.
Blood. This helps regulate the body heat. When the body needs to give off heat, the blood vessels expand, the blood is placed closer to the outside air. When the body needs to conserve heat, the blood vessels contract slowing the rate of heat loss.
Epidermal Products
Hair is a substance that grows out of the skin of mammals. The color, texture and the way it grows are determined by heredity and environment.
Parts of the hair
1. shaft-main hair fiber
2. follicle-coating that encloses the root hair.
3. erector muscle-pushes againsts the oil glands to help lubricate the hair shafts. It also causes the hair to stand when a person is frightened.
Kinds of hair
1. fur-soft, dense hair (found on cats, rabbits, dogs and leopards)
2. fleece-thick, wooly hair (found on sheep)
3. bristle-short, stiff hair (found on hogs)
4. quills-sharp, spiny hair (found on porcupines)
Importance of hair are: They provide protection, warmth and sensation (common on animals with tactile hairs or whiskers. This type of hair helps feel the way around through narrow or dark places).
Nail is a special growth of the epidermis that is made up of hardened skin cells. There are two parts of the nail: matrix (skin below the nail) and lunula (white, crescent-shaped spot that contain smaller cells and less blood).
Claw is a sharp hooked nails of bird.
Hoof is the horny covering protecting the ends of digits of some animals like horses.
Horns are hard projecting appendages growing on heads of some animals like cattle, goat and deer.
Talons are claw found especially on a bird of prey.
Antler is a branch of horns of a male deer or stag.