Measurement: The basis of all scientific work
Objectives:
Upon completion of this lesson, the students should be able to:
- develop the skills in making accurate and precise measurement
- recognize the equivalents of the prefixes used in the SI units
- demonstrate skills in using dimensional analysis in conversion units



What is measurement?
Measurement is the process of finding out how many units there are in something. The basis of all scientific work is measurement. There are various units of measurement depending on what we wish to measure. There are measurements of length, mass, force, volume, time, velocity, density, electric current and many others and these are expressed in different units.
Almost all of us use measurements. The food we eat, the clothes and shoes we wear, the work we do, and many of the games we play involve measurements.
Some of the basic measurements in the chemistry include the following:
How long?
How big?
How heavy?
How hot?
What is scientific notation in measurement?
Scientific notation has the form M x 10n where M is the number between 0 and 10 and n is a positive or negative integer. n is the exponent or power of the number. It expresses the number of times 10 is multiplied by it.
Rules in writing a number in scientific notation:
- Retain one digit before the decimal point.
- Multiply M by 10 raised to the proper value of n, where n is equal to the number of decimal places the point is moved.
- Positive exponent means the decimal point was moved to the left.
- Negative exponent means the decimal point was moved to the right.
Example: The mass of the atmosphere is 5 100 000 000 000 000 tons, write it in scientific notation.
5 100 000 000 000 000 tons = 5.1 x 1015 tons
^
Numbers
| Significant figures
|
|---|---|
34.50
| 3
|
30.55
| 4
|
34.56
| 5
|
34.05
| 4
|
0.345
| 4
|
0.034
| 2
|
0.304
| 3
|
3.000
| 4
|
Significant figures
Significant figures are numbers that are either certain or good estimates of numbers. All numbers greater than zero are significant. A zero, which is part of a measurement, is significant. A zero used just to locate a decimal point is not significant. Only the same number of decimal places as the term with the least number of significant figures. The numbers are rounded off to give the proper number of significant figures.
Rules in rounding off figures
- If the figure to be dropped is greater than 5, increase by one the value of the last figure to be retained.
- If the figure to be dropped is less than 5, the last figure to be retained should not be changed.
- If the number to be dropped is 5, the last figure to be retained is increased by one if it odd, and retained as is, if it is even.
International System of Units (SI Units
The present system of units used is the International System of Units known as the SI Units, which is the revision and extension of the metric system.
SI Base Units
Quantity
| Unit
| Symbol
|
|---|---|---|
Length
| meter
| m
|
Mass
| kilogram
| kg
|
Time
| second
| s
|
Electric Current
| ampere
| A
|
Temperature
| Kelvin
| k
|
Amount of Substance
| mole
| mol
|
Luminous Intensity
| candela
| cd
|
Derived Units
Quantity
| Unit
| Symbol
|
|---|---|---|
Volume
| cubic meter or liter
| m3 or l
|
Density
| kilogram/cubic meter
| kg/m3
|
Speed or Velocity
| meter/second
| m/s
|
Concentration
| moles/cubic meter
| mol/m3
|
Force
| Newton
| N (kg m2/s2)
|
Energy
| Joule
| J (kg m2/s2)
|
Power
| Watt
| W J/s2
|
Quantity of electricity
| Coulomb
| coul (As(
|
Electric potential
| Volt
| V(W/A)
|
Examples:
Indicate the SI base units appropriate to express the following:
- length of a 100 mile race = kilometer
- mass of the horse = kilogram
- volume of a swimming pool = cubic meter
- speed of a racing car = kilometer per hour
- density of metallic gold = grams per cubic centimeter
- area of a basketball court = square meters
- the maximum temperature at the North pole on April 1, 1913 = Kelvin
Table of Prefixes
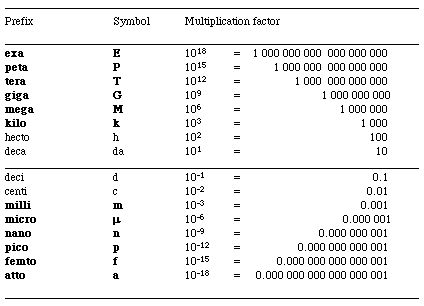
When the name of the unit is preceded by a prefix, that decimal multiplier modifies the size of the unit.
Examples:
a. 1um = _____cm
= _____mm
1um x 10-6 m x 1cm = 10-4 cm
1um 10 m
1um x 10-6 m x 1mm = 10-3 mm
1um 10 m
Conversion of Units: Dimensional Analysis
Using the dimensional analysis or factor-label method simplifies the conversion between various units. If units are treated like numbers, they can be multiplied, divide or cancelled. A conversion factor which is written in the form of ratio is used to change the units given in the data to the units asked for in the answer.
given quantity x conversion factor = desired quantity
Example
1. Convert 8.0 inches to cm
Given: 8.0 inches
Conversion factor: 1 inch = 2.54cm
Solution:
8.0 in x 2.54 cm = 20.32 cm
1 inch
2. Convert 15cm to km
Given: 15 cm
Conversion factors:
1m__
102cm
1km_
103 m
Solution:
15cm x 1m_ x 1km_ = 15/105 km or
102cm 103 m 15 x 10-5 km
Conversion Chart
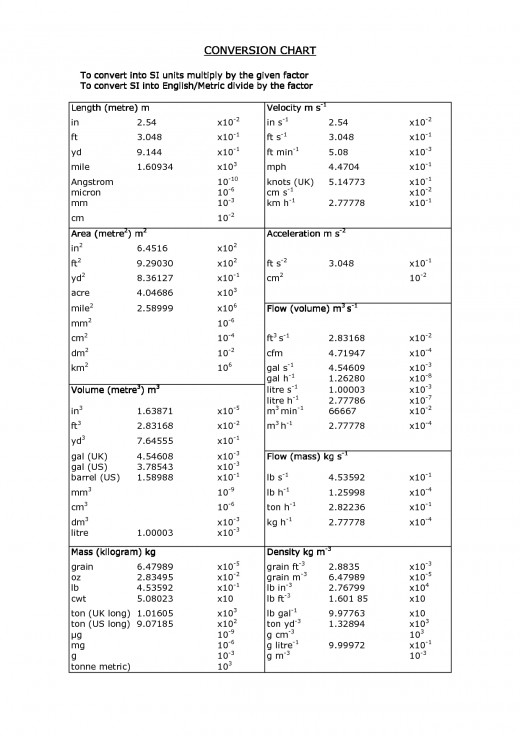
Equivalence between units
Length
1 in = 25.40 mm
1 in = 2.54 cm
1 ft = 30.48 cm
1 m = 39.37 in
1 A (Angstrom) = 10 m
Mass
1 oz = 28.35 g
1 lb = 453.6 g
1 kg = 2.2 lb
Volume
1 qt = 0.946 l
1 gal = 3.785 l
Laboratory Measurements:
Laboratory experiments require measurements of length, mass, volume, and temperature. Meter is the unit of length. Kilogram is the unit of mass. Second is the unit of time. Kelvin is the unit of thermodynamic temperature. The natural unit of capacity is based on a standard unit of length. Volume is length cubed (P). The most common unit of volume used in chemistry is the liter. Density is the mass or quantity of matter of a substance contained in one unit of its volume.
Density = mass per unit volume = mass of body/volume of body
Specific gravity (Relative Density) = mass of solid or liquid/mass of an equal volume of water
Temperature
Temperature is a measure of how hot something is. It is usually measured with a thermometer has a scale that gives an amount of hotness a certain number value. There are two common scales of temperature, the Fahrenheit scale and the Celsius scale. Extremely high temperature may be measured with a pyrometer. Aside from showing how hot an object is, temperature is a measure of the kinetic energy (energy of motion) of molecules that make up an object. When energy is added to an object, the additional energy usually increases the kinetic energy of the molecules and the object gets hotter. For example, energy is added to a gas as it is squeezed, to a liquid as it is stirred, and to a solid as it is hammered. A thermometer shows this increase in energy as a rise in temperature.
Formulas used in the inter conversions of the scales:
ºC = 5/9 (ºF – 32)
ºF = 9/5 ºC + 32
ºK = ºC + 273
Examples:
1. The normal body temperature is 98.6 ºF. What is the temperature in degrees Celsius and Kelvin?
Conversion Factors: ºC = 5/9 (ºF – 32)
ºK = ºC + 273
ºC = 5/9 (98.6 – 32) = 5/9 (66.6) = 37.0 ºC
ºK = 37.0 + 273 = 310ºK
2. Convert 30 ºC to ºF.
Conversion Factor: ºF = 9/5 ºC + 32
ºF = 9x30/5 + 32 = 86ºF
Assignment
A. Solve the following:
1. Complete the following:
a. 13g = _______________________ kg
b. 3451 mg = ___________________g
c. 4.18 g = _____________________mg
d. 17.38 km = ___________________cm
2. A 170 cm track and field athlete weighs 49.8 kg. Is she more likely to be a distance runner or a shot putter?
3. Gasoline is sometimes sold by the liters. How many liters are required to fill a 10.0 gallon gas tank?
4. The distance between the centers of two oxygen atoms in an oxygen molecule is 1.21 A. What is this distance in centimeters and inches?
5. Calculate the density of aluminum if 13.8 cm3 has a mass of 37.3 g.
6. What is the mass of the following?
a. 6.00 cm3 of bromide; density = 2.928 g/cm3
b. 1000 ml of octane; density = 0.702 g/cm3
B. Search on the internet a research conducted on chemistry, chemical industries, or new chemical products.








