Topographic Maps, How to Read and Use Them
By Joan Whetzel
Topographic maps in the US are produced mainly by the US Geological Survey (USGS). These maps help map users pinpoint natural land features (i.e. mountains and rivers) and manmade land features (e.g. mines, towns, structures). They can be used for land navigation. Topographical maps appear to be two dimensional representations of a specific region, but the details actually describe the lay of the land in 3-dimensions. Learning to interpret the graphic details may be a life-saving experience.
Symbols, Legends, Scale and Other Markers
To read a topographic map, like reading any other map, one must understand the symbols, legend, scale and other map markers. All maps have a star rose that indicates the cardinal directions (showing north, south, east, west). Topographic maps also have a magnetic declination, which shows true north, for navigating with compasses. Topographic maps have quadrangle titles (upper and lower right hand corners) that connect them to the map of the next region over.
Topographic map legends provide symbols to help identify distance, direction, latitude and longitude, road types (paved, gravel), and prominent buildings and landmarks (churches, houses, mines, golf courses). In addition, the legend uses colors to identify natural features: green stands for vegetation, blue means water (i.e. rivers, lakes), and purple represents updated information that was not this topographic map in years previous to this one.
Topographic map scales are listed along the bottom. The map scale illustrates the ratio between the distances on the map and actual land distances. A map scale of 1:24,000, for instance, is an indication that 1 inch on the map is equivalent to 24,000 inches (2,000 feet, 0.378787879 miles) in real life. A graphic scale, listed immediately below the map scale, illustrates the distances mile and meter distances for this particular map.
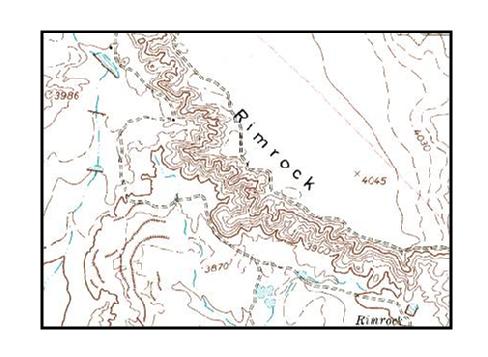
The most prominent feature of topographic maps are the contour lines, which demonstrate elevations for each map's area. The vertical spacing between each contour line is listed below the map scale. Using the contour vertical spacing and the closeness between each contour line, it is possible to determine the height of natural features as well as the slope steepness of the terrain.
Contour Lines
The contour lines are representations of "slices" of the terrain all stacked up on top of each other. Land features start off with wider slices at the bottom and build up to smaller slices on top. When examining the contour lines that illustrate the borders of each "slice, it should indicate how gentle or steep the slope the terrain is. If there are a lot of contour lines packed closely together, it indicates a steep grade like a mountain or cliff. The closer the contour lines, the steeper the slope or incline. Relatively few contour lines, spaced widely apart, on the other hand, represent a gently rolling terrain.
Generally, every 5th contour line is printed as a bold line, which makes it easier to figure out the elevations. For instance, if the elevation scales says that the vertical space between contour lines is 20 feet, that means that for every contour line, there is a difference of 20 feet in elevation from one contour line to the next. Every fifth (bold) contour line, then, represents 100 feet. So instead of figuring out changes in elevation 20 feet at a time, the elevation can be determined 100 feet at a time. This helps tremendously in steep terrains where the contour lines are close together.
Determining Slope
Using the topographic map's contour interval, the rise in elevation for any land formation can be determined. First, count the number of contour lines from the bottom most contour line of the formation up to contour line at the top of the slope. As an example, if there are 10 contour lines between the bottom and top of the slope, and each contour line represents an elevation change of 100 feet, the top of the slope rises 1,000 feet above the foot of the slope. Now determine if the slope is steep or gentle by the spacing between the contour lines. Lines packed close together at about 10 lines per inch on a 1:24,000 scale might indicate a cliff with a 1,000 foot drop. On the other hand, contour lines spaced far apart, at about 1 line every 2 to 3 inches on a scale of 1:24,000 might indicate a really big hill. If you were on an extended hiking and camping trip, and found that you had to get to the top of that slope, it would be easier to climb the really big hill version than the cliff version - unless you're really into rock climbing.
Other Types of Maps
Thereare 5 other types of maps that are used for gaining other forms of information. They are:
1. Road Maps - Perhaps the most familiar type of map, road maps assist drivers in travelling around cities, states, and internationally. Major manmade features are represented (buildings, hospitals, historical sites, airports) parks and green spaces, waterways, and, most importantly, major and minor roads - intra-city roads, intra-state, and interstates are represented by lines of varying widths or boldness.
2. Climate Maps - These maps illustrate the natural boundaries between regions based on the amount of rainfall and snowfall each region receives annually. They also show some natural land features like topographic maps (only without the contour lines).
3. Resource Maps - These maps show natural land features, like topographic maps. But they also pinpoint the natural resources for each region. The resources may be financial or economic, agricultural, mining, or industrial (e.g. computers, petroleum).
4. Physical Maps - These maps show the natural boundaries between grasslands, deserts, mountainous regions, and forests using many of the same map key symbols as a topographic map. Shading or tinting is used to indicate changes in elevation, rather than contour lines.
5. Political Maps - These are state, country and international maps showing the borders between a state's counties, between the states in a country like the US or provinces in countries like Canada, and between countries as best seen in a map of Europe, Central America or South America. These types of maps are generally published on globes, atlases or in large regional maps.
Bibliography
Vasiley, Boris M.S. How To Read Topographical. http://www.ghosttowns.com/topotmaps.html
USGS. Topographic Map Symbols.http://egsc.usgs.gov/isb/pubs/booklets/symbols/reading.html
Raider Mountain. What is a Topographic Map?
http://raider.mountunion.edu/~mcnaugma/Topographic%20Maps/what_is_a_topographic_map.htm
Merriam Webster Online Dictionary. Contour, Contour Lines, Contour Intervals, and Topography.http://www.merriam-webster.com
Geospatial Training and Analysis Cooperative. What Is a Topographic Map?
http://geology.isu.edu/geostac/Field_Exercise/topomaps/topo_map.htm
University of Texas at Arlington. Contour Lines.http://www.uta.edu/paleomap/geol1435/contour.htm
Trails.com. What is Meant by a Contour Interval on a Topographical Map?
http://www.trails.com/facts_3631_meant-contour-interval-topographic-map.html
Reading Topographical Maps. Contour Intervals.http://www.map-reading.com/ch10-3.php
University of Mount Union. Contour Lines.http://raider.mountunion.edu/~mcnaugma/Topographic%20Maps/contour.htm
USGS. Reading Topographic Maps.http://egsc.usgs.gov/isb/pubs/booklets/symbols/reading.html
National Wildfire Coordinating Group. Estimating Slope.http://www.nwcg.gov/pms/pubs/475/PMS475_chap2b.pdf
Wilderness Manuals. Percentage of Slopes.http://www.wildernessmanuals.com/manual_1/chpt_9/6.html
Map Town. Reference --- Type of Maps.http://www.maptown.com/referencemaptypes.html
My Teacher. Pages: Types of Maps.http://www.myteacherpages.com/webpages/TTravis/social_studies_class.cfm?subpage=648434