Regulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes and Prokaryotes
The idea of regulation of gene expression centers on the evolutionary selection of energy conservation over energy profligacy. In other words, gene regulation exists because only specific sequences of our genetic code at any given time are necessary to be expressed. Both prokaryotes and eukaryotes alike share this discriminating sense of gene expression, although they go about it in separate ways.
Prokaryote's Expression of Genes:
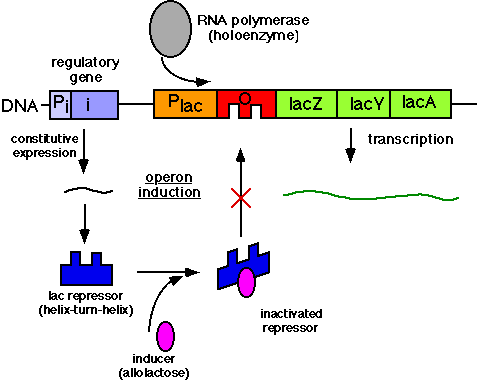
Prokaryotes rely heavily on regulating gene expression during, or before, transcription of mRNA. The operon holds the genetic sequence that is to be transcribed and translated into proteins, and a promoter and operator (being part of the operon) constitute the starting point and regulatory site (respectively) of transcription. Regulation of transcription and the subsequent proteins that it codes for occurs, therefore, at the operator as repressors bind to the operator and disable the association of RNA Polymerase and the coding of mRNA. Repressors can be natively active or inactive, and thus enzymes are inducible or repressible. In the lacoperon, for example, repressors are natively active and must be inactivated by the arrival of lactose (or its chemical signal allolactose), which binds to repressors and disables their ability to bind to the operator (which disables RNA Polymerase binding). In this sense, the arrival of lactose induced the synthesis of enzymes necessary to break it down. The tryptophan operon is just the inverse, and is thus called a repressible enzyme pathway. This being up until now a discussion of negative gene regulation, positive gene regulation refers to the procurement of transcription of a gene. When levels of glucose, for example, are low in a cell a regulatory protein called cyclic AMP binds to catabolite activator proteins that then bind to the promoter of an operon and increase the rate of transcription, thereby effectively stimulating gene expression.
Eukaryote's Expression of Genes:
Eukaryotes are more complex and can regulate gene expression at a number of sites along the pathway of gene expression. Before transcription, the chromatin structure can be modified so as to be more or less conducive to gene expression. Through acetylation (addition of acetyl groups) and methylation (addition of methyl groups) of histones (the proteins that the DNA is wrapped around) the chromatin structure is de-compacted or compacted, respectively. The latter restricts gene expression and the former enables expression. Eukaryotic regulation of genes during transcription involves the binding of repressors so as to block activator binding to enhancers or the blockage of activators to proteins. This represents an inhibition of RNA Polymerase and transcription, whereas inversely, without the repressors, activators bind to enhancers, DNA-bending proteins bend the DNA, and the enhancers increase RNA Polymerase’s affinity for the Promoter. After pre-mRNA is transcribed, regulation continues as alternative splicing accounts for the different expression of genes as introns are cut and exons are ligated in different ways producing different proteins. Eukaryotes nuclear membrane also filters mRNA after processing, leaving some mRNAs behind. After exiting the nucleus, further regulation occurs as mRNA is subjected to varying levels of longevity (which is delineated by the un-translated region). Finally, regulation during translation occurs as repressors can bind to the UTR of the mRNA and inhibit the binding of said mRNA to the ribosome. Post-translational regulation refers to the processing of the finished polypeptide (as most must be processed), the phosphorylation or de-phosphorylation of the protein, and transportation of the protein to its destined location, wherein the protein can be activated or deactivated.