Stroke- Classification
Stroke
STROKE-CLASSIFICATION
The sudden death of brain cells due to the disturbance in the blood vessels that supply blood to the brain result in stroke. This sudden death of brain cells is due to the lack of blood supply (ischemia) caused by thrombosis or embolism or due to a hemorrhage in the brain. This results in the abnormal functioning of the brain. A stroke is also called as cerebrovascular accident. Stroke leads to permanent neurological damage, complications and even death, if it is not properly diagnosed and treated.
Classifications of stroke
There are two major types of strokes and they are ischemic and hemorrhagic strokes.
Ischemic stroke
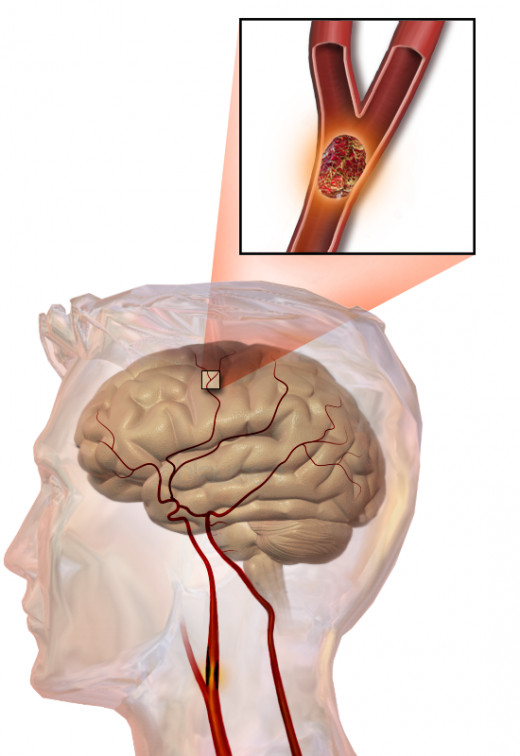
Ischemic stroke is caused due to the interruption of blood supply in the brain and 80 % of the strokes are occurred due to this. Hemorrhagic stroke is caused due to the rupture of blood vessel or an abnormal vascular structure in the brain.
Blood supply is decreased to the part of the brain which leads to the dysfunction and necrosis of the brain tissue in that area. Thrombosis, embolism, systemic hypo-perfusion, and venous thrombosis are the four major reasons for the occurrence of stroke.
Thrombotic stroke
A blood clot or thrombus is formed around atherosclerotic plaques resulting in thrombotic stroke. The development of symptomatic thrombotic stroke is slower as the artery blockage is caused gradually. If the thrombus breaks off at a point, it is called embolus, which will lead to an embolic stroke. Depending on the type of vessel in which the thrombus is formed, thrombotic stroke is divided into two types. The types of thrombotic strokes are large vessel disease and small vessel disease.
(a) Large vessel disease form thrombi in large vessels such as common and internal carotids, vertebral and Circle of Willis.
(b) Small vessel disease form thrombi in small arteries inside the brain such as branches of the circle of Willis, middle cerebral artery, stem, and arteries coming from the distal vertebra and basilar artery.
Embolic stroke
Embolus originates from elsewhere and causes blockage in an artery. This embolus is a moving particle or debris in the arterial bloodstream that leads to embolic stroke. Embolus is mostly a thrombus, but it can be other substances such as fat, air, cancer cells, or clumps of bacteria. Local therapy solves the problem temporarily as the embolus occurs from elsewhere. As the beginning of the embolic blockage is sudden and the symptoms are maximal even at the beginning stage, the source of the embolus must be identified. The symptoms are temporary because the embolus is reabsorbed partially and travels to different location or dissolves altogether. Most commonly the emboli arise from the heart, but it can originate from elsewhere in the arterial tree.
Systemic hypoperfusion
The reduced blood flow to all parts of the body results in systemic hypoperfusion. It is due to cardiac pump failure occurred due to cardiac arrest or reduced cardiac output. Cardiac arrest or reduced cardiac output is due to myocardial infarction, pulmonary embolism, pericardial effusion or bleeding. Low oxygen content or hypoxemia may give rise to hypoperfusion.
Venous thrombosis
Cerebral venous sinus thrombosis is caused due to the increased venous pressure locally, which goes beyond the pressure generated by the arteries and leads to stroke.
Hemorrhagic stroke
The two types of hemorrhage are intracerebral hemorrhage and intracranial hemorrhage.
Intracerebral hemorrhage
The bleeding directly into the brain tissue leads to progressively enlarging hematoma or pooling of blood. This type of bleeding happens in small arteries or arterioles and most common reasons of bleeding are hypertension, trauma, bleeding disorders, amyloid angiopathy, illicit use of drug, and vascular malformations. The growth of hematoma continues till the pressure from the surrounding tissue limits its growth or it decompresses by draining into the ventricular system, cerebral spinal fluid or the pial surface. One third of the intracerebral bleed is in the brain’s ventricles. The mortality rate of intracerebral hemerrhage is 44% after 30 days of the stroke, which is higher than the ischemic stroke and also than the deadly subarachnoid hemorrhage.
Intracranial hemorrhage
The accumulation of blood in any place with in the skull vault is known as intracranial hemorrhage. There is a difference between intra-axial hemorrhage and extra-axial hemorrhage. Intra-axial hemorrhage or blood inside the brain is because of intraparenchymal hemorrhage or intraventricular hemorrhage. Extra-axial hemorrhage or blood inside the skull, but outside the brain is due to epidural hematoma, subdural hematoma and subarachnoid hemorrhage.