Viral Hepatitis: Clinical Relevance Of Its Immunology And Pathogenesis
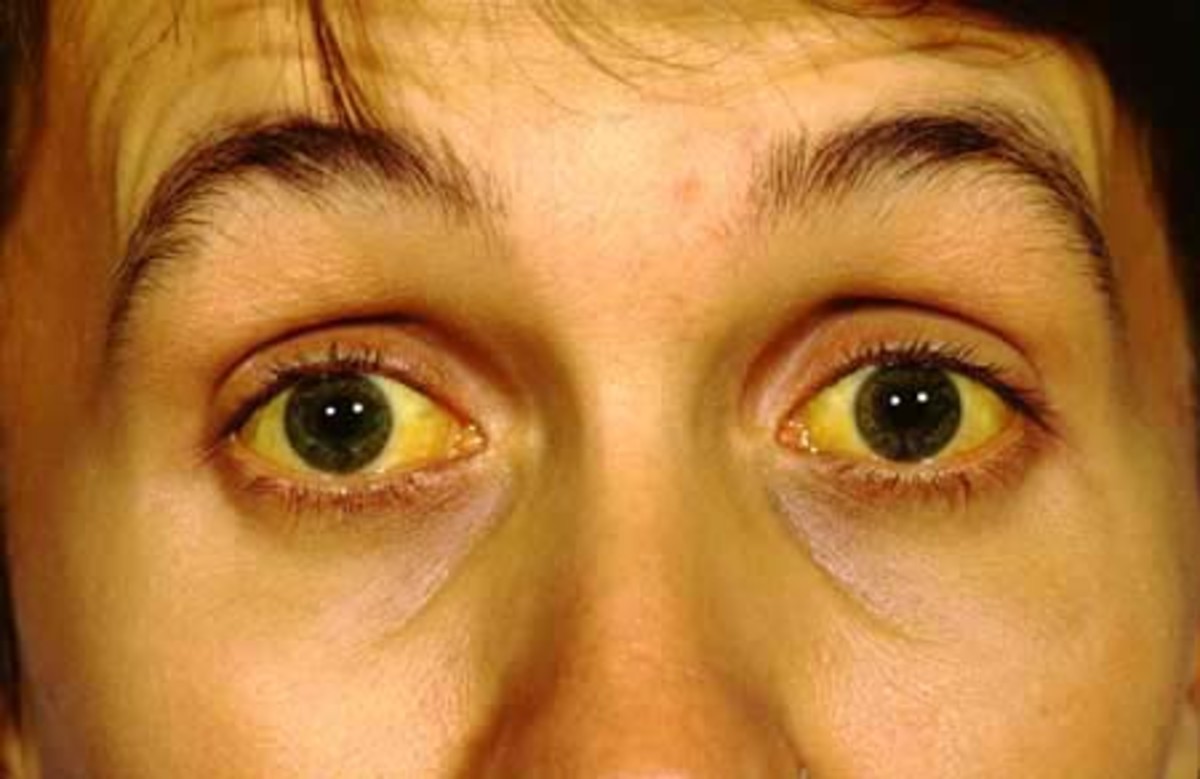
A Viral Hepatitis C Patient

The Immunology Of Viral Hepatitis
The HBsAg circulates in blood of infected persons and carriers. It is an antigenic but being devoid of nucleic acid, it is non-infectious. The first antibody to develop after infection is anti-HBc. It is followed by the appearance of anti-HBe and anti-HBs. The antibodies confer immunity. Free core antigen has been demonstrated only in the hepatocytes, but anti-HBc appears in the blood during the acute stage of infection and indicates active virus replication. A third antigen HBeAg appears in the blood soon after HBsAg appears, but the former disappears shortly. Presence of HBeAg suggests active viral replication. Persistence of HBeAg beyond 10 weeks points to the carrier state and portends the development of chronic hepatitis. Anti-HBe develops after disappearance of HBeAg and its appearance suggests good immunological response with a good chance for recovery.
The delta (d) agent is a recently discovered defective RNA virus which requires the presence of hepatitis B virus to produce infection. It occurs largely as a superinfection in carriers of B virus. It may cause a transient infection or severe acute or fulminant hepatitis. It may worse pre-existing chronic liver disease.
Non-A Non-B (NANB) Viruses: These are also important sources of infection and their proportion varies in different outbreaks. Post-transfusion hepatitis is probably caused by NANB viruses in a majority of cases. The NANB viruses are spread either by fecal-oral route or parenterally through blood and blood products. When they break out as epidemics, they show an incubation of 5 weeks. They can also spread parenterally or even by sexual contact. In this case, the incubation period is 8 weeks. Outbreaks of NANB hepatitis have occurred in India in particular which has accounted for 15 to 30% of all cases of sporadic acute viral hepatitis. It is unusual for NANB infection to become chronic or develop carrier state.
An Unconscious Hepatitis Patient
Infectious Diseases
The Pathogenesis Of Viral Hepatitis
The virus of hepatitis B is not directly cytopathogenic. It is thought that the injury to liver cells by HBV in acute hepatitis is partly immunologically-mediated. Immune complexes appear in blood prior to the onset of liver injury. They may account for the serum sickness like syndrome observed in the early phase. Cellular immunity has also been thought to play a role in altering the host’s response to the virus and the progression to the chronic carrier state. In the case of hepatitis A, the role of immunological factors in causing liver cell necrosis is less clear.
Pathology: The lesions caused by viruses A, B and NANB are all similar. In uncomplicated hepatitis, the essential lesions are ballooning of hepatocytes, acidophilic degeneration leading to the presence of Councilman bodies and focal necrosis or cell drop-outs. Changes are morepronounced in the centrizonal regions. There is infiltration by small lymphocytes. Plasma cells and eosinophils, most marked in the portal regions. Kupffer cells undergo hyperplasia. Many large multinucleated hepatocytes are formed. There is also a variable degree of cholestasis. The pathological changes are seen diffusely involving all the lobules.
Necrosis of liver cells is a prominent feature in severe cases. Necrosis involving many adjacent hepatocytes is described as confluent necorsis. The term “submassive” necrosis is used to denote necrosis involving several adjacent lobules. The necrosis may extend between adjacent central zones, portal zones or between adjacent central and portal zones. If the reticulum is intact, full regeneration is possible and recovery is complete. If the reticulum collapses, collagenous tissue is laid down and this leads to fibrosis, which bridges adjacent zones. These cases have a more unfavourable prognosis and many of them progress to subacute necrosis or to chronic hepatitis and cirrhosis. When necrosis is submassive or massive and fulminant, the liver shrinks in size and this carries a grave prognosis. With the onset of recovery, regenerative changes and Kupffer cell activity become evident.
© 2014 Funom Theophilus Makama