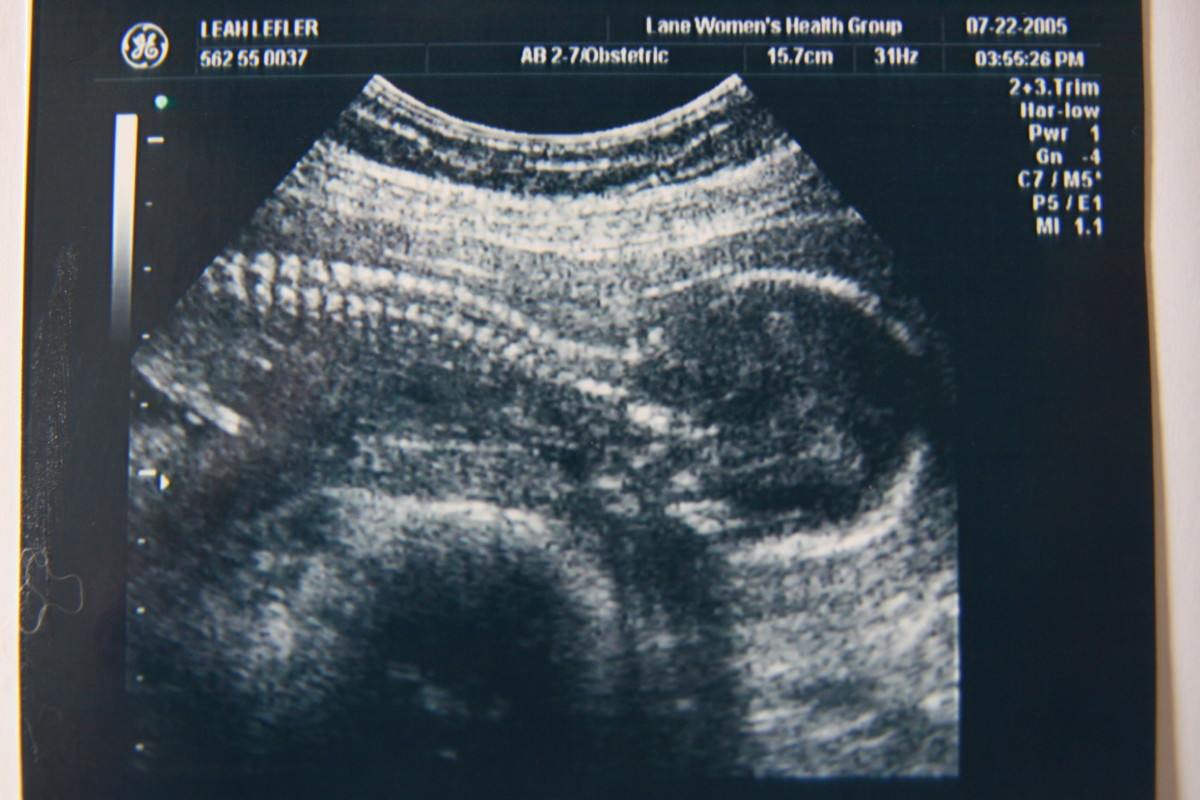
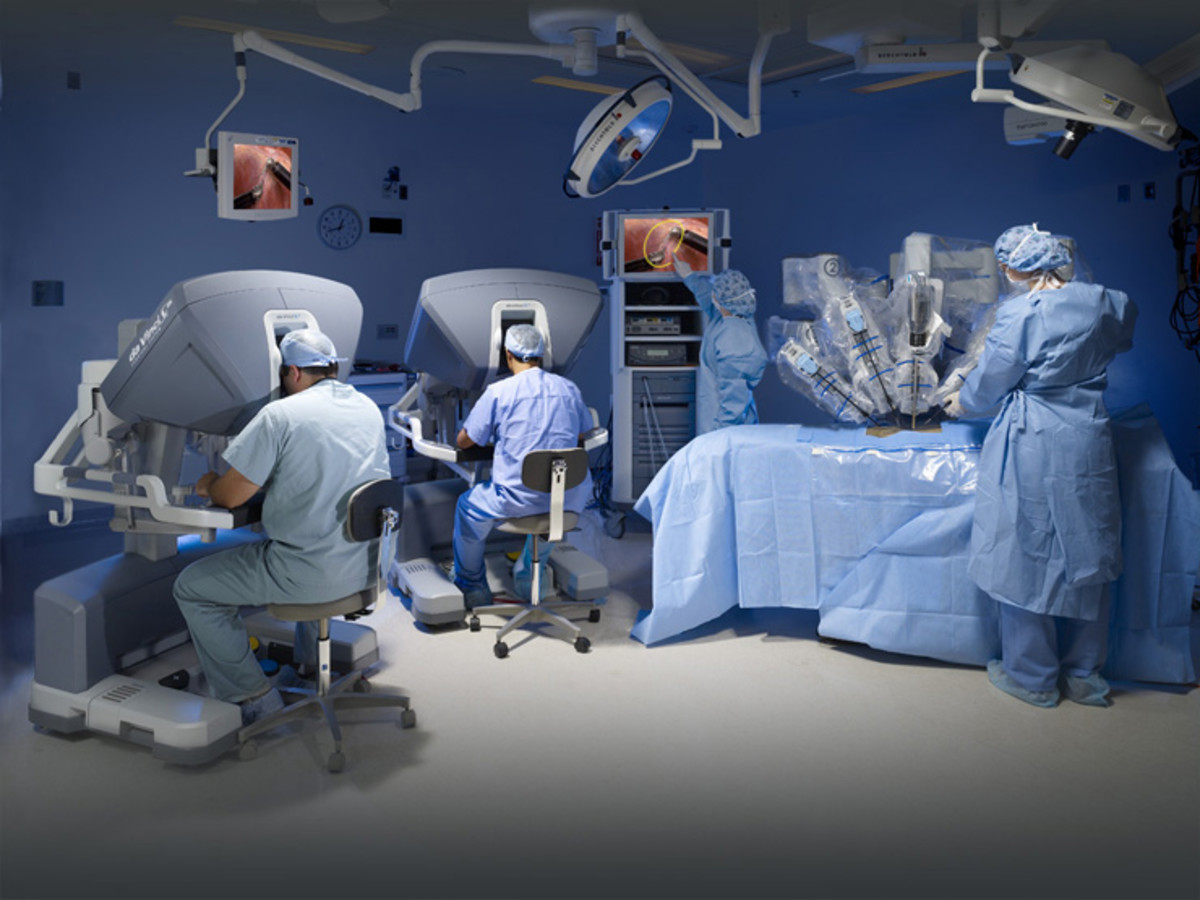
ART – The Art of Assisted Reproductive Technology
Assisted Reproductive Technology - What is In Vitro Fertilization?
Every year, millions of couples try to conceive a child; unfortunately, many find that they cannot. The process to find out how and why they have infertility can be long and arduous.
Usually, conception occurs when an egg cell (ovum) in a woman is released from an ovary, travels through a fallopian tube, and is fertilized by the man's sperm. The fertilized egg then continues to travel to the uterus while it undergoes numerous cell divisions. The fertilized egg implants in the uterus and results in pregnancy.
Usually, conception occurs when an egg cell (ovum) in a woman is released from an ovary, travels through a Fallopian tube, and is fertilized by the man's sperm. The fertilized egg continues to travel while it undergoes numerous cell divisions. It then rests in the uterus to grow.
In 1977, in an experimental procedure called in vitro fertilization (IVF), doctors joined a woman’s egg and a man’s sperm in a glass dish in a laboratory. For the first time, conception happened outside a woman’s body. Nine months later, on July 25, 1978, Louise Joy Brown, the world's first successful "test-tube" baby was born in Great Britain
Assisted reproductive technology (ART) is the general term used in referring to the methods used to achieve pregnancy by artificial or partially artificial means. Assisted reproductive technology is used primarily in couples suffering with infertility issues, however, ART is also used with couples who may be fertile, yet have genetic reasons for using reproductive technology. Assisted reproductive technology can also reduce the risk of infection when a communicable disease, i.e. Aids, is present, yet the couple wants to become pregnant.
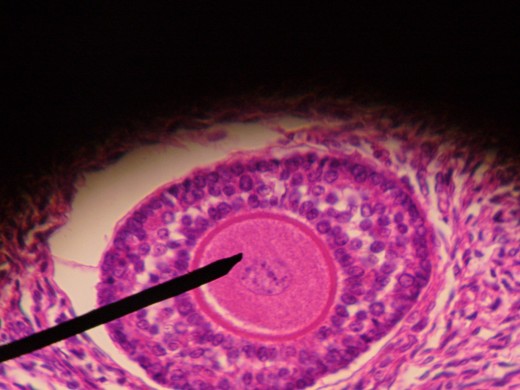
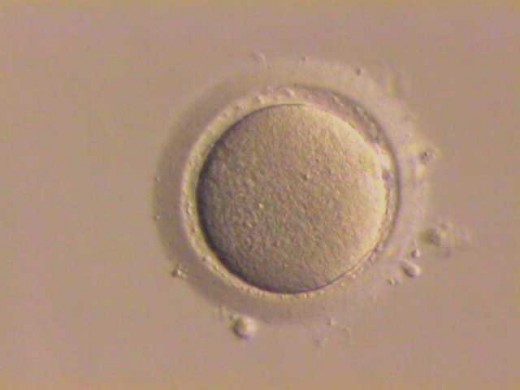
Primary Follicle and Oocytes

Terms used in Assisted Reproductive Technology
Terminology
Ovum – the egg or gamete
Oocyte - An oocyte is an immature egg, or immature ovum. Oocytes develop to maturity from within a follicle.
IUI – (intrauterine insemination) a small tube is used to place specially washed sperm directly into the uterus. IUI is more commonly referred to as artificial insemination (AI). IUI and AI are one and the same fertility treatment.
IVF – (In Vitro Fertilization) this is one of the most commonly used procedures. IVF is the process where the eggs are combined with sperm in a dish in a laboratory. Once fertilization has occurred, the resulting embryos develop for 3 to 5 days before being placed in the uterus.
Embryo transfer – the process where one or several embryos are placed into the uterus
AI – (Artificial Insemination) when sperm is placed into a female’s uterus (intrauterine) or cervix (intracervical) using artificial means rather than by natural copulation.
OCR – (Transvaginal ovum retrieval) a small needle is inserted through the back of the vagina and guided via ultrasound into the ovarian follicles to collect the fluid that contains the eggs.
AZH – (Assisted zona hatching) is performed shortly before the embryo is transferred to the uterus. A smll opening is made in the outer layer surrounding the egg in order to help the embryo hatch out and aid in the implantation process of the growing embryo.
ICSI – (Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection) is helpful when sperm counts are low or previous IVF attempts have failed. ICSI involves injecting a single sperm into the center of an egg using a microscopic needle. This method is also sometimes used with donor sperm.
ZIFT – (Zygote intrafallopian transfer) as with GIFT, eggs are mixed with sperm in a dish in a lab, then surgically placed into the fallopian tubes. But, as with IVF, the embryos aren’t transferred until after fertilization occurs. This procedure is no longer commonly performed because it has a lower success rate than IVF.
Zygote - A zygote is a single cell which has formed as the result of the merging of an egg cell and a sperm cell. The formation of a zygote represents the moment at which conception occurs.
GIFT – (Gamete intrafallopian transfer) eggs are combined with sperm in a dish in a lab, then surgically injected into the fallopian tubes using a laparoscope or fiber-thin tube. Fertilization happens iside the body, not in a laboratory, and the embryo implants naturally. This procedure was once commonly practiced, but is rarely used today because the success rate of IVF is usually much greater.
Embryo - The development of the embryo is called embryogenesis. Once a sperm fertilizes an egg cell, the result is a cell called a zygote that has half of the DNA of each of the two parents. The zygote will begin to divide by mitosis to produce a multicellular organism. The result of this process is an embryo.
Cryopreservation – eggs, sperm and reproductive tissue can be preserved for later IVF.
AH – (Assisted Hatching) once an embryo is selected for transfer, the zona pellucida is thinned or breached. The shell is left intact so that it will protect the embryo until it is ready to break free, and the thinning or breaching of the shell will allow the embryo to easily separate so that it can implant.
SUZI – (Sub-zonal insemination) is a type of in vitro fertilization that involves carefully selecting sperm and injecting them underneath the outer layer of the egg. This treatment is helpful when low sperm counts are a factor.
IVF - Invitro Fertilization
IVF, ART and Getting Pregnant
While there is no consensus on the definition, generally, with the use of assisted reproductive technology, intercourse is bypassed and insemination or fertilization in a laboratory is used.
Many, but not all ART procedures are used in conjunction with IVF.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), defines ART to include “all fertility treatments in which both eggs and sperm are handled. In general, ART procedures involve surgically removing eggs from a woman’s ovaries, combining them with sperm in the laboratory, and returning them to the woman’s body or donating them to another woman.” According to CDC, “they do not include treatments in which only sperm are handled (i.e., IUI or AI) or procedures in which a woman takes medicine only to stimulate egg production without the intention of having eggs retrieved.”
Fertility medications as well as ART techniques are the most common types of assisted reproductive technology used. Most fertility medications are used to stimulate the development of follicles in the ovary which is often followed by an ART procedure in the hopes of attaining a successful pregnancy.
Almost one out of every three cycles of ART results in the birth of a baby. However, ART procedures are invasive and expensive.
Getting Pregnant
IVF and other Assisted Reproductive Technologies