Fibers and Resins for Fiber Reinforced Plastics




Glass Cloth, Woven and Non Woven
Woven Roving is a woven material consisting of a number of strands of glass (or plastic) fiber collected into a parallel runs. The fiber has no twist to it and is very coarsely woven into a cloth-like structure. It is not referred to as cloth although it looks very much like cloth. Woven roving is best used in areas where high strength is required. Because the weaving readily appears through the set resin it is not good for finish work. FRP using woven roving alone is quite stiff and has some limited flexibility.
Woven roving is ideal where high strength is needed such as in car or truck bodies (especially off-road applications) and in boating where high stress is put upon the material.
Class Cloth is a cloth made of woven glass fibers. These fiber bundles may have a twist to them (unlike woven roving) and the material looks very much like clothing cloth except that it is pure white with a high sheen. There are two or three grades of glass cloth with varying degrees of weave. Some are quite finely woven; others quite course. Glass cloth is good for medium strength applications, but is still not good for finish work as the weaving will show through the resin.
Glass cloth is often used on top of (or in conjunction with) woven roving where high strength and flexibility are required. Glass cloth is a more flexible material in FRP that woven roving.
Chopped Strand Mat is a non-oriented non-woven cloth with glass fibers randomly distributed throughout the material. It is excellent for finish work, but has the lowest amount reinforcing strength of the three FRP materials listed here. It is often sandwiched with glass cloth (which provides structural strength) and woven roving as the finishing layer in FRP projects.
It does not have the same strength as woven roving of glass cloth and should only be used as the primary reinforcing material if structural strength does not need to be as high as in car bodies or boats. It will work well as a freestanding form material (statue), table, or chair since a limited amount of weight will be supported by it and the resin.
Note: I have seen boats made with chopped glass or chopped mat only. You'll never see me ride in one though. They aren't strong enough to withstand a submerged log or other obstruction in the water. It's just a very cheap way to make a very expensive boat. And almost all boats seem to be made this way these days. Making a hot tub or bathtub this way is fine, but you won't hit a log on the way to the marina in a bathtub.
When used in layers, usually in this order;
- resin
- woven roving
- resin
- glass cloth
- resin
- glass mat
-
resin
is extremely stong and provides an excellent surface for priming and painting. FRP is up to six times stronger than steel per pound.
In some circumstances, such as adding a woven cloth protective layer to a foam surfboard form or a wooden boat, the first layer of resin is not required. During layup in these circumstances the cloth will be laid over the supporting structure and liquid resin poured and "brushed" into the fabric and underlying supporting layer.
High Tech Fibers
Click thumbnail to view full-size


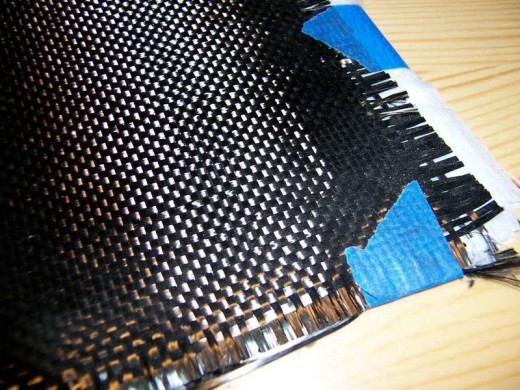
Other Fiber: Kevlar & Carbon Fiber
Two other popular materials to use in FRP are Kevlartm and Carbon fiber. Both materials have very high tensile strength and bond readily with plastic resin.
Kevlar is used with resin to make boat hulls, aircraft and bicycle frames. Despite it's strength it is susceptible to ultraviolet light and degrades rapidly in direct sunlight. It is a very good material in temperature extremes though losing only about 10% of it's strength in heat and actually becoming stronger in low temperatures.
Carbon Fiber is typically baked Aramid or Kevlar. The plastic cloth is cooked in an oxygen free oven to create carbonized fabric. It used similarly to Kevlar, but has even better strength retention in high heat applications. Carbon fiber is even lighter than Kevlar, is not prone to ultraviolet light degradation and is therefore used in high heat high stress applications where the weight savings and strength are combined for maximum effect.
It is currently used in tennis rackets, fishing rods, rowing sculls, and is the primary material in Boeing's 727 Dreamliner.
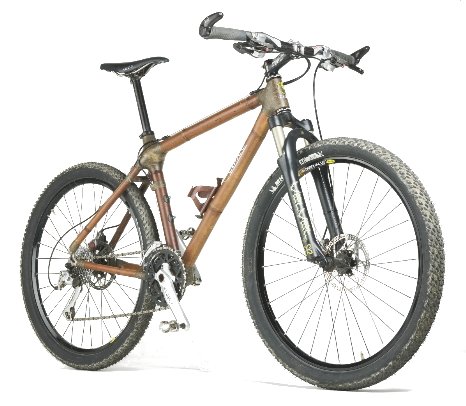
Bamboo Mountain Bike
Click thumbnail to view full-size

Natural Fibers
Other fibers that can be used with resin include, but are not limited to.
Cotton fiber/cloth,Hemp fiber & cloth and Flax.
Cotton cloth is used with phenolic resins to make printed circuit boards.
There as an attempt to recycle chicken feathers some years ago by making circuit boards with feather fiber and epoxy. This effort lost funding before any real steps were taken to explore this material.
Hemp fiber/cloth is currently being used with fiberglass epoxy resin to make bamboo bicycle frames. (see video) No, the type of resin does not have to be used just with fiberglass.
Craig Calfee Bamboo Bike
Plastic Resin
There are three main types of resin. Epoxy, Polyesters, and VinylEster which are all two part thermosetting plastic resins. Each has advantages and disadvantages, but recent advances in Polyesters have made this type of resin superior for all but a limited number of applications.
All three plastics are called thermosetting because they must cure within certain temperature ranges. All three plastics are also "exothermic" which means they generate heat as they cure. None will cure at all at freezing temperatures and all three will cure much faster at higher temperatures.
Epoxy resins:
- Are ideal for high strength applications and are resistant to chemical attack and high heat
- Heat cured epoxy is more heat and chemical resistant than "room temperature" cured epoxy
- Will degrade in ultraviolet or sunlight
- Will not melt Styrofoamtm
- Catalysts (hardener) comprise 25% to 50% of the activated resin.
-
Are the strongest of the three with more flex and tensile strength
-
Is an excellent resin for many different types of fibers, not just fiber-glass. (see bamboo bike above)
Polyester resins:
- Are more susceptible to higher temperatures
- Are quite stable in ultraviolet and direct sunlight
- Polyesters are chemically non-reactive and considered inert by OSHA
- They are relatively resistant to chemicals
- Will melt Styrofoam.
- Catalysts comprise less than 10% of the active resin. The catalyst is MEKP.
- Are brittle and have less tensile strength compared to epoxy
Vinylester Resins:
- Are less susceptible to high temperatures than polyester, but more susceptible than epoxy.
- Are stable in ultraviolet and sunlight
- Are more resistant to chemicals than polyester
- Catalysts comprise less than 10% of the active resin. The catalyst, like polyester, is MEKP.
-
Have better strength overall than polyesters, but less than epoxy.
Vinylesters have the properties of both polyester and epoxy resins since they share the chemistry of both. Vinylester is typically stronger than polyester, yet weaker than epoxy. Vinylesters are very good at resisting water absorption and are relatively stable in sunlight which makes them a popular choice for boatbuilders.
Styrofoam Molds: Since Styrofoam is so easy to create objects with it is often used with glass and epoxy to make a master mold from which polyester and glass can be used to make finished products. Styrofoam can easily be worked with knives, course files, and sandpaper.
Styrofoam, glass cloth, and epoxy resin were the original materials used to build the first generation of mass produced surfboards.
* Polyester is any polymer made up of an alcohol/acid base. In a way polyester is a generic term because the group includes, but is not limited to, PET, polycarbonate, and polybutirate.
Further Protecting Your Creation
Ultra-Violet Light (UV)
UV can have a devastating effect on resins, especially epoxy. Unlike water absorption, UV will cause the cured resin to crumble and break away. So providing some way protecting your FRP item from direct sunlight is important.
Water Absorption
Beside Ultra Violet (UV) light the other naturally occurring element likely to damage your fiber reinforced resin creation is water. Water incursion will cause the layers to come apart or "de-laminate." This may take years, but it will eventually have a devastating effect on your FRP.
You should always consider painting the finished product whatever it is. Paint provides an additional layer or protection to your hard work. Paints have the ability to:
- Provide a moisture barrier
- Provide additional UV protection
- Give the final product a "professional" look
When painting consider the type of resin used and choose the paint accordingly.
If you've used an Epoxy resin you should consider an epoxy paint as well, though a polyester paint will work, but a two part paint will provide better UV and moisture protection. if your resin is polyester or polyvinyl then consider a polyester one-paint instead.
FRP Products
This composite material is used to make fiberglass showers, garage doors, swimming pools, bathtubs, roofing tiles, tanks, planters, truck tonneau covers, pipes, tent poles, fishing rods, antenna masts, RADAR radome covers, boats, car bodies, sculptural elements, walls, and virtually countless other uses.
See my hub "How to Fiberglass Like a Pro" for instructions on fiberglassing with epoxy or polester resins.
eBook Candidate?
Would this Article make a good eBook?
Disclaimer
The author was not compensated in any way, either monetarily, with discounts, or freebies by any of the companies mentioned.
Though the author does make a small profit for the word count of this article none of that comes directly from the manufacturers mentioned. The author also stands to make a small profit from advertising attached to this article.
The author has no control over either the advertising or the contents of those ads.