Your Guide to Understanding the Glycemic Index
The Glycemic Index
Science has long suspected that not all carbohydrates are created equally. With the inception of the glycemic index, science is now able to quantify that inequality. The glycemic index measures how much and how quickly carbohydrate-based foods raise the blood glucose (blood sugar) level. But a food's glycemic index number is only part of the story; to thoroughly understand the impact a particular food will have on your blood glucose level, you also need to know the glycemic load.
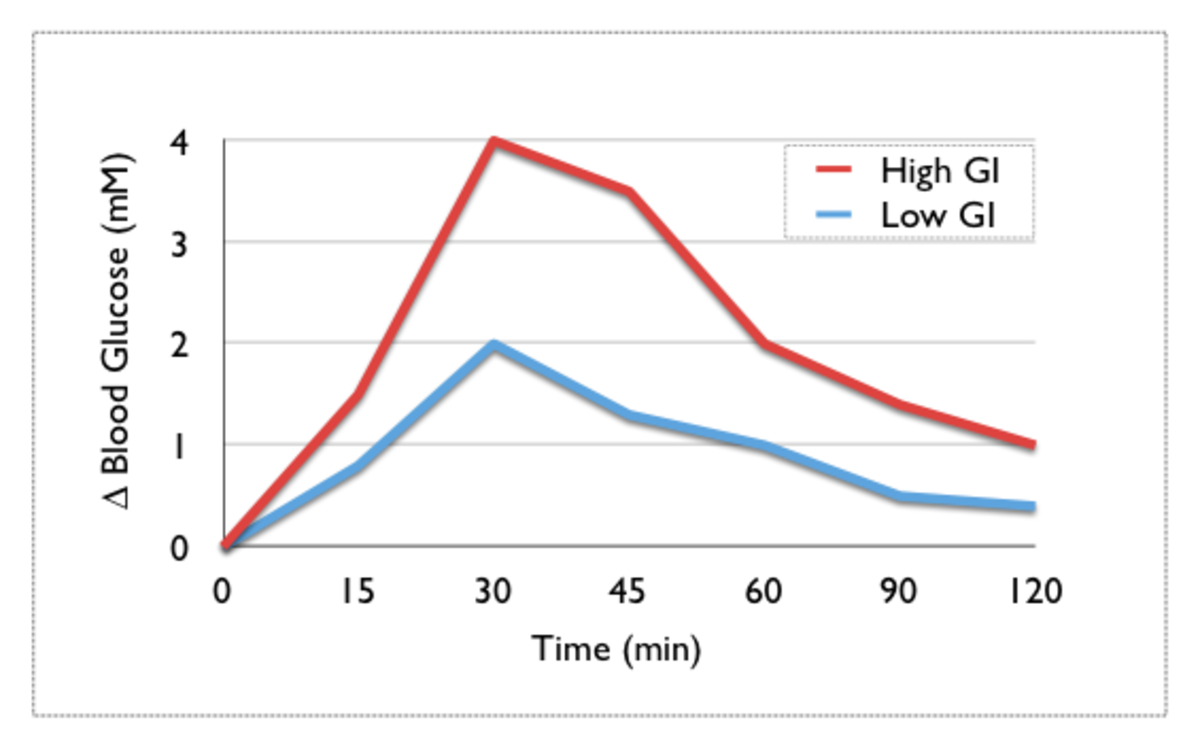
The glycemic index measures a particular food's effects on blood sugar levels against glucose or white bread's effects. Once that relationship is determined, the food is assigned a glycemic index number.
The glycemic load of a particular food is based upon the grams of carbohydrate in a portion of that food and its glycemic index. Glycemic index and glycemic load were developed together to describe the quality and quantity in a meal or diet of its carbohydrates.

Video: What Is the Glycemic Index?
What Is the Importance of the Glycemic Index?
You might consider the information about the glycemic index to be all well and good for people with diabetes, but you're not one of them, so why should you be concerned? If you are overweight or obese, there is a good chance that you have developed insulin resistance. Insulin resistance, along with increased weight makes you an excellent candidate to develop type 2 diabetes--the chronic disease that is effecting more and more people who adhere to the standard Western diet. Beginning to moderate your eating habits by making informed decisions about the food you eat is the first step to taking control of your long-term health.
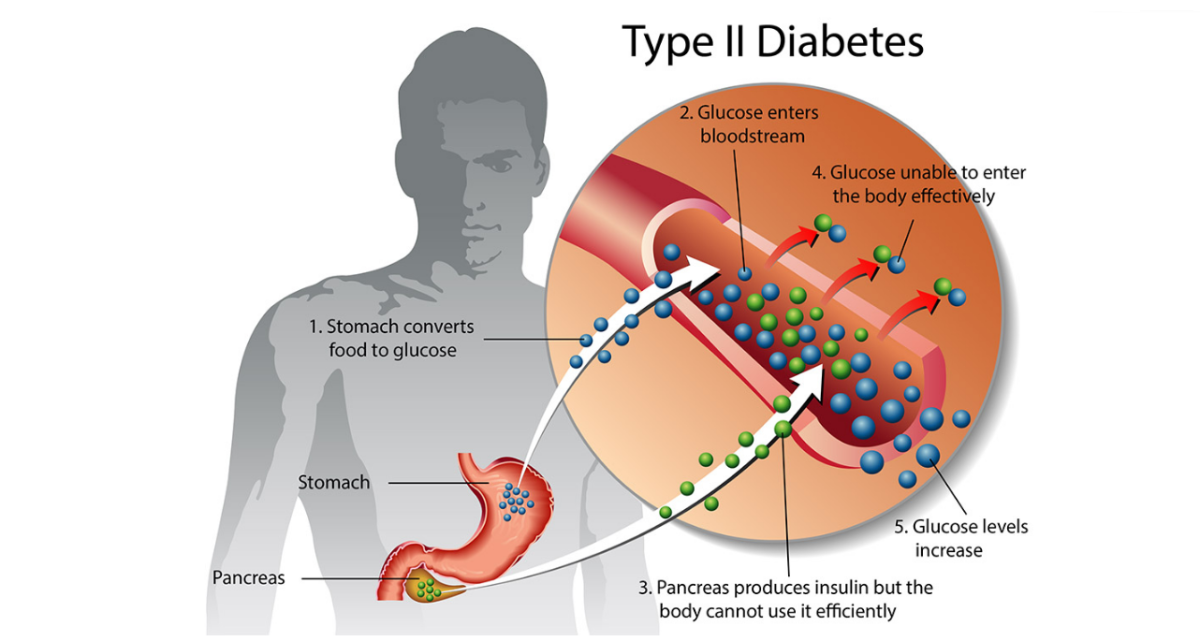
Carbohydrate-based foods are broken down by the digestive processes into the basic energy substance, glucose. In response to the presence of glucose in the blood stream, the beta cells of the pancreas release insulin. Insulin is the gatekeeper to cell walls; it must be present for glucose to move from the circulating blood into the individual cells of your body. When insufficient insulin is produced--or the body requires more insulin than normal to perform the same tasks (as in insulin resistance)--too much glucose remains in your blood stream, causing your blood glucose levels to rise.
Just as putting sugar in your car's gas tank would gum up the works, so does excess glucose in the blood stream. "Sticky" blood--elevated blood glucose--can cause build-up in your blood vessels. This build-up is called arteriosclerosis. Such build-up in the arteries supplying blood to your heart muscle results in coronary artery disease, the leading cause of myocardial infarctions. The kidneys become affected over time through filtering blood with elevated glucose levels. Your body begins to heal more slowly. And if all this isn't enough, you cannot lose weight effectively when your blood glucose levels are altered.
Related Hubs
- How To Manage Your Blood Sugar Levels
Whether you have diabetes or hypoglycemia (low blood sugar), you will need to take control of your blood glucose levels. There are a number of factors which cause your blood sugar levels to change throughout the day. Understanding these will help you - Glycemic Index Food List
If you are trying to lose weight and adapt a healthier life style, pay attention to the Glycemic index. Visit this page for a full a list of foods by their Glycemic index. Get current news on the Glycemic Indes - Weight Watchers new program, Points Plus (WW Points Plus)
PointsPlus is the new name for the Weight Watchers plan, and its a good name. Weight Watchers built a great business on teaching people to watch their food intake by associating point values to all foods... - How to use Weight Watchers weight loss systems by yourself for free (or almost free)
So you think you want to follow the Weight Watchers points plus system, but dont feel you can afford it. You are not alone. Here are some suggestions to reduce the cost...
Where Do I Find Information on the Glycemic Index of Food?
There are many resources available both online and offline that provide the glycemic index of carbohydrate-based foods. The most comprehensive online resource that provides the glycemic index of more than 1,600 foods is provided by the University of Sydney. Here you can enter specific foods to learn their glycemic index, you can search broad food terms to receive a list of foods ranked by their glycemic index and you can also find glycemic load values of food.
After you begin to familiarize yourself with the glycemic values of foods, you'll begin to see patterns in some values such as breads and pastas made from whole grain will have lower glycemic values than those made from white flour. The lower the glycemic index of a food, the less it will spike your blood glucose levels. You don't have to avoid all foods with higher glycemic levels all the time; the key is moderation and information. Once you take advantage of the information available, you can make choices based on that information.
The most important person in your health care team is you.

Research Related to the Glycemic Index
The study titled "The Possible Benefits of Nuts in Type 2 Diabetes" published in the Sept. 1, 2008 publication "Journal of Nutrition" examined the potential benefits different types of nuts may play in helping to regulate blood glucose levels. It is accepted by the scientific community that nuts may have positive effects on lipids in the blood and one study has demonstrated that the addition of nuts to the diet reduced the incidence of coronary heart disease in study participants.
The Mediterranean diet, now a model of a healthy diet whose proponents include the American Heart Association, includes small portions of nuts in its daily eating plans. This diet first came into popularity when researchers discovered the good health and longevity of a group of people living in a region of Greece whose lifestyle includes this diet and regular physical activity. Scientists, in working to determine the health benefits of this eating plan, are studying all its potential health benefits.
In this study, researchers noted that when nuts where eaten in the same meal as carbohydrate-based foods, the blood glucose levels after the meal were lower than when the same meal was eaten without the addition of the nuts. This is a preliminary finding that will require more scientific-based studies before it can be positively concluded that nuts may help to regulate after-meal blood sugar levels. Even so, this study's researchers point to the known nutritional benefits of nuts in the diet as a reason for them to be included in the diet of those with diabetes.
It can be reasoned that if nuts are healthy and are to be included in a diabetic diet, they are also a good inclusion in the diets of people who do not have diabetes to aid in the prevention of insulin resistance, metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes by helping to moderate blood glucose levels.
Sources
- The Glycemic Index
- International table of glycemic index and glycemic load values: 2002 Am J Clin Nutr
- WHFoods
Almonds - Possible Benefits of Nuts in Type 2 Diabetes
"Journal of Nutrition"; David J.A. Jenkins et al; Sept. 1, 2008 - 5 Fruits with a Low Glycemic Index
5 Fruits with a Low Glycemic Index. Not all sweet fruits are off-limits if you are living with diabetes. Check out these healthy fruit options to be incorporated into your meal plan. Fruits with low GI written by Registered Dietitians.