What is the use of Accounting

Meaning of Accounting
In 1941, the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA) defined accounting as the art of recording, classifying, and summarizing in a significant manner and in terms of money, transactions and events which are, in part, at least, of a financial character, and interpreting the results thereof.
With greater economic development, the meaning of the term accounting gradually became broader. In 1966 the American Accounting Association (AAA) defined Accounting as;
The process of identifying, measuring and communicating economic information to permit informed judgments and decisions by users of the information.
Further, in 1970 the Accounting Principles Board of AICPA stated that the function of accounting is;
To provide quantitative information, primarily financial in nature, about economic entities, that is intended to be useful in making economic decisions.
Further, Accounting is defined as:
The process of identifying, measuring, recording and communicating the economic events are considered in terms of economic and business transactions of the organization to interested users of the information.
Characteristics of the Accounting
The above definition contains four essential characteristics of the accounting:
- Economic events
- Identification, measurement, recording, and communication
- Organization
- Interested users of information
Economic Events
An economic event has been defined as a happening of consequence to a business entity. Economic events are classified into external and internal types.
An external event, involves the transfer or exchange of something of value between two or more entities. It is called a transaction. The following are some examples of transactions:
- Sale of shoes by XYZ Company to customers.
- Payment of wages to employees by ABC Limited.
- Payment of monthly rent to the landlord.
- Purchase of raw materials by an enterprise from some other business enterprise.
- Purchase of ticket from an airline.
An internal event is an economic event that occurs entirely within one enterprise, e.g. supply of raw material or equipment by the stores department to the manufacturing department.
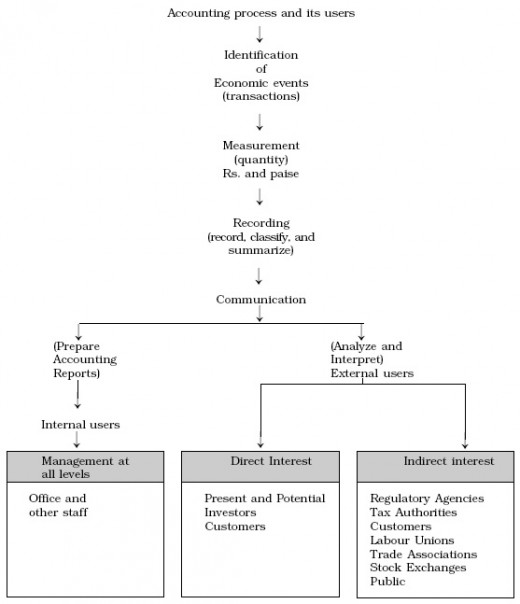
Identification, Measurement, Recording and Communication
Identification: It means determining what to record, i.e., to identify events which are to be recorded. It involves observing activities and selecting those events that are considered to be the evidence of economic activity. Further, these events should be related to a business organization. The business transactions and other economic events are evaluated for considering whether it has to be recorded as an accounting transaction. The value of human resources, changes in managerial policies or change in personnel are important but none of these items are recorded in financial accounts. However, when a company makes a cash sale or purchase, it is recorded in the books of accounts.
Measurement: It means quantification (including estimates) of business transactions into financial terms by using monetary unit, i.e. rupees and paise, as a measuring unit. If an event cannot be quantified in monetary terms, it is not considered for recording in financial accounts. That is why important items like the appointment of a new managing director, signing of contracts or changes in personnel are not shown in the books of accounts.
Recording: Once the economic events are identified and measured in financial terms, they are recorded in a chronological order and systematic manner. An item should be written in both words and numbers. The amount should be included in the totals of the books of account. The accountant also clarifies by summarizing these items.
Communication: The economic events are classified, measured and recorded in a order that the pertinent information is generated and communicated in a certain form to management and other internal and external users. The information is communicated through preparation and distribution of accounting reports. The most common reports are in the form of financial statements (Balance Sheet and Profit and Loss Statement).
The accounting information system should be designed in such a way that the right information is communicated to the right person at the right time. Reports can be daily, weekly, monthly, or quarterly, depending upon the needs of the user. An important element in the communication process is the accountant's ability and responsibility to interpret the reported information. This is done by analyzing and explaining the meaning, uses and limitations of reported data with the help of the ratios, percentages etc.
Organization
It is an entity performing business activities which can be for a profit or not-for-profit motive. The activities can be organized by choosing appropriate form of organization to suit the level of business operations. It can either be sole trader-ship, partnership, company, cooperative society or board such as Cantonment board, Municipal board, Cricket board.
Interested Users of Information
Different categories of users need different kinds of information for making decisions. The users can be divided into two broad groups: internal users, external users.
Internal users are the persons who manage the business, i.e. management at the top, middle, and lower levels. Their requirement of information is different because they make different types of decisions. The top level is more concerned with strategic planning; the middle level is concerned equally with operational planning and control; and the lower level is considered more with execution and controlling operations. Information is supplied on different aspects, e.g. cash resources, sale estimates, result of operations, financial position, sources and application of funds.
External users are the persons other than internal users (officers and staff concerned with decision-making in a business organization) come in the group of external users. External users can be divided into two groups:
- Those having direct interest; and
- Those having indirect interest in a business organization.
The main sources of information for external users are annual, half-yearly, and quarterly reports of business organizations. These reports state the financial position and performance, and give the auditors reports, director's report and other information. Half-yearly and quarterly financial reports are un-audited. Besides these reports, the external users can access the websites of companies and stock exchanges to obtain updated performance reports and current decisions of the board directors.
- External users having direct financial interest: Investors and creditors-present and potential-are the external users having direct interest. Investors (owners), on the basis of quantities of information, decide about buying, holding or selling investments in a business entity. Creditors (banks, financial institutions, debenture holders and other lenders), evaluate the risk of granting credit or lending money to a particular business organization on the basis of accounting and other information obtained about that organization.
- External users having indirect financial and non-financial interest: Tax authorities, regulatory agencies (such as Department of company affairs, Registrar of joint stock companies, Securities Exchange Board of India), customers, labor unions, trade associations, stock exchanges and others are indirectly interested in the company's financial strength, its ability to meet short-term and long-term obligations, its future earning power, etc. for making various decisions.