Treatment of stroke with physiotherapy
What is the role of physiotherapists in treatment of acute/chronic strokes?
Physiotherapists make a plan to rehabilitate the patient utilizing different type of techniques, which they learn through their physiotherapy classes and academics. Physiotherapists teach patients about home exercise programs after the patients achieve considerable recovery. Physiotherapists or physical therapists evaluate which muscles and ligaments still have power left and assess whether the patient is using those muscles and ligaments in functional movement and ADLs or not. If not, then physical therapists teach the patients on how to use them effectively. If the patient is already utilizing those muscles or ligaments, then they help the patients in improving their quality of movement and add voluntary control exercise in their present treatment protocol. If it is necessary, then a physiotherapist can prescribe a lower limb or upper limb splint. Also, PT doctors can asses the patient's daily needs and activities according to splint wear. Physiotherapists choose different types of work for them. Aerobic exercise is an important physical treatment modality to increase endurance and stamina. PT physicians also help in improving perception and cognition deficits if any. Physiotherapists also ask the patient for their interest and can include recreational activity in the treatment regimen. Posture awareness training also plays an important in PT.
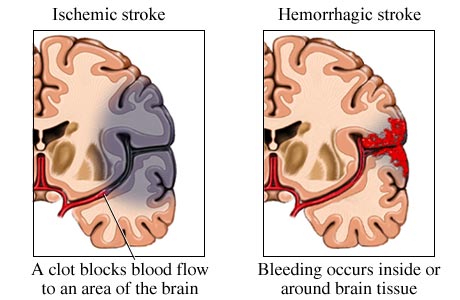
Different types of strokes and their treatment
If a patient is suffering from a stroke due to blood clot formation, i.e., ischemia, then (tPA - Tissue Plasminogen Activator) thrombolytics in three hours of onset of stroke provide best chance of recovery for stroke patients.
If a patient is suffering from stroke due to bleeding, i.e., hemorrhage, then (tPA - Tissue Plasminogen Activator) thrombolytics will only worsen the situation so accurate diagnosis through physical examination is necessary before proceeding towards further therapy.
For hemorrhagic strokes, physicians can prescribe blood thinners such as Coumadin, heparin, and Aspirin to reduce bleeding and prevent further damage.
Physical therapy for recovery/compensation of patients suffering from strokes
According to international stroke literature, the most vital question is recovery or compensation. On an interesting note, recovery after stroke is usually dependent on the size of lesion, location of brain involvement, and the time duration of getting therapy and several other things according to which we can get to know that the the patient will recover.
Some patients are able to achieve compete recovery within 1 month of stroke and live normal life. Full recovery without residual dysfunction is possible in patients suffering from hemiparesis but might not be a case with patients suffering from hemiplegia.
In some cases where there is more damage to the involved parts, the patient is not able to achieve complete recovery but functionally they can achieve some recovery. Gaining full recovery is difficult for these patients, so for these patients, a physician takes the route of compensation which does not represent a true complete recovery.
In this case, physical therapists try to help the patients to get well with rehabilitation including physical therapy, exercise, drugs, and medications. PT doctors try to train affected ligaments and muscles through stretching, strengthening, proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation, and other therapies to achieve an optimal level of independence.
This rehabilitative training teaches the patient's brain with capacity of plasticity to perform certain activities without utilization of infarcted part of brain. In simple words, normally functioning parts of the brain take over the function of dysfunctional and infarcted part of brains to control movement of body resulting in increased ability to perform near normal activity independently.
Location of lesion and other things mentioned above play a vital role in gaining at least if not complete but near normal recovery.
But in chronic cases of stroke, it is now thought that neural plasticity plays a vital role. In this case, the surrounding unaffected neurons connect to the affected area and help in providing a collateral circuit to initiate function. In this way, true recovery in such chronic stroke patients has become a possibility. With appropriate and continuous physical treatment, there are chances of achieving true recovery in patients suffering from chronic stroke too but this differs in an individual to individual.
Least but not last, a question still remains in everyone's mind that "how much true complete recovery can be expected from patients suffering from chronic stroke, but still there are hopes that in about another 5 to 10 years, the rehabilitation process of chronic stroke patients might be more advanced and physical therapists and patients will not have to rely on their destiny.
Advanced therapies that can be included in current rehabilitation protocols
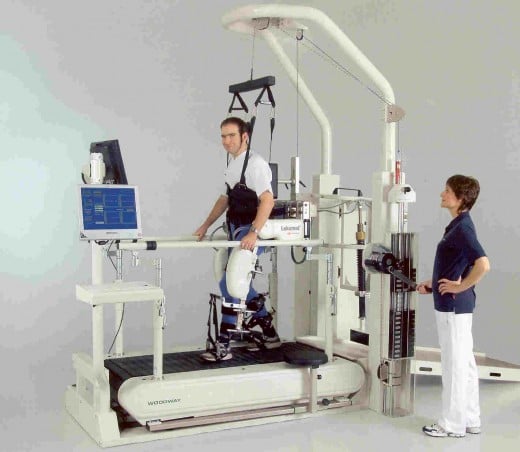
For Lower Extremities:
Use of an automated treadmill known as Locomat to help rebuild muscles in patients suffering from stroke.
Body-Weight Support Gait Training
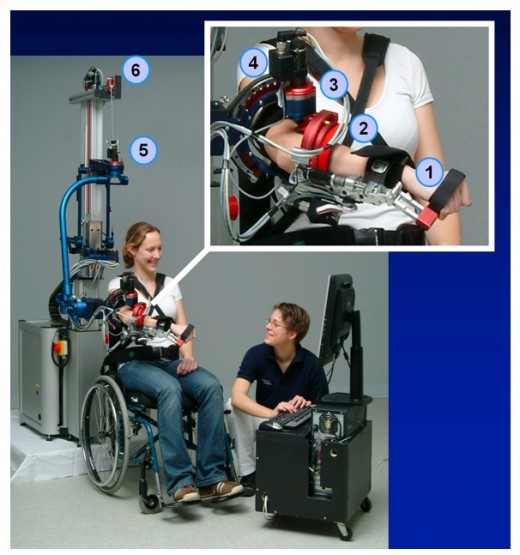
For Upper Extremities:
Functional Task Training
Strength Training for spastic group of muscles
Virtual reality training
Bimanual Training
Robotic Training