Umbilical Cord Blood Transplantation for Leukemia and Cancer
Featured book on Amazon: Umbilical Cord Blood: A Future for Regenerative Medicine
Transplantation of umbilical cord blood is consolidated as a therapy against leukemia and also for treatment of cancer. Due to more awareness about the benefits of umbilical cord blood in treatment of many critical illnesses, there are millions of parents around the world who are preserving, storing, and banking their baby’s umbilical cord blood rich in life-giving stem cells. It was in 1988 in Paris when a 5-year-old boy suffering from Fanconi anemia underwent first umbilical cord blood transplant. Today after 22 years of that procedure, umbilical cord blood transplantation has been established as a treatment not only for leukemia but also for many other diseases including sickle cell disease, other metabolic disorders, and even cancer. Though the stem cells necessary for a bone marrow transplant can be obtained directly from the bone through a spinal tap or through peripheral blood stem cell harvest, but umbilical cord blood transplants are especially suited for children and adults weighing less than 40 kg. In total, there have been in the world thousands of such transplants. The statistics clearly show that these transplants are increasing from year to year and are already beginning to see positive results even in adults. There are differences between the donation of bone marrow and umbilical cord blood. The number of stem cells in cord blood is much lower than those we can get through the bone, however, are much more vital cells and have a much lower requirement for compatibility. In emergency situations, cord blood units that are already identified are much more easily available in cord blood banks.
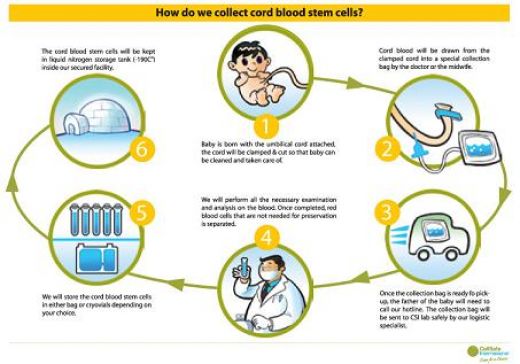
Umbilical Cord Blood Banking Process
- Carolina is 4 months pregnant. Her gynecologist gives her the opportunity to donate or bank her baby’s cord blood and tells her that this is once in a lifetime chance to save her baby from any critical illnesses he/she might get in the future.
- Carolina confirms with her husband and they both agree and consent for umbilical cord blood banking.
- Umbilical cord blood is rich in stem cells compared with normal blood.
- The blood collection is performed during the birth when the baby and the placenta are attached and are going to be detached.
- After collecting the umbilical cord blood, it is frozen and stored.
- Cord blood banking causes no risk to either the baby or the mother.
- The only requirement is that the parents, especially mother sign a consent to undergo a test to check that she has no blood-borne diseases and the baby took birth without complications.
- After quality control, umbilical cord blood is stored in banks and is available when a patient needs it.