Equity Portfolio Management

Options give investors and hedgers more alternatives. In this hub we will examine the role options can play in equities portfolio management. We will see how you can identify strategy trade-off's and select strategies given a certain market forecast. Specifically, we will examine three strategies - the use of call options as a leveraged means to participate in market moves, the use of puts to hedge a portfolio and selling covered calls to earn extra income in a flat or declining market.
One widely used strategy involving equity options, is as a leveraged means of participating in stock price gains, or in the case of an index product, broad market moves. Leverage in stock investing typically means buying on margin, where, as we have seen, the investor only pays some portion of the total purchase price. Call options can achieve a greater degree of leverage when purchased as an alternative to owning the actual underlying asset.
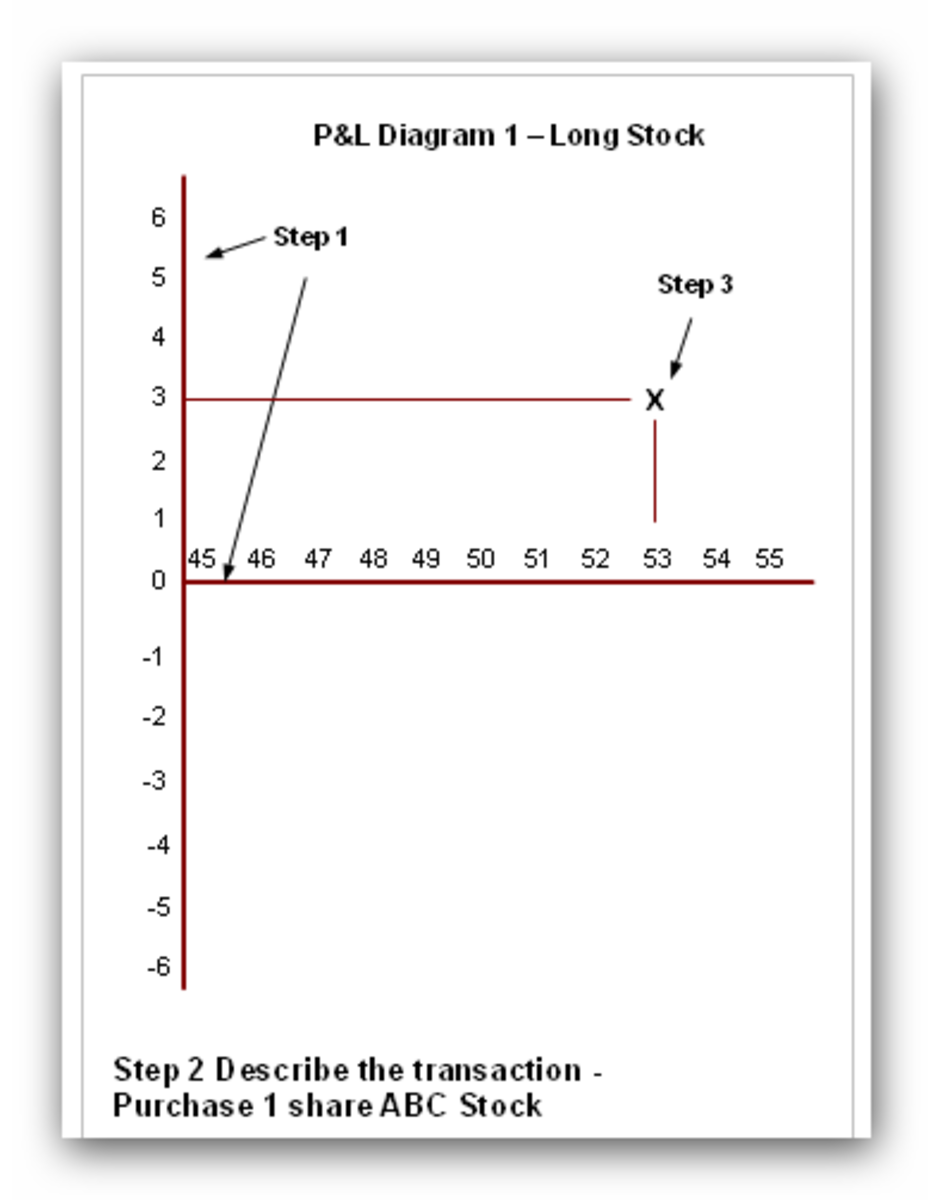
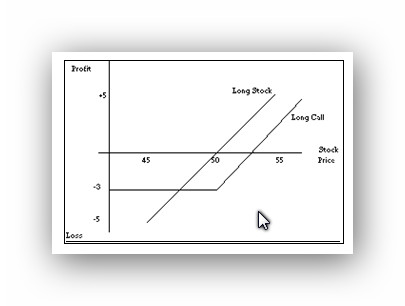
The graphic below compares two strategies over various market outcomes using the following call option as an example. Purchasing the stock at $50, the investor outlays $5,000 (excluding margin considerations) for 100 shares. The owner risks losing the entire investment in the event of bankruptcy. The owner breaks even, when the stock is at $50 per share. Alternatively the investor could purchase a June $50 call for $3, for a total investment of $300. He risks losing the $300 if the stock price at expiry is less than $50. However, for this relatively small investment, he can participate in stock price gains. Above the break-even of $53, the call option holder would profit $1 for each $1 gain in price.
Lets Compare Strategies
Purchase ABC stock at $50............................ Purchase Jun 50 call for $3
Cost $5,000....................................................$300
Profit unlimited potential................................. unlimited potential
Loss if stock falls to $0 - $5,000...................... limited to $300
B/E $50 per share...........................................$53 per share
Life unlimited..................................................limited
Profit at $65 = $1,500 or 30% profit............... $1,200 or 400% profit
To summarize, the long stock position employs $5,000 capital, has unlimited upside potential a downside risk of the owner losing the entire investment, and breaks even at $50. The June $50 call employs $300 capital, has unlimited upside potential, limited downside risk, breaks even at $53. But, it is important to remember that options have a limited life and may expire prior to the stock price increase.
Here is the real difference that is not captured by the profit/loss diagram. The profit as a percent of the investment is much greater with the option strategy due to its degree of leverage. For instance, if the stock price rises to $65, the stock position earns a 30 percent profit, however, the option position earns 400 percent profit!
Similarly, puts may be purchased as an alternative to shorting stock. The below graph compares the pay-off diagram of the two strategies.
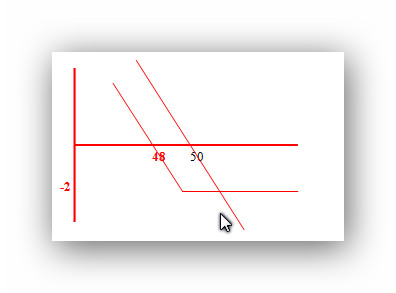
Compare Strategies
Short ABC stock at $50........................................Purchase June $50 put for $2
Cost --.................................................................$200
Profit if stock falls to $0 - $5,000............................if stock falls to $0 - $4,800
Loss unlimited......................................................limited to $200
B/E $50 per share................................................$48 per share
Life unlimited........................................................limited
Profit at $40 = $1,000..........................................$800 or 400 percent
As in the case with calls, puts can be purchased as a leveraged means to speculate on stock price declines. Beyond leverage, the advantages of puts relative to shorting stock is that losses are limited to thepremium paid, however, like calls, puts have a limited life.
The Protective Put
Puts can be purchased in conjunction with stocks as a kind of insurance policy to protect the investor from a decline in the stock portfolio. The protective put strategy is simply the purchase of puts in an amount equal to shares held. The below graphic presents the expiration pay-off of the long stock position. This strategy is useful when a long-term stock investor anticipates a short-term market correction and is worried about potential falling prices.
Remember, the put increases in value as the underlying stock price falls.
Let's look at an example. An investor buys 100 shares of New York Biotech stock for $36 per share. He is optimistic about the long-term prospects but concerned about an earnings announcement due out in early October. Therefore he buys 1 slightly out-of-the-money put for $1.
The below pay-off grid reveals the Profit and Loss for the protective put strategy. The investor has all of the upside potential, less the $1 premium, and is limited on the downside to a loss of $2 if the earning are lower than expected.
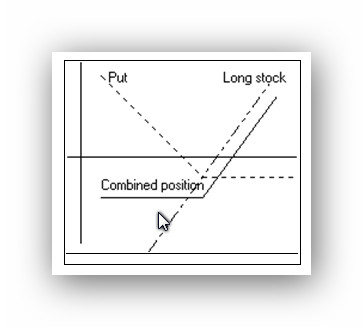
The following grid shows the potential profit or loss at various stock prices.
Price.............. Stock P/L................ Put P/L............ Combined
42 .......................+6.......................... -1 ......................+5
40 .......................+4 ..........................-1 ......................+3
38 .......................+2 ..........................-1 ......................+1
36 .........................0 ..........................-1 .......................-1
34 ........................-2 ............................0 .......................-2
32 ........................-4 ..........................+2 .......................-2
30 ........................-6 ..........................+4 .......................-2
28 ........................-8 ..........................+6 .......................-2
The Covered Call
Another options strategy we will examine is covered call writing. Like the protective put, this is also a combination option and stock strategy. It is best used when an investor anticipates a period of stable stock prices -- that is not expecting prices to rise or fall by very much in the near future. It allows the holder to earn additional income in the amount of the option premium received. The strategy generally entails the selling or writing of 1 out-of-the-money call for each 100 shares of stock held. The call is considered "covered" in that should the option be exercised, the call holder can simply deliver the stocks he already holds. Conversely, an "uncovered" or naked position is the sale of a call without a corresponding position in the underlying market.
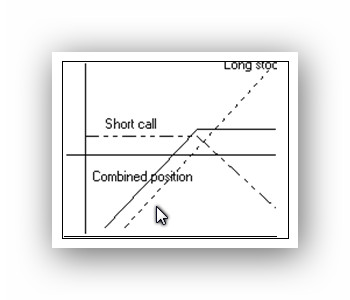
Price................. Stock P/L ...............Call P/L .............Combined
53 ......................+4 1/4 .....................-1 3/8 ................+2 7/8
51 ......................+2 1/4 .....................+ 5/8 .................+2 7/8
49 ......................+1/4 ........................+1 5/8 ...............+1 7/8
47 ......................-1 3/4 ......................+1 5/8 ................- 1/8
45 ......................-3 3/4 ......................+1 5/8 ................-2 1/8
This is an example of this strategy. Assume the holder of ABM stock forecasts stable prices -- within a point up or down from now until year end. The investor may sell a covered call, written out-of-the-money, in order to earn a few extra points on the stock. He chooses the 50 call, instead of an at or in the money call, because he does not want the stock to be called away.
This chart presents the profit and loss associated with the position at various levels of the stock at expiration. If the stock price remains between 47 and 49, as expected, the combined position outperforms the long stock position by the amount of the options premium received. Notice, however, if a sudden unexpected rally happens, the holder will likely lose the stock as it is called away at a price above $50 per share with his gain limited to 2 7/8.
Ever thought about trading stock options?
Let's look at another example. In March 1996, the S&P 500 Index stands at 640. We hold a $5 million indexed stock portfolio tied to the S&P 500. Here are current option prices.
Underlying ............................Call ..................................Put
Apr 625 ................................25 ....................................7 3/8
Apr 635 ................................19 ....................................11
Apr 650 ..................................9 1/2 ..............................14 5/8
May 625 ................................25 1/2 .............................11 3/4
May 635 ................................22 1/8 ..............................14 1/2
May 650 ................................17 3/8 ..............................20 5/8
What strategy should we choose if you expected a substantial market correction in April but a rally near the end of the year?
You could have chosen to buy any of the April puts, in 'at' or out of the money. If we believe the index will fall by a lot, say 5 percent to 608, the out-of-the-money put is the cheapest and affords the greatest degree of leverage. We would not want to sell our stock portfolio because we expect a stock market rally near the end of the year.
As you see from these examples, index options offer a means to participate in broad market moves and / or protect the value of diversified portfolio that is indexed to the market. These are the most popular index products available to investors.
Tick ...................................Index .................................Exchange
OEX ..................................S&P 100 Index ...................CBOE
SPX .................................. S&P 500 Index ...................CBOE
XMI ....................................Major Market Index .............AMEX
VLE ...................................Value Line Index .................PHLX
RUT ...................................Russell 2000 Index .............CBOE
MID ....................................S&P MidCap Index .............AMEX
NDX ...................................NASDAQ 100 Index ............CBOE
Index options work the same way as equity options, with two major exceptions. Index options are often European style exercise -- meaning they can only be exercised at expiration -- and are cash settled.