Vetoing in the UN - A Childish Endemic?
A Brief Overview and Background Information
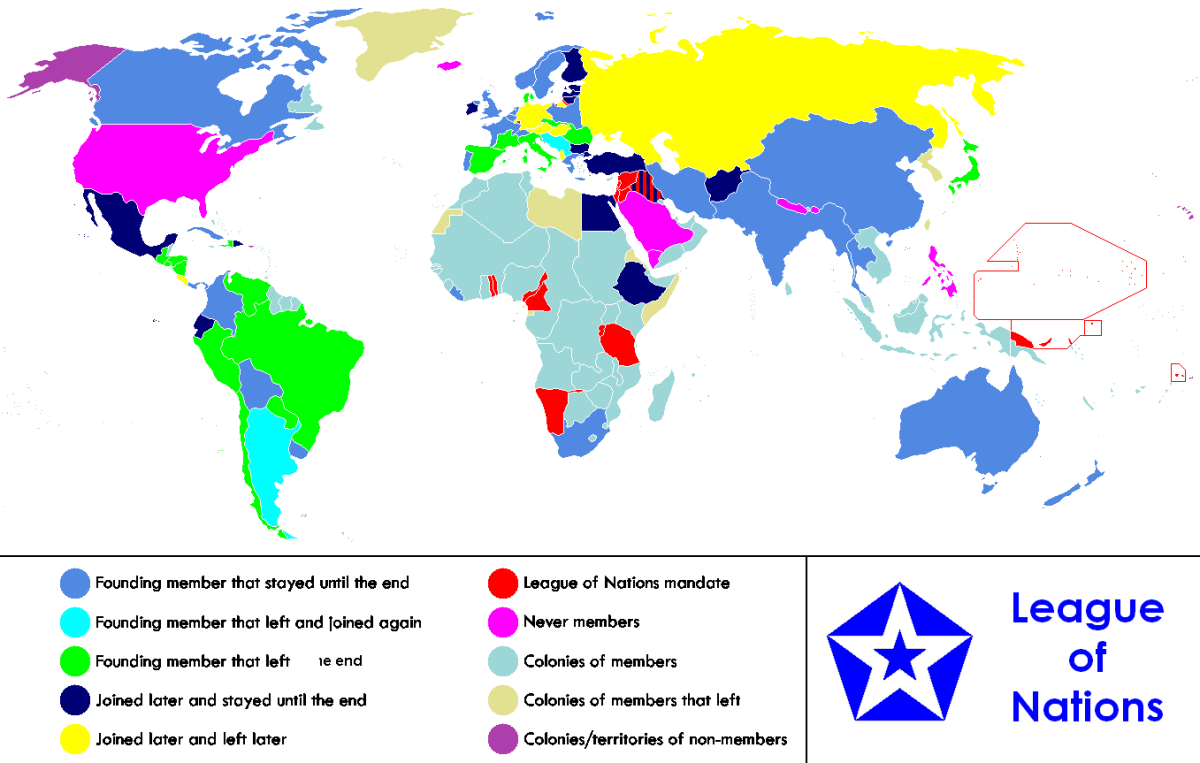
The United Nations (UN) is an international body which formally was given power for the first time on the 24th October 1945. Following the failure of its predecessor The League of Nations, the UN was given additional powers, more inclusive membership (The League of Nations lacked the Soviet Union as a member) and an important role for the great powers. Today the UN has 193 member states who actively engage across a range of committees and regularly send delegates to the General Assembly for debate and discussion of resolutions.
The General Assembly passes resolutions based upon a 2/3 majority present and voting for the resolution. In the GA small nations such as Lithuania, Estonia or Cuba are placed on an equal playing field with much larger nations like Russia or the USA.
A step above the regular debating in the General Assembly is the UN Security Council (UNSC). The UNSC is a body of fifteen nations, ten of which are elected every two years. The other five are considered key powers in the world and are given permanent seats. The list of nations with permanent UNSC seats are:
- United States of America
- People's Republic of China
- Russian Federation
- United Kingdom
- France
The voting of the UNSC is significantly less democratic than voting in the GA. Article 27 of the UN charter lays out voting rules:
- Each member of the Security Council shall have one vote.
- Decisions of the Security Council on procedural matters shall be made by an affirmative vote of nine members.
- Decisions of the Security Council on all other matters shall be made by an affirmative vote of nine members including the concurring votes of the permanent members; provided that, in decisions under Chapter VI, and under paragraph 3 of Article 52, a party to a dispute shall abstain from voting.
Effectively this means that resolutions can only pass in the UNSC with the approval of all five permanent members. In effect the five permanent seats on the Security Council can filter what the UNSC says, which is the key issue I wish to raise in this article.
Vetoing in the UNSC by Country
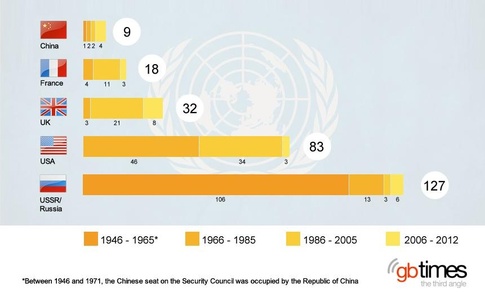

Use of the veto
The veto is frequently used by some permanent members of the security council. Its original purpose was to prevent radical or volatile change from happening which could threaten global security.
However its modern day use and application has been criticized by many people as protecting and serving the interests of the powerful nations and their allies.
Such an example which is frequently cited is the USA's regular vetoing of resolutions which condemn the state of Israel. The reasoning behind this is Israel is a close ally of the USA and receives a lot of funding from them. This has allowed Israel to commit what many view as war crimes against the Palestinian people without any international repercussions.
Another of the permanent members, Russia (Soviet Union), regularly vetoed resolutions which sought to bring new nations into the UN. The reasoning behind the Soviet Union doing so was that the USA and her allies refused to recognize the Soviet Republics established by the USSR in Eastern Europe.
Despite China's seemingly glowing record of only 6 vetoes over the course of their term as a Permanent Member I should highlight that they often choose to abstain rather than veto. This still means the resolution cannot pass and doesn't get recorded as a veto for China.
A recent example of a UN resolution being vetoed includes the resolution to condemn, threaten to impose sanctions and pave the way for a military intervention. The final votes broke down as follows: (Permanent UNSC Members are underlined)
Voting For: Bosnia-Herzegovina, Colombia, France, Gabon, Germany, Nigeria, Portugal, UK, US
Vetoing: China, Russia
Abstainers: India, South Africa, Brazil, Lebanon
There are a couple of points I wish to make regarding this:
- Of the nations voting for the resolution over half are in Europe and 2/3 can safely be classified as MEDC's.
- The rising powers of China, Russia1, India, Brazil and South Africa (Affectionately known as BRICS or CRIBS) seem to be reacting against the actions of the MEDC's. Every one of the BRICS members either vetoed or abstained from voting on the resolution. We are seeing a different power base emerge in the 21st century to the world of 1945 when the UN was created. However, it doesn't seem that the security council is changing in membership to reflect this.2
Footnotes:
1.Russia's place in BRICS has started to be questioned by several economists following its drastic economic collapse in 2009. It was the only BRIC nation to experience a GDP loss during that year. http://blogs.ft.com/economistsforum/2010/01/does-russia-belong-in-the-brics/
2.Although Nationalist China was replaced with Communist China the context was circumstantial following the military defeat of Nationalist China and the expulsion of its leaders to Taiwan. Realistically a nation as weak and small as Taiwan in 1979 should not have had a security council seat.

A Quick Survey
Should the veto powers of the UNSC Permanent Members be removed?
How much do you know about UN Vetos?
view quiz statisticsConclusion and Recommendations for Remedial of the UNSC
In conclusion I wish to draw together a few points regarding the UNSC and the veto power held by its five permanent members. I then wish to take a step back and provide a brief solution to remedy what I view as a system dominated by the elites.
Firstly, power is undeniably concentrated in the hands of the USA, UK, France, Russia and China.
Secondly, each of these nations is willing to use the power to place their own needs above those of the international community.
Thirdly, there is no way, apart from complete agreement of the UNSC that another permanent seat can be granted. Conversely there is no way a nation can lose their UNSC seat unless they give it up. This means nations, like Britain and France, are in the UNSC whilst more powerful nations, such as Germany, India or Brazil are excluded from it.
This could lead to a crisis of legitimacy in the UN over the coming decades. The rise of BRIC, collapse of the UK, French and Russian economies in the late 2000s financial crisis and the rise of APE (Anti-Political Establishment) Parties across the globe all threaten the UN's legitimacy, its values and its continued survival. If action is not taken the UN could become another failure akin to the League of Nations.