- HubPages»
- Technology»
- Consumer Electronics & Personal Gadgets»
- Portable Electronics
How a Camera Works


Whether as a professional or just as a hobby, photography is a fun thing to learn. There are many different types of cameras, different styles of photography, and many subjects. I have found it helpful to learn about how the camera works and expand on what I know to produce a good picture. Here are some of the things I have learned about.
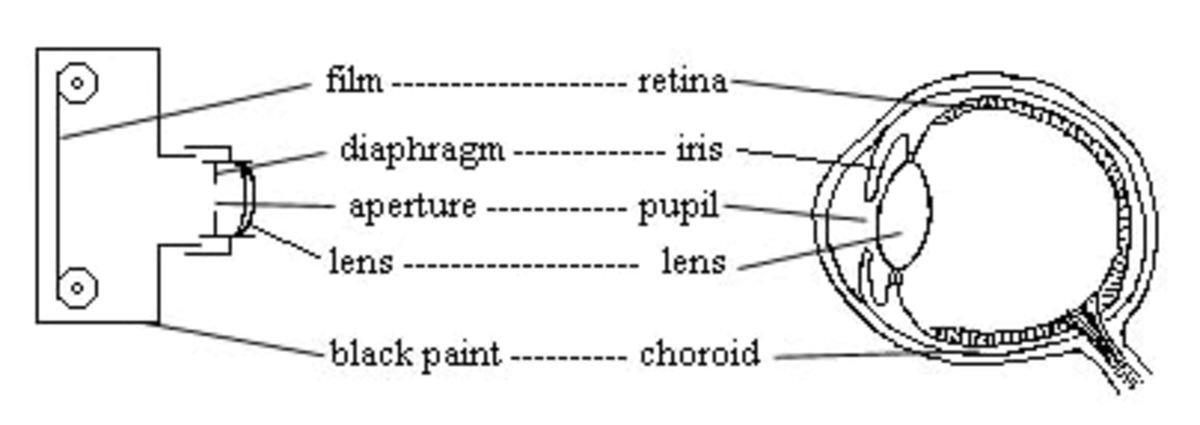
The camera looks like a complicated piece of technology. It really isn’t. It is simply a “light-proof box” with a pattern of mirrors directing small amounts of light at the right time. This is either done with one lens or two. A lens is a piece of curved glass or plastic. A single-lens reflex uses the same lens to view the picture and to take the picture and a direct vision compact camera uses two different lenses for both jobs.
The way an SLR camera works is fairly simple. When looking through the eyepiece, the light bouncing off the subject goes into your camera through the lens. Then it goes onto a mirror, bounces up, and goes into a pentaprism. A pentaprism is a piece of glass with five sides. Once in the glass, it bounces around until it reaches the eyepiece. This is the image you see. When you finally press the button on your camera, the little mirror moves out of the way and the light moves all the way to the back of the camera. There, the light either goes onto your film and creates a chemical reaction, or, if you have a digital camera, it hits an arrangement of cells. Each cell releases a very small electrical charge. This creates your final product.
A direct vision compact camera, or compact, works in a very similar way. A difference is that there is one lens for viewing and another for taking the actual picture. A compact is smaller and less weight than an SLR and that is why it is called a compact. Compacts don’t have pentaprisms or a movable mirror, so they are smaller.
Flash on a camera is another part to learn about. Flash bulbs at one time could only be used once. This was because they burned magnesium, a metal. This burned with a white light which could be made even whiter with a blue filter covering the bulb. Now, flash is made by electrical currents from batteries. The currents go through xenon gas to be a bright, white light.
The shutter is another feature to know about. The shutter is like a gate that controls the length of time the light is allowed to pass through the lens and onto the film or cells. There are two types of shutters: the leaf type and the focal-plane shutter. The leaf type is made of many thin metal blades that are opened and closed. This type works at 1/500th of a second. The focal-plane shutter is made of two rubbery fabrics that go across the focal plane, the area of the camera where the light is focused. The amount of space between the two pieces of fabric determines the shutter speed. It can go up to 1/4,000th of a second!
One other part of the camera you need to know about is focus. Your eyes focus and adjust automatically to any subject. Your camera may not. Even if it has autofocus, it may not focus on the subject you want it to. This can be seen in these two pictures: the one on the left focuses on the background, and the one on the right is focused correctly. The camera usually will focus on the center of the frame. Manual focus could be better for some as it is more accurate and lets you choose what to focus on. With autofocus, the camera sends out an infrared beam. This beam is bounced back to the camera and is measured either by the intensity of the bounce back, the distance it took to come back, or the amount of time it took to come back. Then a mini-computer in the camera finds the distance and changes the lens constantly until it finds the best, sharpest image.
I have learned a lot in using cameras. I now realize that the way the camera works is fairly simple. I also know that things like flash, the shutter, and focus are very important to know about to be able to use correctly. I plan to use this knowledge to the best. Then I can take the best possible shots whether I go on to be a professional photographer or if I’ll keep doing it just for fun!
If you have any questions, I'd be happy to answer or research a bit more and get back to you!