- HubPages»
- Technology»
- Computers & Software»
- Computer Science & Programming»
- Computer Programming Tutorials
How to create java socket | How to make java socket server | Complete java tutorial for java socket
Basics of Java Socket
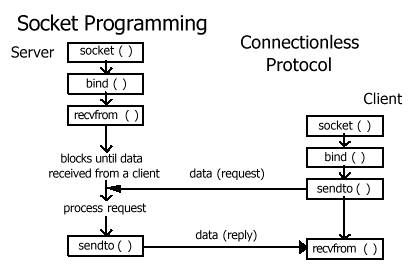
Java Socket is an extension from one of UNIX’s most important ideas. Java socket allows programmer to treat a connection in a network as another stream onto which bytes can be written to and from which bytes can be read. Java Socket is a connection between 2 hosts. This java tutorial includes descriptions of various operations that can be performed with java socket along with sample codes. Java sockets are classifies into 2, sockets for client side is simply called as Socket and for server side is called as ServerSocket. Operations that can be performed by a java socket is as follows
· Connect to a remote machine
· Send data
· Receive data
· Close a machine
· Bind to port
· Listening for incoming data
· Accept connections from remote machines on bound port

Java Socket for clients
Life cycle of client socket
· A new socket is constructed using Socket class constructor.
· A connection to remote host is tried by the socket.
· Once connection is established, the local and remote hosts exchanges information. Both client and server can receive and send data simultaneously.
· When the transmission is complete, one or both side can close the connection.
Java.net.Socket is the fundamental class for performing Client-side operation.
The method of Socket class is used to establish and terminate connection. This class provides streams to the programmer.
Constructors
Socket class has 4 constructors. In these constructors, hosts can be specified as an InetAddress or a string and ports are always specified as int values ranging from 0 to 65,535.
1) public Socket(String host, int port)throws UnknownException, IOException
A TCP socket to the specified port on the specified host will be created and attempt to connect to a remote host is being made.
host - it is expressed as in string.
port – a port no in which host is to be communicated.
UnknownException- If DNS can’t resolve the host name then this exception will be thrown.
IOException- If the socket can’t be opened for some other reason this exception will occur.
import java.net.*;
import java.io.*;
public class portscan
{
public static void main(String a[])
{
If(a.length>0)
host=a0];
for (int i=1;i<1024;i++)
{
try
{
InetAddress addr=InetAddress.getByName(host);
for(int i=1024;i<65536;i++)
{
try{
Socket s=new Socket(host, i);
System.out.println(“There is a server on port”+i+”of”+host);
}
catch(UnknownHostException ie)
{
System.out.println(ie);
}
}
}
catch(IOException e)
{
System.out.println(e);
}
}
}
2) public Socket(InetAddress host, int port)throws IOException
This constructor creates a TCP socket to the specified port on the specified host.
InetAddress host- to specify the host rather than hostname.
port – a port no in which host is to be communicated.
IOException- If the socket can’t be opened for some other reason this exception will occur.
import java.net.*;
import java.io.*;
public class portserver 1024
{
public static void main(String a[])
{
String host=’localhost’;
If(a.length>0)
host=a0];
for (int i=1;i<1024;i++)
{
try
{
InetAddress addr=InetAddress.getByName(host);
for(int i=1024;i<65536;i++)
{
try{
Socket s=new Socket(addr, i);
System.out.println(“There is a server on port”+i+”of”+host);
}
catch(IOException ie)
{
System.out.println(ie);
}
}
}
catch(Exception e)
{
System.out.println(e);
}
}
}
3) public Socket(String host, int port, InetAddress intref, int localport)throws IOException
Tries to connect to a port on the specified host by creating a socket.
host - it is expressed as in string.
port – a port no in which host is to be communicated.
InetAddress intref- used to connect from the local network interface.
Localport-used to choose from the available port between 1024 and 65,535. It takes the value 0.
IOException- If the socket can’t be opened for some other reason this exception will occur.
4) public Socket(InetAddress host, int port, InetAddress intref, int localport)throws IOException
This constructor is used to try to connect to be specified host by providing InetAddress instead of host name as string.
5) ProtectedSocket()
This will create a new socket without connecting it.
6) ProtectedSocket(SocketImpl impl)
This will also create a new socket without connecting it. But it implements SocketImpl object. If SocketImpl object is not needed then null can be passed to the constructor.
Getting Socket Information
Socket object has only one field, a SocketImpl which has native field code for all the fields of Socket.
Some main methods used are
public InetAddress getInetAddress() – Tells to which remote host the socket is connect to or connection is now closed.
public int getPort() – Tells to which port the socket is connected to on the remote host.
public int getLocalPort() – To find the port number of the local end of connection.
public InetAddress getLocalAddress() – To find the network interface to which the socket is bounded.
public InputStream getInputStream() throws IOException – return an input stream that can read data from the socket into a program.
public OutputStream getOutputStream() throws IOException – Return a row OutputStream for writing data from application to the other end of the socket.
Java Socket for Servers
ServerSocket class is used to write java socket server programs. It will runs on the server and listens for incoming TCP connections.
Basic life cycle of Java Socket Server (ServerSocket class)
· A ServerSocket() constructor is used to create new java socket for server.
· The ServerSocket() listens for the connection with the help of accept() method, which will return a socket object when a client attempts to make a connection.
· Sockets getInputStream() or getOutputStream() are used to send and receive data.
· The client-server communication exists, until it is time to close the connection.
· The server, the client or both close the connection.
· Server calls accept() method and waits for next connection.
Constructors
1. public ServerSocket(int port) throws IOException, BindException
It will create a java socket server on the port specified by the argument. If 0 is passed the available ports between 1024 and 65,535 will be selected. The argument ports are the ports selected by the System.
2. public ServerSocket(int port, int queueLength)throws IOException, BindException
Create a java socket server (ServerSocket) on the specified port with queueLength for incoming connections.
The maximum queueLength is 5, if 0 is passed, available ports will be chosen.
3. public ServerSocket(int port, int queueLength InetAddress BindAddress)throws IOException, BindException
Create a java socket server( ServerSocket) on the specified port with queueLength for incoming requests and in addition it binds the ServerSocket only to the specified IP address. This is useful for Servers that run on Systems with several IP address.
Accepting and Closing connections
In java socket programming 2 methods are used to accept and close the connection between client and server.
accept() method
public Socket accept() throws IOException
Block or stops the flow of execution and waits until a client connects when a client is connected. This method returns a Socket object getInputStream() and getOutputStream methods can be used to exchange data between client and server.
Example:
ServerSocket SS= new ServerSocket(6750);
While(true)
{
Socket con = SS.accept();
OutputStreamWriter out = new OutputStreamWriter(con.getOutputStream());
out.Writer(“connected to server”);
con.close();
}
close() method
public void close() throws IOException
Free up port for other connections. It allows another java socket service to bind to the port. It can close itself automatically when a program dies.
get() method
ServerSocket class provides 2 getter methods. They are
1. getInetAddress()
return the address being used by the server.
try
{
ServerSocket SS=new ServerSocket(80);
InetAddress add=SS.getInetAddress();
}
2. getlocalPort()
Returns a port which is being listened. This can be used in peer to peer multi socket program.
try
{
ServerSocket SS=new ServerSocket(0);
System.out.println(“The server is on port”+SS.getLocalPort());
}
Socket Option
The only socket option supported by ServerSocket class is So-TIMEOUT which is the amount of time in milliseconds that accept() waits for incoming connection before throwing an interrupted IOException. It is 0 then accept() will never time out.
Methods
1. setTimeout(int timeout)
Sets the So-TIMEOUT field for Server Socket object and the countdown starts when accept() is invoked.
2. getTimeout(int timeout)
Returns current So-TIMEOUT value to the ServerSocket.
Java Tutorial program to create FTP client – server program
Client Program:
importjava.io.*;
importjava.net.*;
class ftpclient
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
Socket client;
PrintStream ps;
String msg, line;
String fn;
Byte b[]=new Byte[500];
Int i=0;
try
{
Client=new Socket(InetAddress.getByName(“127.0.0.1”,3330);
ps=new PrintStream(client.getOutputStream(),true);
ps.println(“Transfer the file”);
DataInputStream dis=new DataInputStream(client.getInputStream());
FileOutputStream fos=new FileOutputStream(out.txt”);
DataOutputStream dos=new DataOutputStream(fos);
Line=ds.readLine();
System.out.println(“File Transferring…”);
dos.writeCars(line);
System.out.println(“File tTransferred…”);
}
Catch(Exception e)
{
System.out.println(e);
}
}
}
Server Program:
import java.io.*;
import java.net.*;
class FTPServer
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
ServerSocket server;
Socket con;
String msg, ofname;
try
{
Server= new ServerSocket(3330);
con=server.accept();
System.out.println(“Connection established”);
BufferedReader dis= new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(con.getInputStream());
String str1=dis.readLine();
System.out.println(“Client”+str1);
System.out.println(“Starting File transfer”);
File f=new File(“file path”);
FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream;
DataInputStream disf=new DataInputStream(fis);
DataOutputStream dos=new DataOutputStream(con.getoutputStream());
While(msg=disf.reaadLine()!=null)
{
System.out.println(“File transfer complete”);
con.close();
}
}
Catch(Exception e)
{
System.out.println(e);
}
}