Business Analyst
Business Analysis

Business Analysis
Every business needs to improve themselves to succeed and sustain succeed able. To improve their business, every business needs to identify and provide appropriate solutions to their customers and stakeholders regarding their business problems. To identify and develop a software solution is very crucially and important in any business and that is called Business Analysis.
Business Analyst
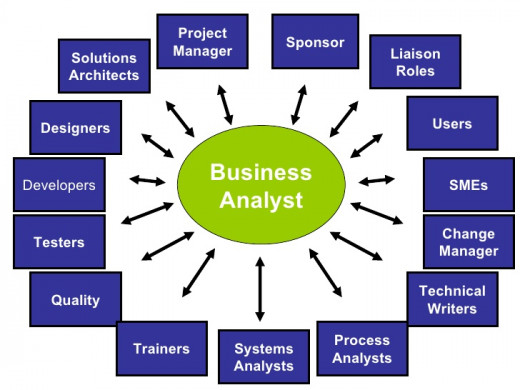
Who is Business Analyst?
Basically Business Analyst is Communication Bridge between Business stock holders and Technical stock holders. Business Analyst work as a problem solver for both sides. For any successful project Business Analyst plays very crucial roles in a team. Business Analyst has to understand business and technical stock holder’s requirements, issues and questions and based on that he/she has to resolve their issue, it is a very important task for Business Analyst. Business Analyst’s main job is to gather business and technical requirements and document those requirements in a suitable format for business stock holders and technical stock holders. Business Analyst provides the efficient information about business to technical people for successful development of projects. Business Analyst’s task is to understand the business flow and gather requirements from the clients and discuss with technical team to find out better business solution. Also, Business Analyst has to validate those requirements from the business side. Business Analyst should be good problem solver during the implementation.
Business Analyst Roles
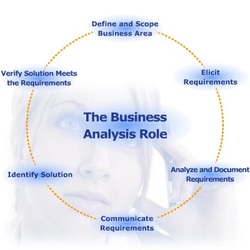
Business Analyst knowledge areas:
- Business Analysis Planning and Monitoring
- Elicitation
- Requirements Controlling and Communication
- Innovativeness Analysis
- Requirements Analysis
- Solution Valuation and Endorsement
An organized business analysis procedure will comprise of the following:
- Understanding the business
- Analyzing competition
- Analyzing the market
- Defining and scoping the project
- Gathering requirements
- Analyzing and documenting requirements
- Communicating requirements
- Identifying a solution
Some basic things which Business Analyst should know…
An actor: Someone or Something that interacts with the system is called the actor in any business. Actor is never part of the system or he/she/it is always outside the system.
Difference between primary and secondary actor: Primary Actor: Someone/Something who takes help from system in business, Secondary Actor: Someone who gives help to system in business
Sign Off: When Business analyst gets the approval on the requirements, is called sign off.
Stakeholder: Someone who can be affected by the project or someone who can affect the project is call Stakeholder.
Kickoff: The day when the project is getting started. eg: My project kicked off last month.
Go Live: The day when the project is used entirely by the client is called as Go Live.
SDLC
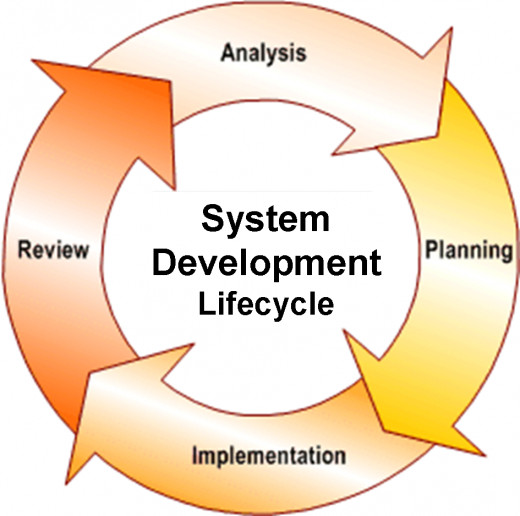
What is SDLC?
S - Software (System)
D- Development
L - Life
C – Cycle
It is the process to develop the software.
Steps of SDLC
• Scope Identification: Business Analyst/Project Manager
• Planning: Project Manager
• Analysis: Business Analyst
• Design: Designers/Architect
• Development: Developer
• Testing / Debugging: Software Testers
• Deployment / Installation: Developers/Deployment Engineers
• User Training and User Acceptance: Business Analyst/Project Managers
The systems development life cycle (SDLC) is a model which is used in project management that describes the different phases which involved in system development project from the begging of study of possibility of project through maintenance of the accomplished application/system.
There are several SDLC methodologies have been established in the market to monitor the processes. Some are The Waterfall model which was the original SDLC method; The Agile method; The RAD (Rapid Application Development); The V-shape model; The Fountain model; The Spiral model; The Iterative model; build and fix. Generally most of the models are collective into some sort of hybrid methodology. Irrespective of any type of the model or formula is chosen to develop new application or system, documentation is very important thig and typically documentation is done in parallel with the development of process. May be some approaches is better for particular types of project, but end of the project the most important thing is how carefully the plan was followed.
In overall, an SDLC methodology follows the subsequent steps:
- Evaluate the existing system. Find out inefficiencies. This.This can be done by cross-examining users of the system and denoting with personnel support.
- Address inefficiencies in the current system with suggestion for upgrading and address the new system requirements.
- Design the Project system. Laid out the plans regarding the physical structure, operating system, software design, hardware.
- Develop the project system. Acquired and fixed the new mechanisms and agendas. Confirmed all the aspects of new system, and if needed modification must be completed. Provide the training to users of the new system. User must be skilled in its use.
- System can be put on use by different way. The old system slowly phased in and replaced with new system or lock down the entire old system and implement the new system all at once.
- Evaluate the new system once is active and run for a while. Maintenance must be retained up carefully at all times. Users of the new system should keep themselves up to date regarding latest adjustments.
Which Phase of SDLC is more important?
What is UML?
UML stands for Unified, Modeling, Language
UML is a visual language that let you model software and process. UML is made up of notation and diagrams.
There are four different types of UML Diagrams.
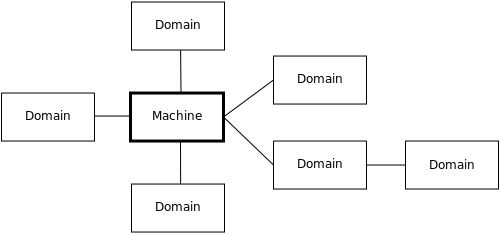
• Context Diagram: Context diagram is the highest level view of a system. It is similar to block diagram. Context Diagram is very high level diagram that represents the actors outside a system that could interact with that system. Context Diagram shows system as a whole and its inputs and outputs from / to actors.
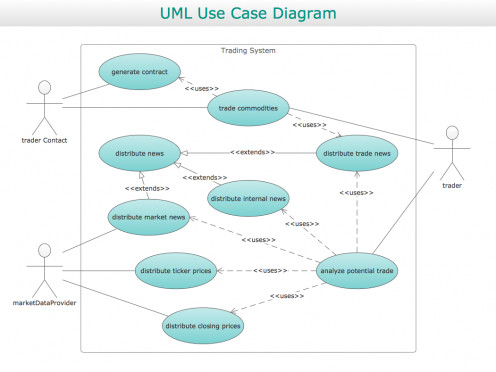
• Use Case Diagram: Use Case Diagram are created to visualize the relationship between Actors and Use Cases. Use case diagram shows the relationship between the actor and the different use cases in which the actor is involved.
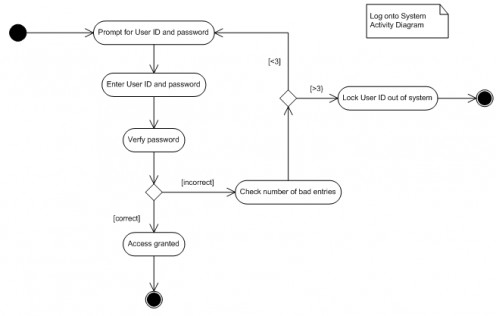
• Activity Diagram: Activity Diagram is used to demonstrate the sequence of activities. Activity Diagram shows the workflow from begin point to the end point with detail and the many decision point. Activity diagram are beneficial for business modeling where detail processing is involved. Very limited number of shapes are used in Activity diagram.
• Sequence Diagram: Sequence diagram is also called as Interaction diagram. Sequence diagram shows how processes function with one another and which order. A sequence diagram shows how objects interface in time series.
Diagrams