61
61- 0
Hpv: Types, Infection, Symptoms, Cancer, Warts, Transmission and More...
What is HPV? What are the types of HPV? How can one get infected with HPV? What are the symptoms of HPV? What is HPV cancer? What diseases caused by High-risk HPV? We answer all these questions and more...
- 0
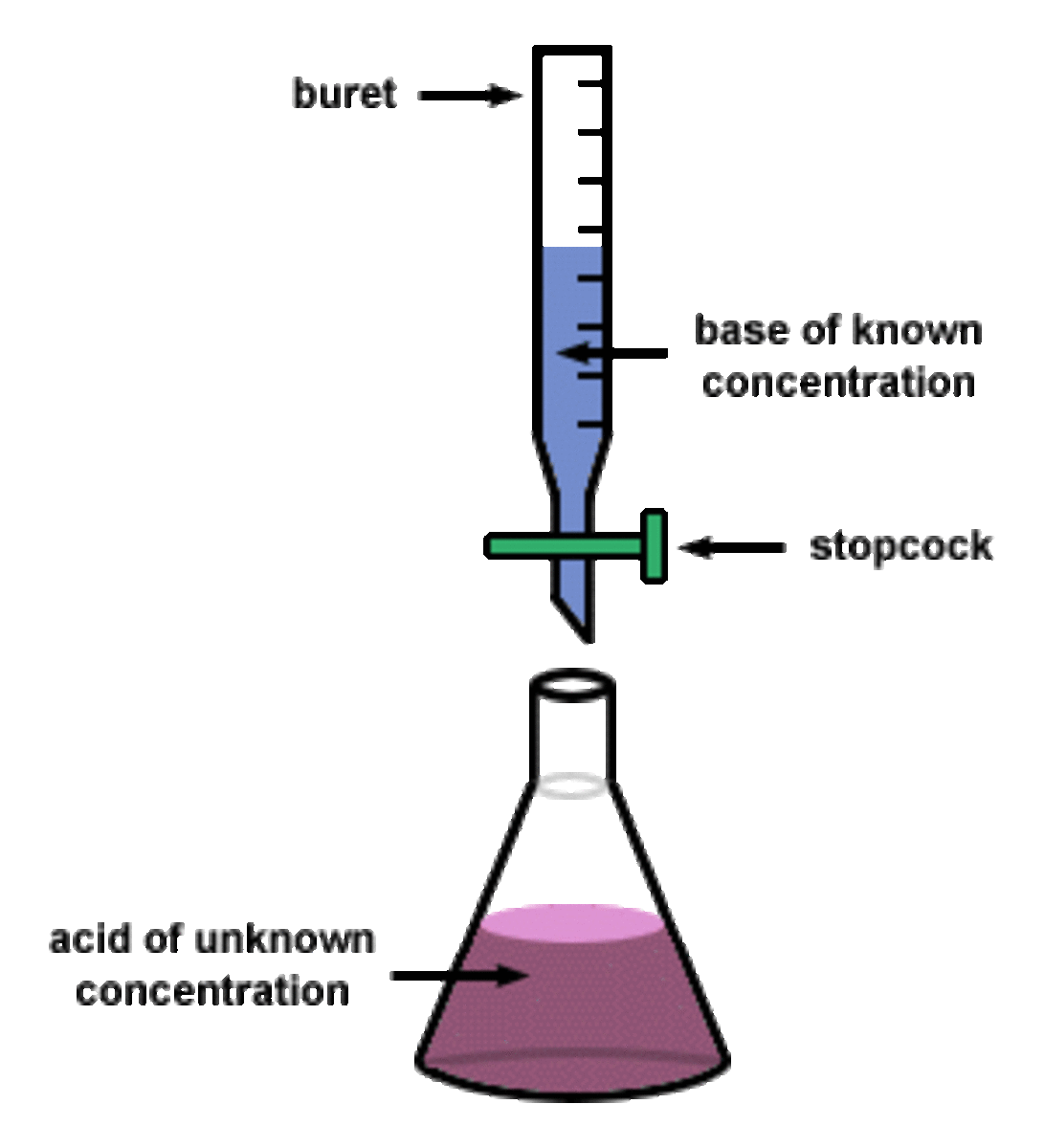
Different Methods of Measuring Drug Potency, Concentration, Efficacy - Epharmacology
Learn how to measure a drug's concentration, potency and efficacy! We talk about Titration, Spectrophotometry, Fluorimetry, Immunoassay (RIA, ELISA) Mass Spectrometry, Bioassay, Voltammetry & HPLC!
- 0
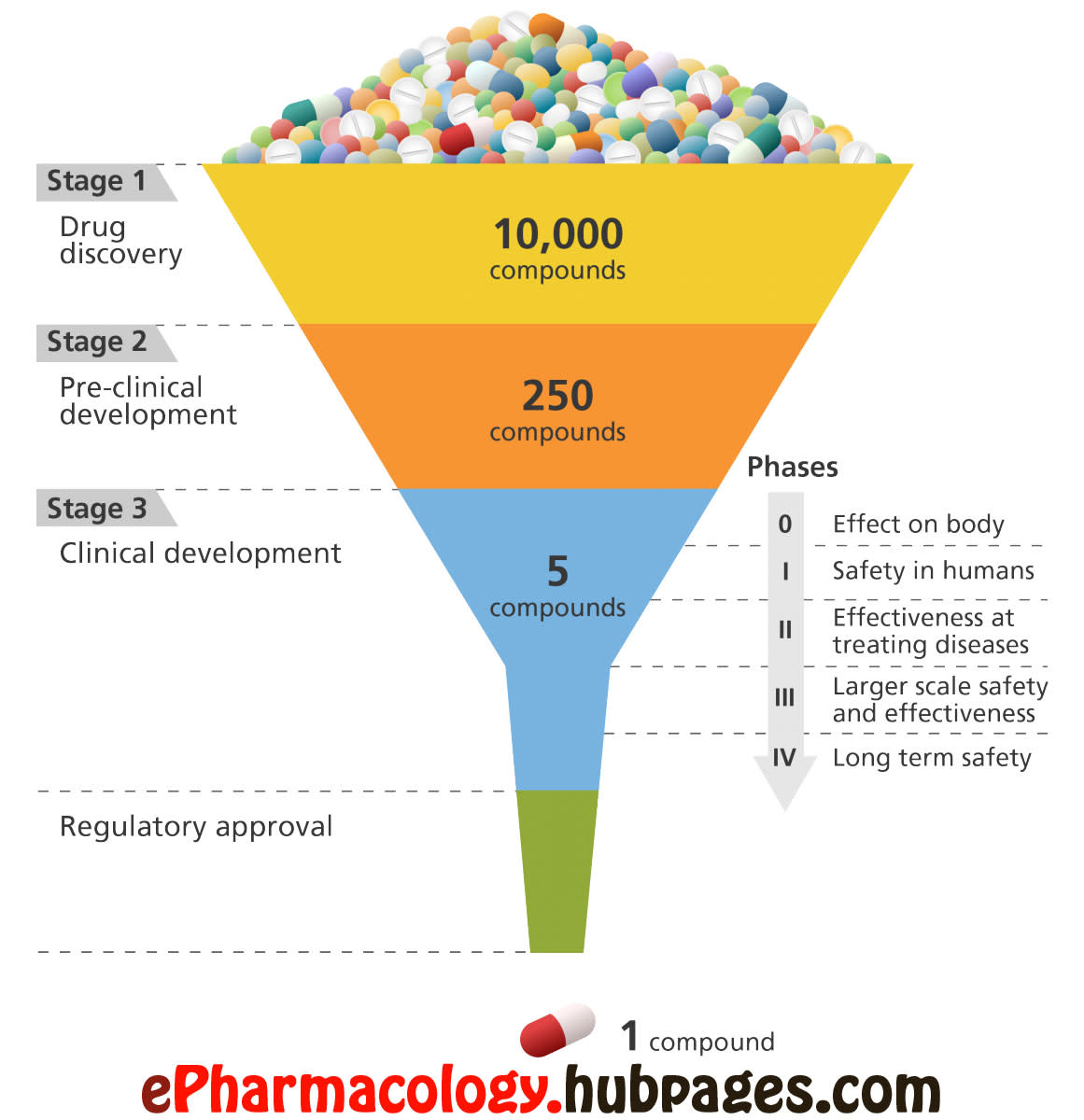
How are drugs developed and approved? The drug development process - ePharmacology
Learn how drugs are developed from preclinical to clinical stage! Here we discuss the drug development pipeline and talk in details about the different phases of clinical trials!
- 0
Ion Channels - Definition, Types, Description of Sodium, Calcium-Potassium and Chloride Ion Channels
Definition of ion channels, types of ion channels, description of gated ion channels and discussion of sodium, potassium, calcium and chloride ion channels - ePharmacology
- 0
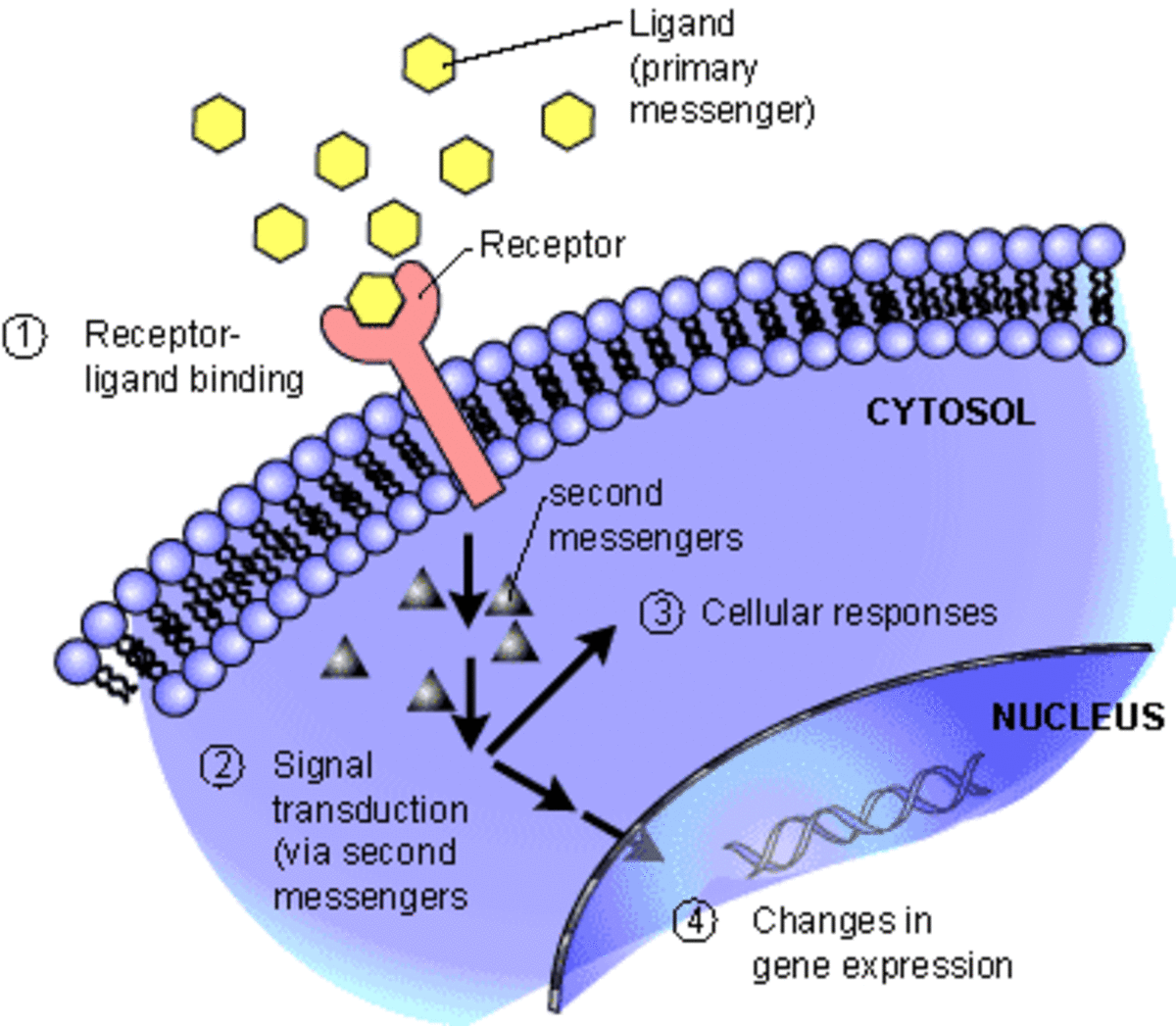
Life cycle of receptors, G proteins and Second Messengers (Definition, Examples - cAMP, IP3, PIP2- Functions and more)
How receptors are synthesized and regulated? Definition and examples of second messengers and how they work and their pathways and details about G protein coupled receptors - ePharmacology
- 0
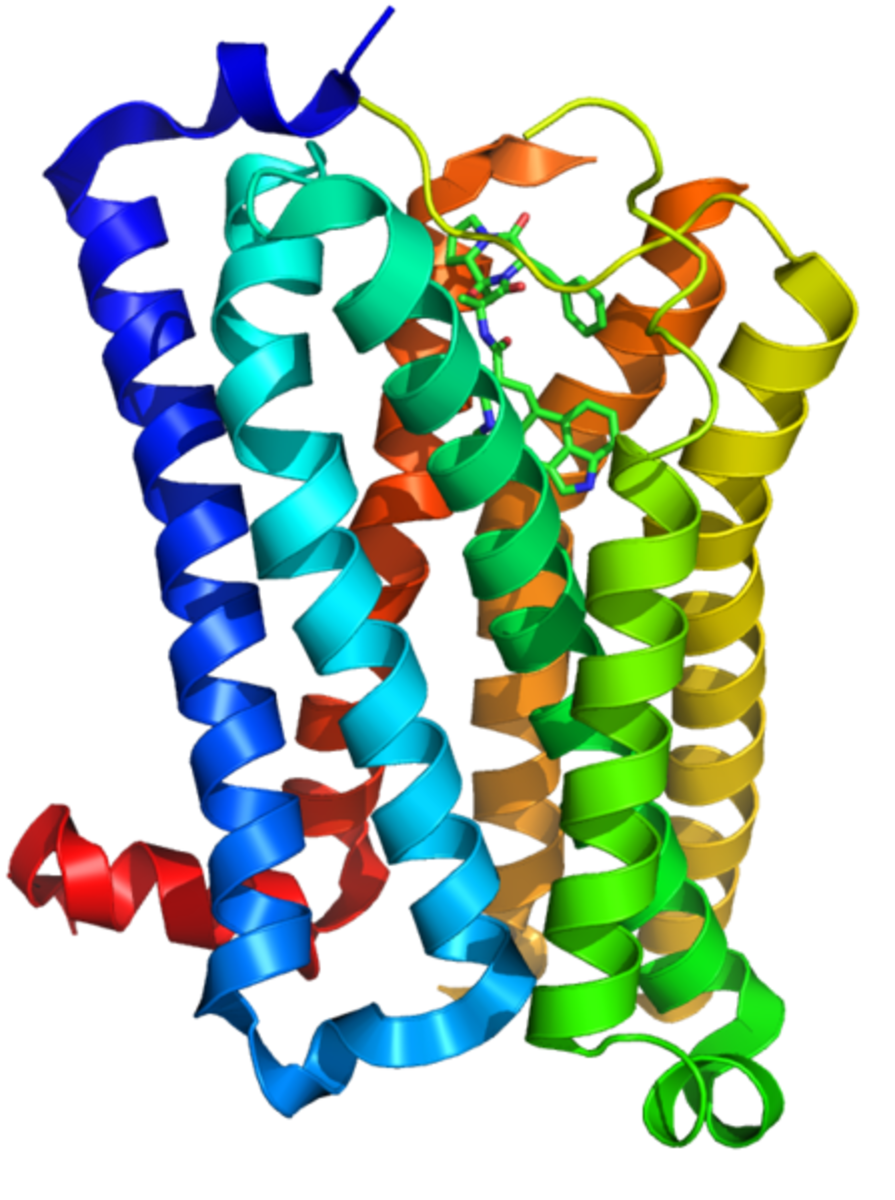
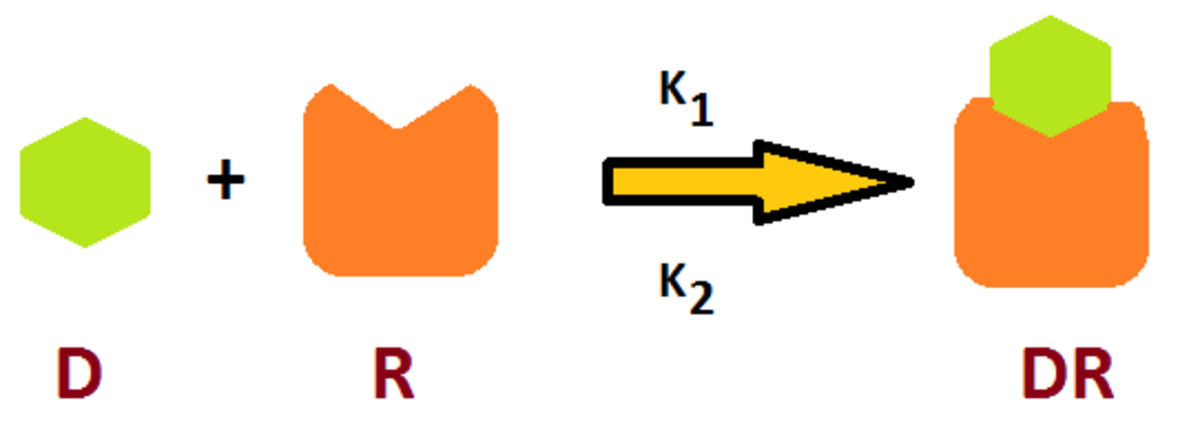
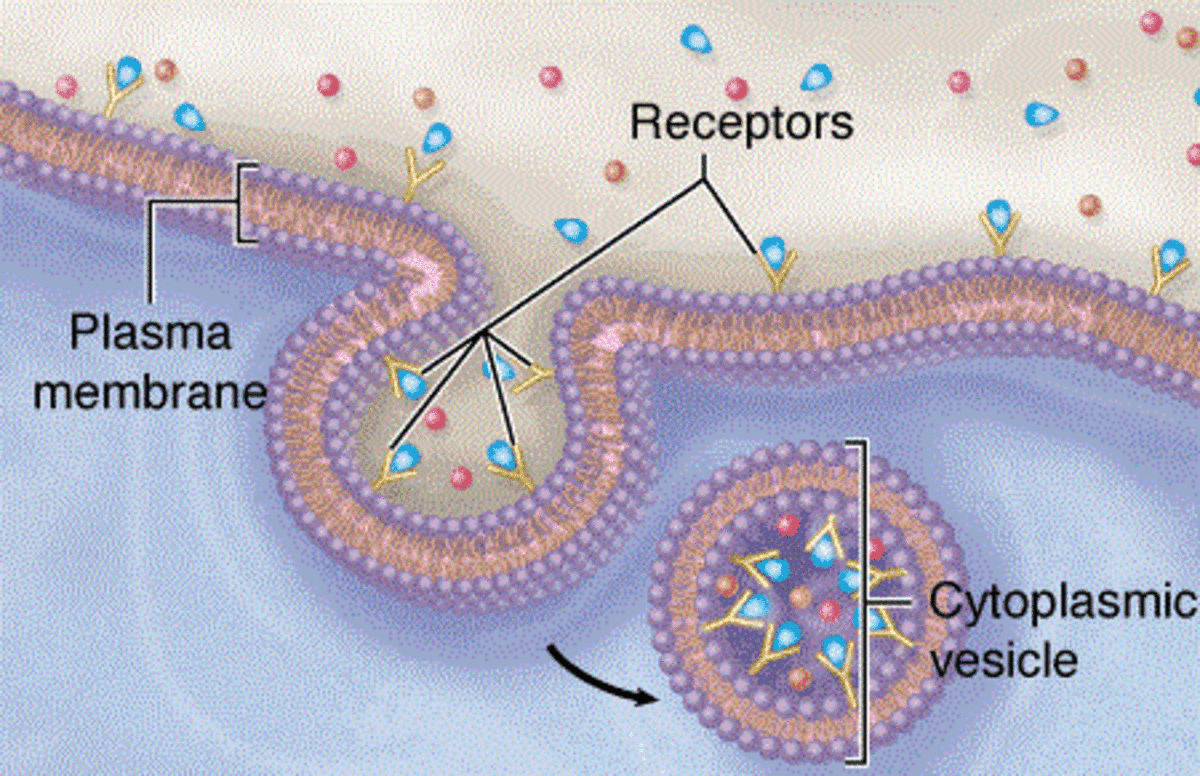
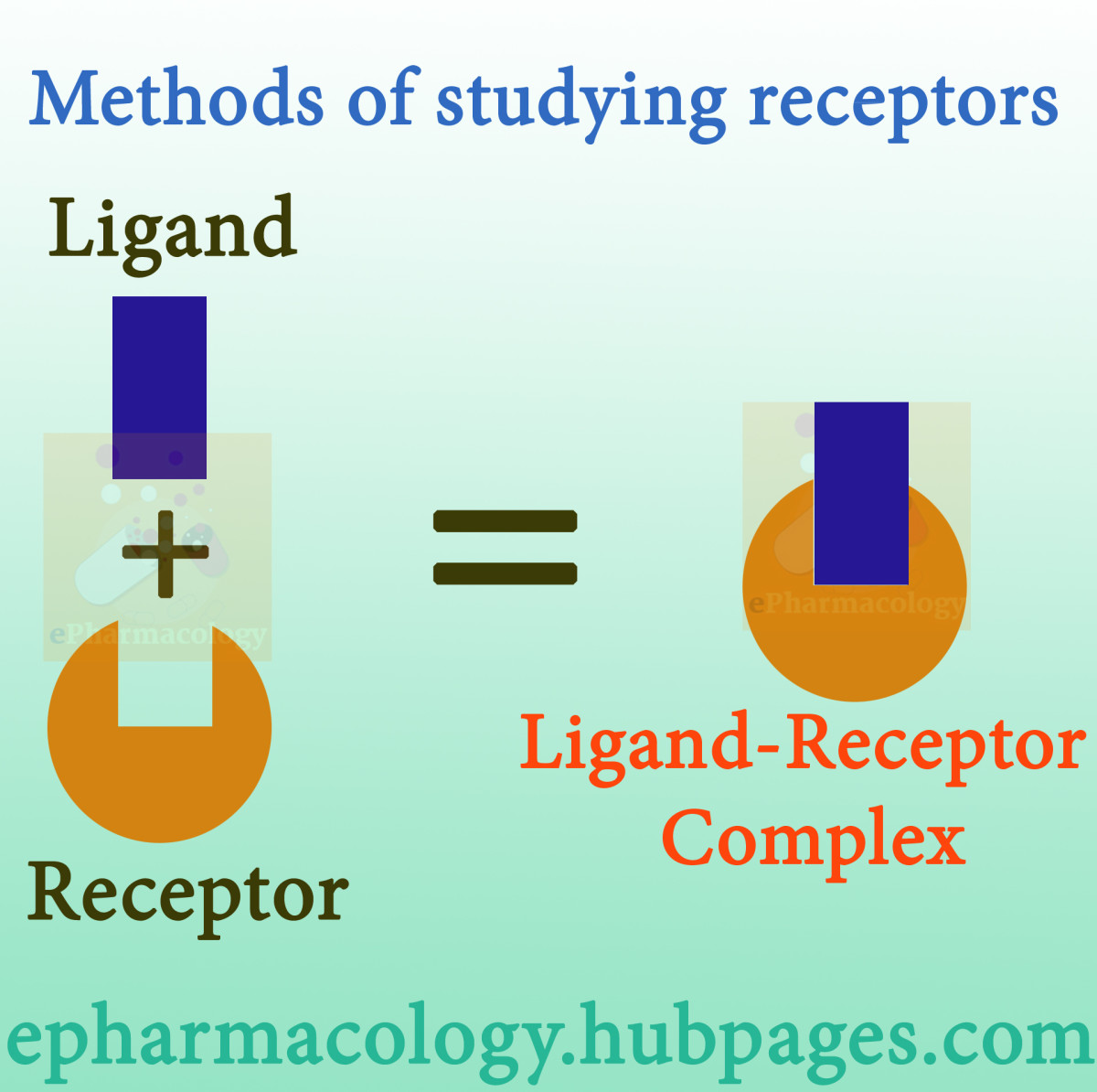
Receptors: Methods of studying receptors, number of receptors per cell and regulation of receptor - ePharmacology
How are receptors studied? How many receptors are in a cell? How are receptors regulated inside a cell?
- 0
Types, Mechanism of action and more of: 5-Hydroxytryptamine receptors, Opioid receptors, GABA receptors - ePharmacology
Learn about the types, mechanism of action, function, location and much more of 5-Hydroxytryptamine (Serotonin) receptors, Opioid receptors, GABA receptors - ePharmacology
- 1
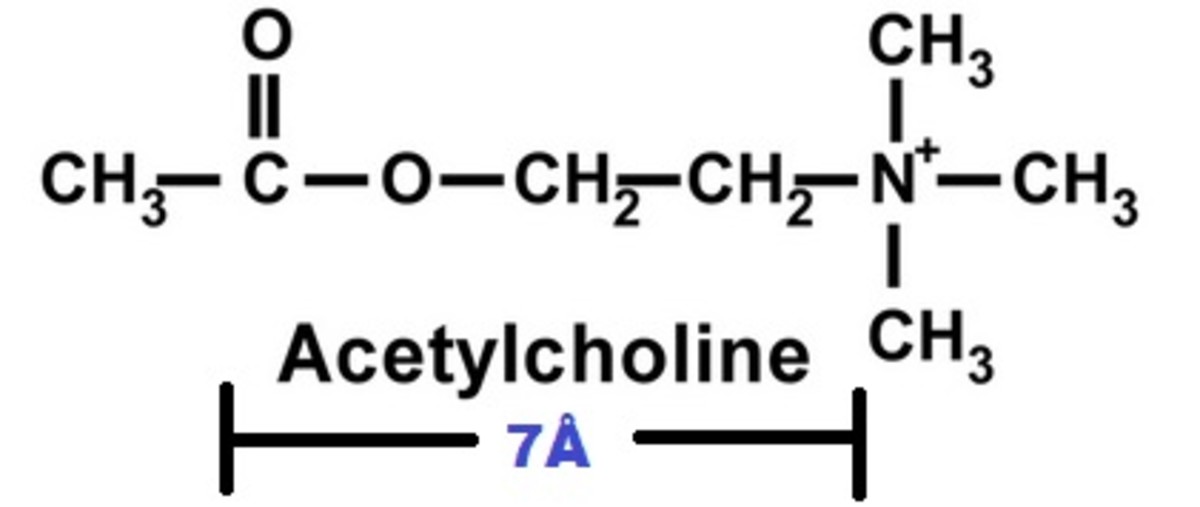
Individual Receptors: Cholinergic receptor, Adrenergic receptor, Histamine receptor & Dopamine receptor - ePharmacology
Learn about cholinergic receptors, adrenergic receptors, histamine receptors and dopamine receptors at ePharmacology.hubpages.com
- 0
How drugs work? - Different drug receptors (eg Tyrosine Kinase receptors, Hormone receptors, nuclear receptors) - ePharm
Drugs act through interacting with different receptors like tyrosine kinase receptors, hormone receptors, ion channel receptors and more....
- 0
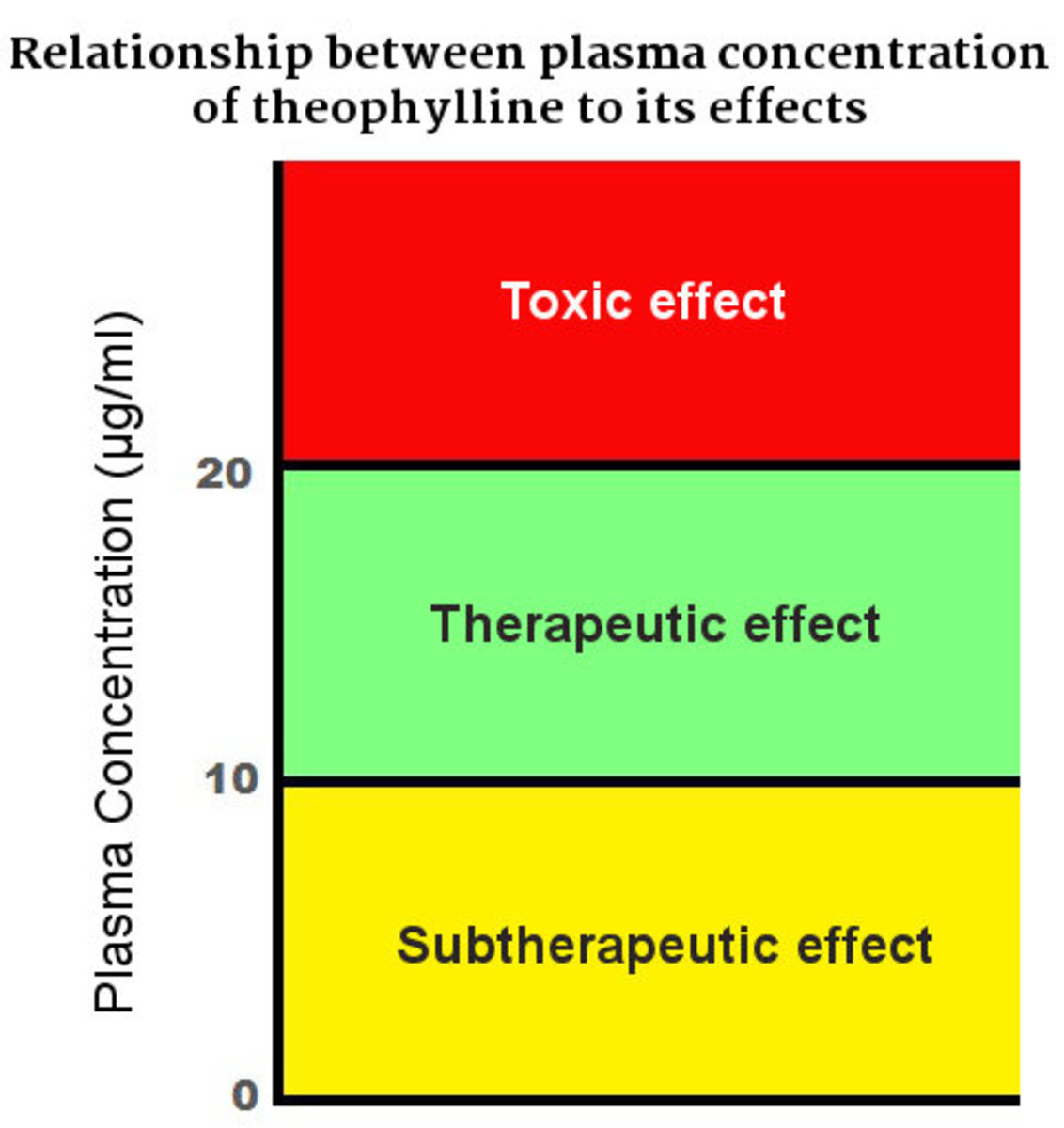
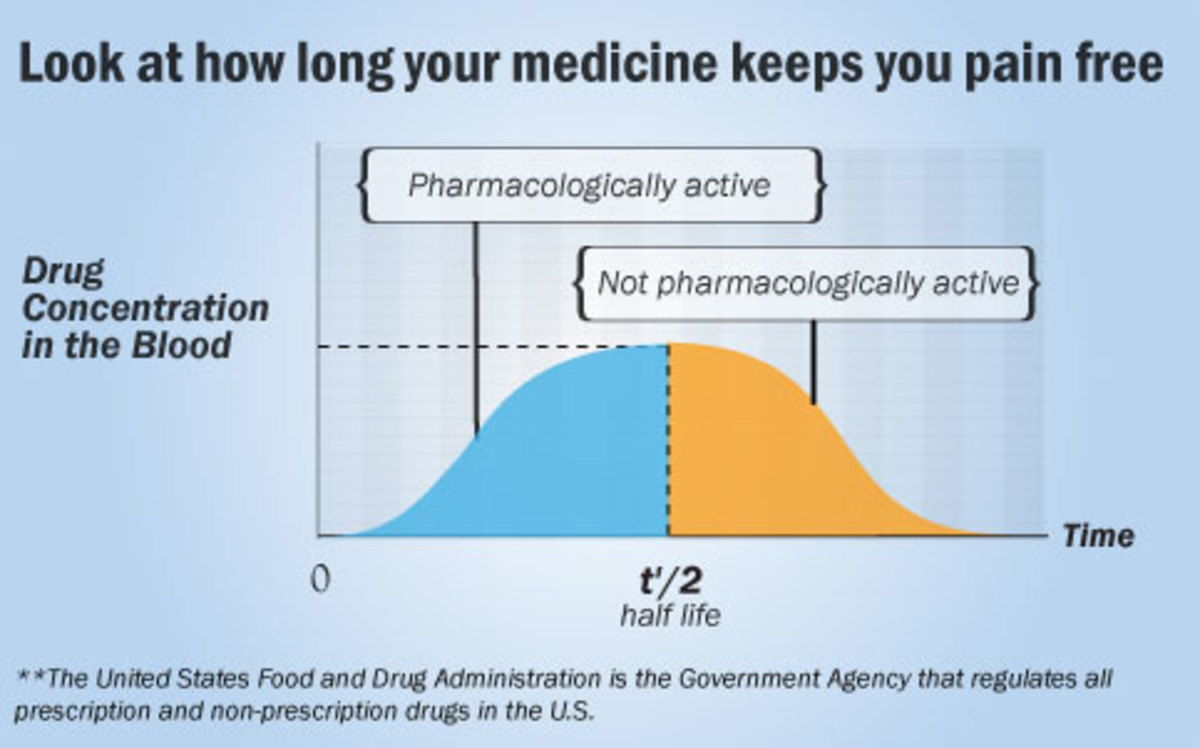
Understanding the Half Life of a Drug: Definition, Types, Formula, and Equation
What is the half life of a drug? Learn about the types, equation, and formula for the half life, as well as how to calculate a drug dose schedule.
- 0
How are drugs distributed in the body? - Distribution of drugs - ePharmacology
There are many factors that determine the distribution of drugs in the body. Find out what they are...
- 2
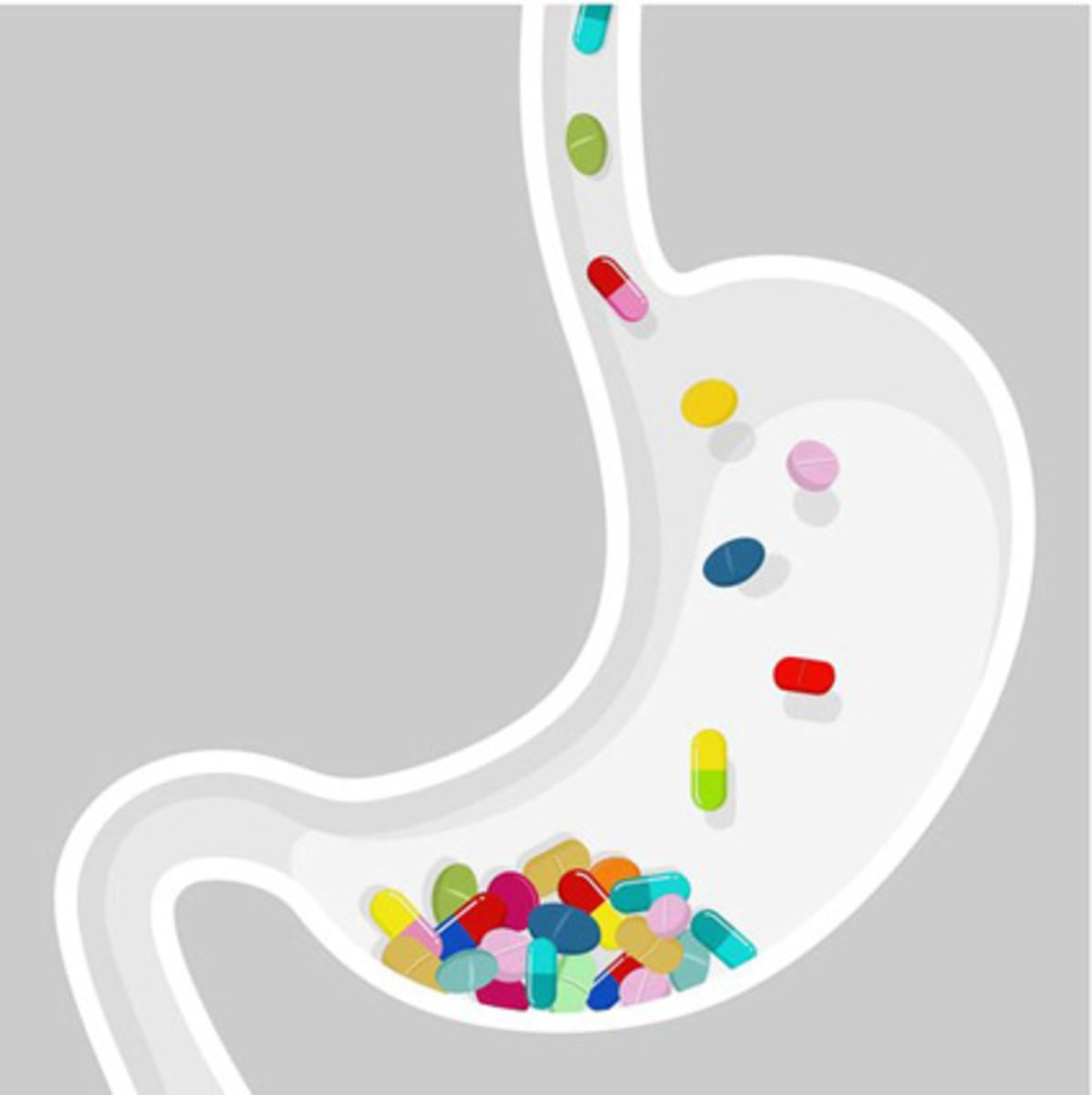
Absorption of drugs: how drugs are absorbed in the body? ePharmacology
Absorption of drug occurs from the alimentary tract, muscle, subcutaneous tissue, skin and respiratory tract. Whatever the sites of absorption, it is modified by several factors. For example, when a drug is administered by oral route, presence of food, pH of the gut, rate of gastric emptying may...
- 4
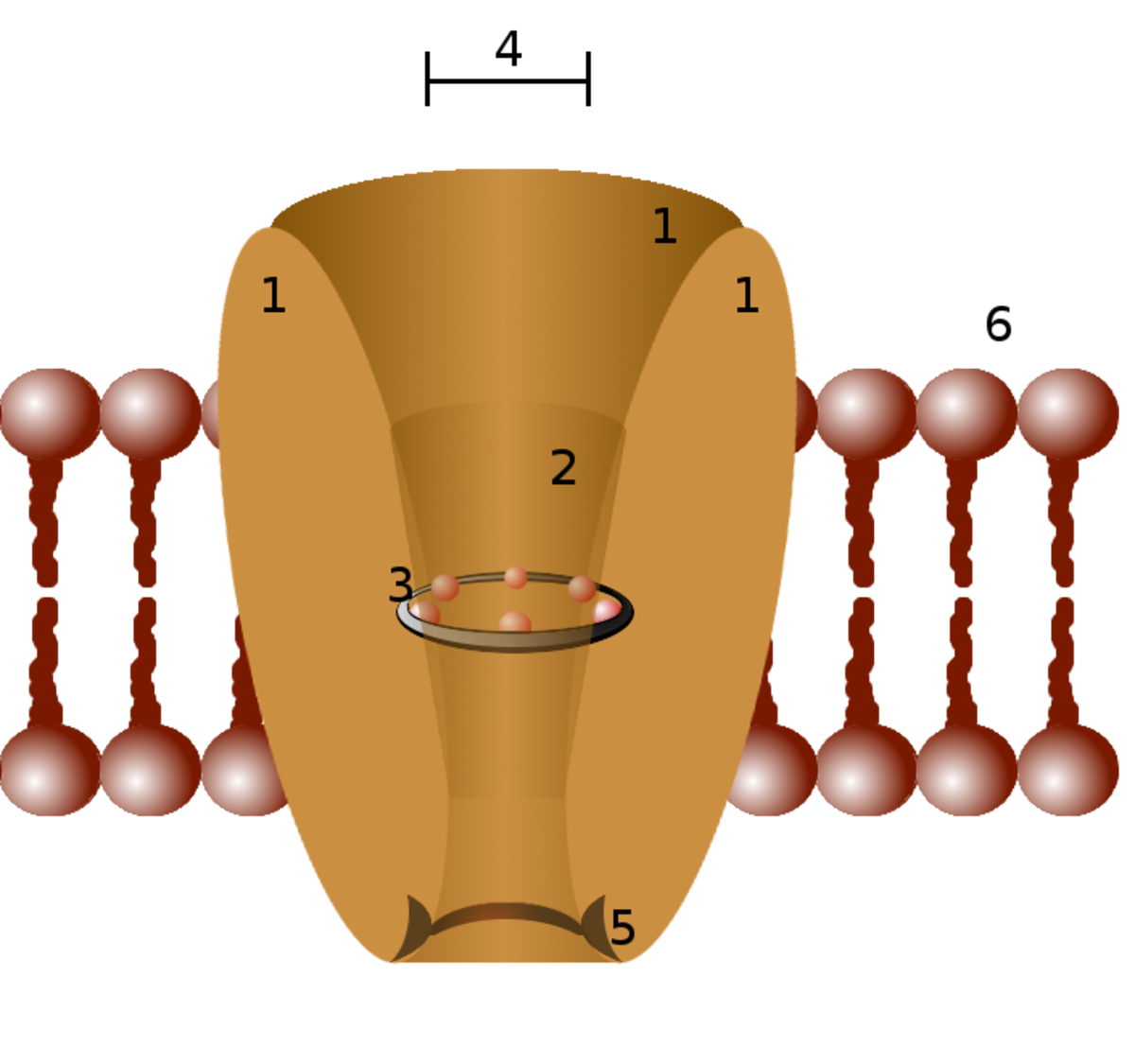
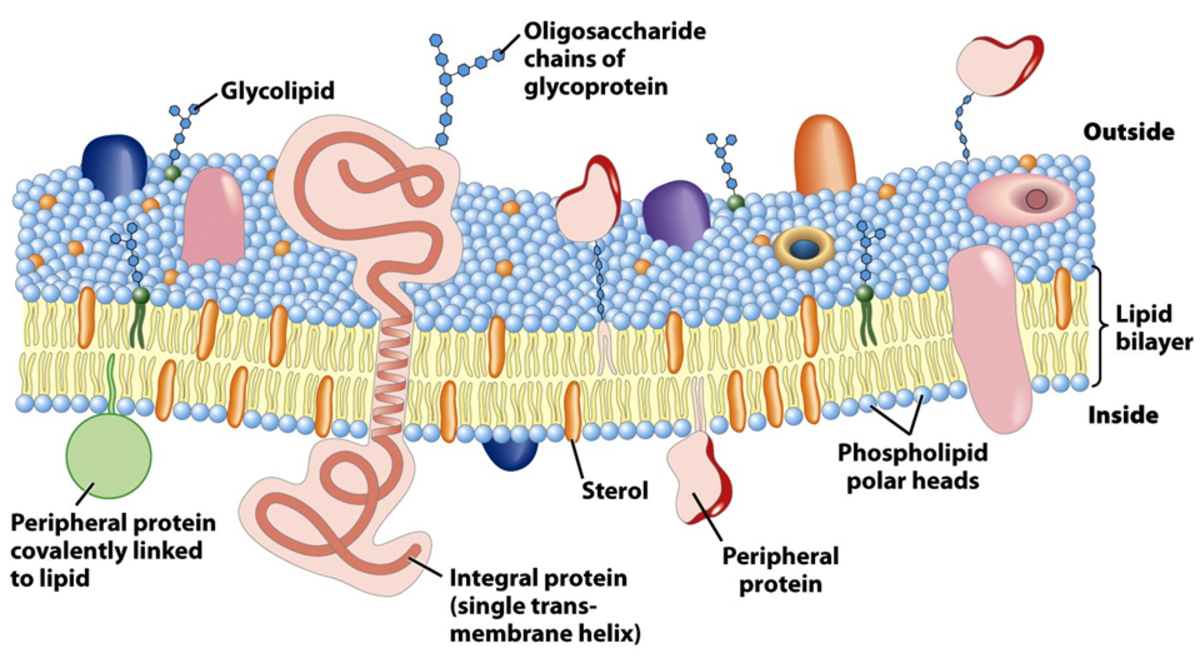
What Are the Different Modes of Biotransportation of Drugs? How Do Drugs Move Across the Cell Membrane?
Plasma membrane acts as an important biological barrier for the movement of drugs. Movements of drugs occur by simple diffusion, filtration, facilitated diffusion, active transport, endocytosis, and ion-pair transport. Among them, most of the drugs move by simple diffusion. Simple diffusion does...
- 0
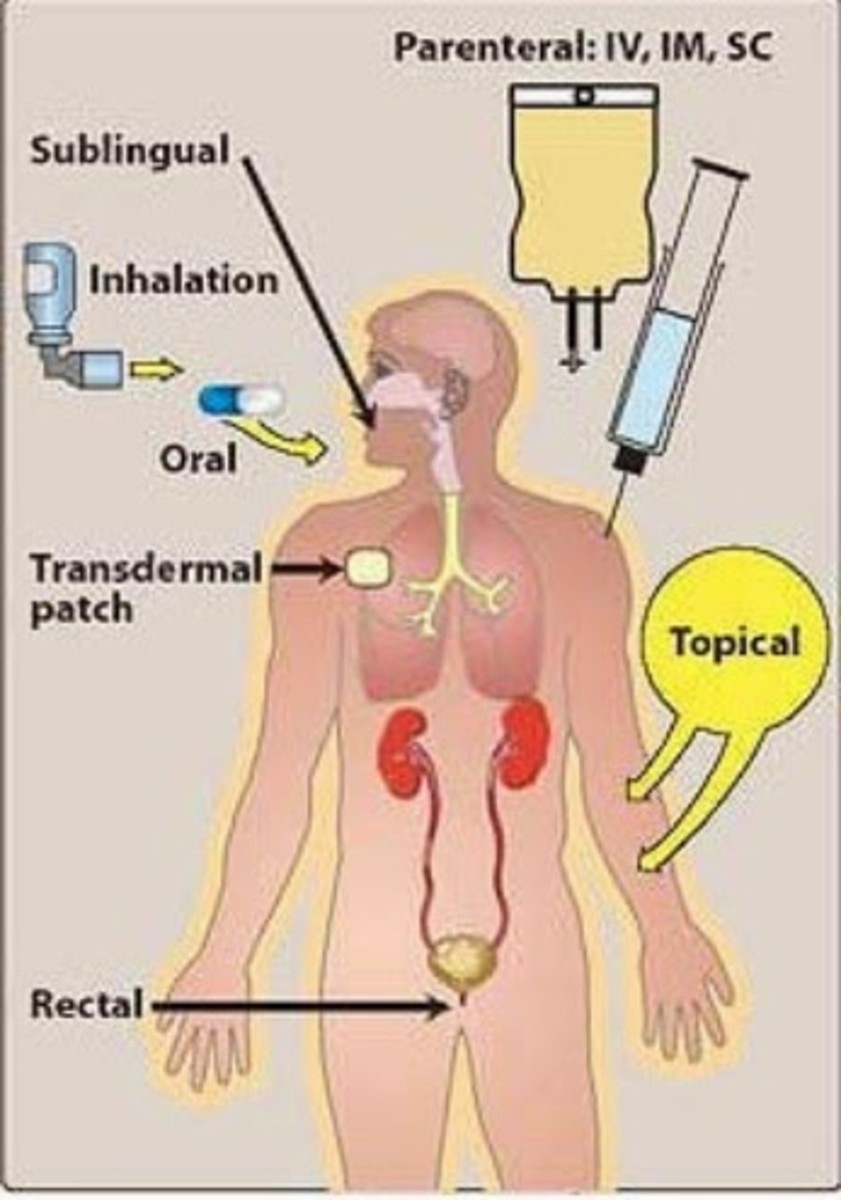
Methods of administering drugs into the body - ePharmacology
Drugs are administered into the body by various routes / methods: enteral, parenteral, topical or site specific. No single route is ideal for all drugs. Among them oral (swallow), intramuscular, and intravenous administration are common. Each method has advantage and disadvantage. Nowadays...
- 0
What are the dosage forms of drugs?
Drugs are found in various formulations (solid, semisolid, liquid, and gas). Solid dosage forms include tablet, capsule, powder, granule, and suppository. Semisolid preparations include cream, ointment, and paste.Solutions (syrup, elixir) and suppositories are the liquid preparations.Aerosol is...
- 0
Characteristics of drugs (Part 2)
Today we will discuss the rest of the characteristics of drugs: Partition coefficient, Dosage form, Salt preparation, Affinity to bind and Potency!
- 0
Characteristics of Drugs: Part 1
What makes a drug unique? This article discusses the first four characteristics of a drug: molecular weight and size, stereoisomer, structure-activity relationship, and ionization constant.
- 5
How are drugs classified and grouped? - ePharmacology
There are four ways of classifying drugs? Do you know all of them? If not, then read to find out...
- 2
How Drugs are Named? Drug Nomenclature
Where do drug names come from? How do we name a drug? Why there are so many name of a single drug? Read to find out...
- 16
What Are the Pharmaceutical Sources of Drugs?
What are the sources of drugs? Plants, Animals, Minerals, Laboratories and Microorganisms! Read to know in details about the different drug sources...
- 4
Pharmacological Effects, Prodrugs (Definition, Examples) and Sources of Drug Information
Learn what is pharmacological effect and its types, what are prodrugs along with examples, what is pharmacopeia and much more...
- 26
Free Online Pharmacology Lessons / Course / Class for FREE! Learn pharmacology online -Introduction to Pharmacology
Learn pharmacology online for free! We provide free pharmacology lessons. Pharmacology - the study of drugs. Learn the basic concepts of pharmacology. Learn about pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic.