 76
76- 2
Lung Compliance and Elastance
Lung compliance is the ability of the lungs to expand. Elastance measures the work that has to be exerted by the muscles of inspiration to expand the lungs. Factors affecting these are discussed here.
- 0
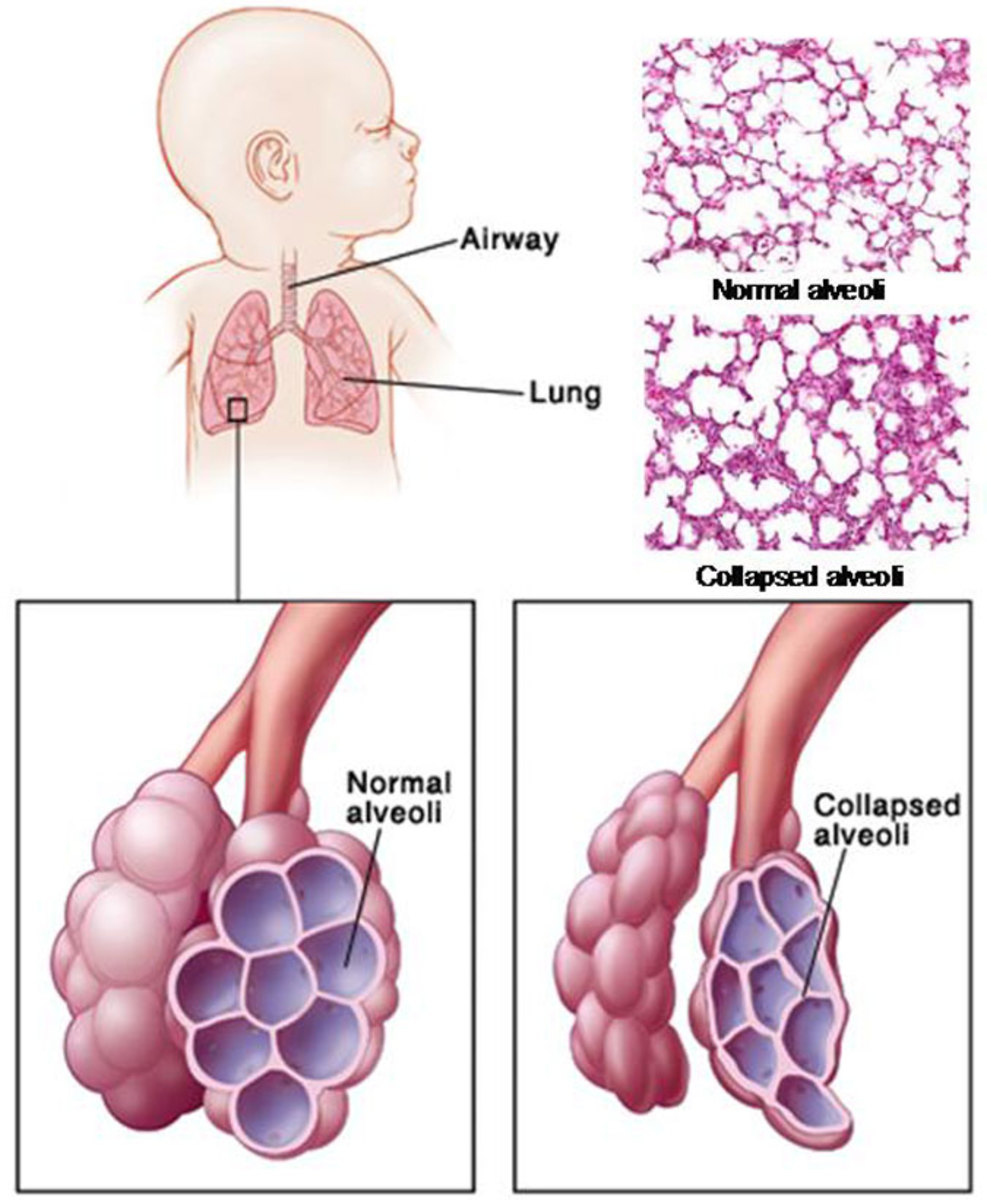
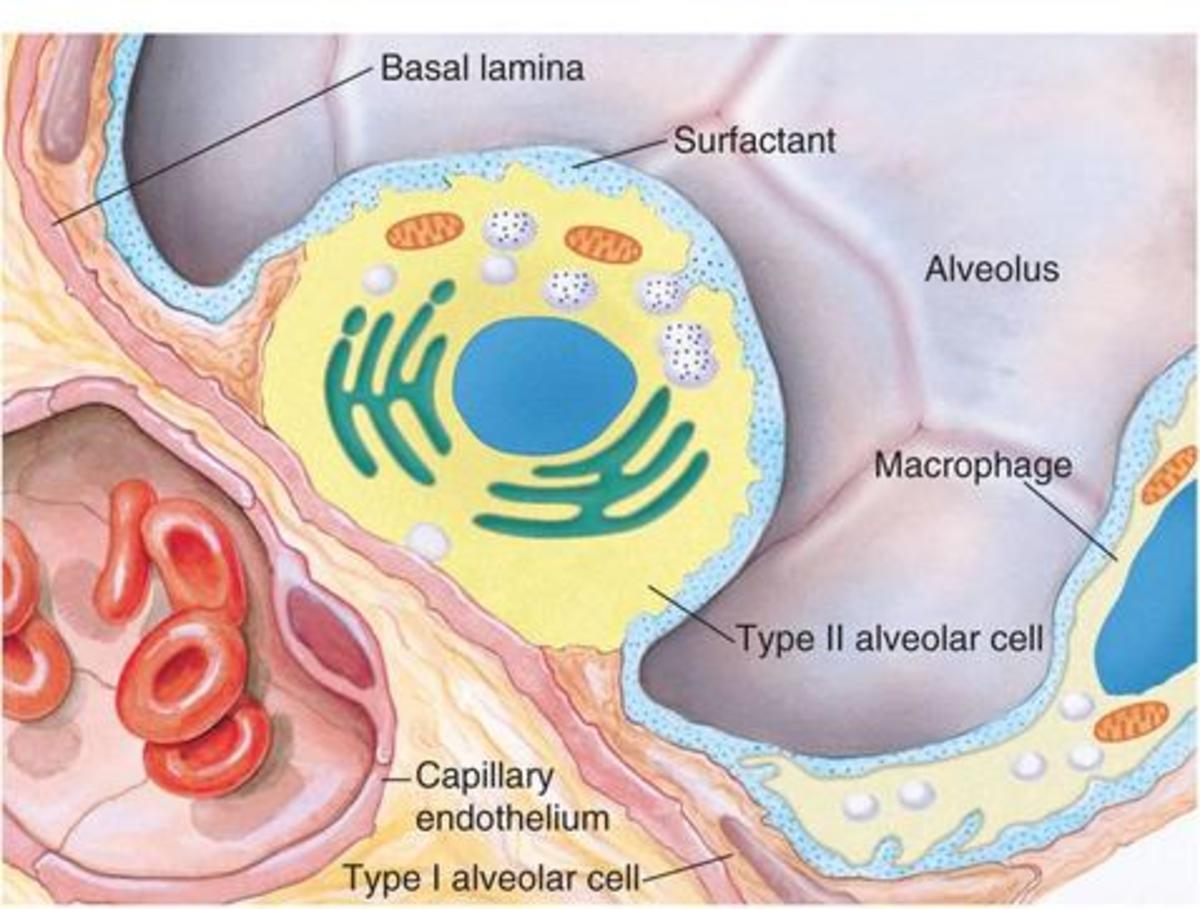
Surfactant: Lowering Pulmonary Surface Tension
Surface tension increases the tendency of the alveoli to collapse. Surfactant decreases the surface tension in the lungs and thus decreases the work of breathing, minimizes collapse and oedema.
- 1
Airway Resistance and Flow Dynamics
A resistance to the inflow and out-flow of air is exerted by the walls of the airways. The impact of airway resistance, the flow dynamics and the factors governing the resistance are discussed here.
- 4
Lung Pressures and Lung Compliance
Airflow between the lungs and the environment occurs via a pressure gradient. This article is on the changes in alveolar and pleural pressure changes in a breathing cycle and the resulting volume changes.
- 3
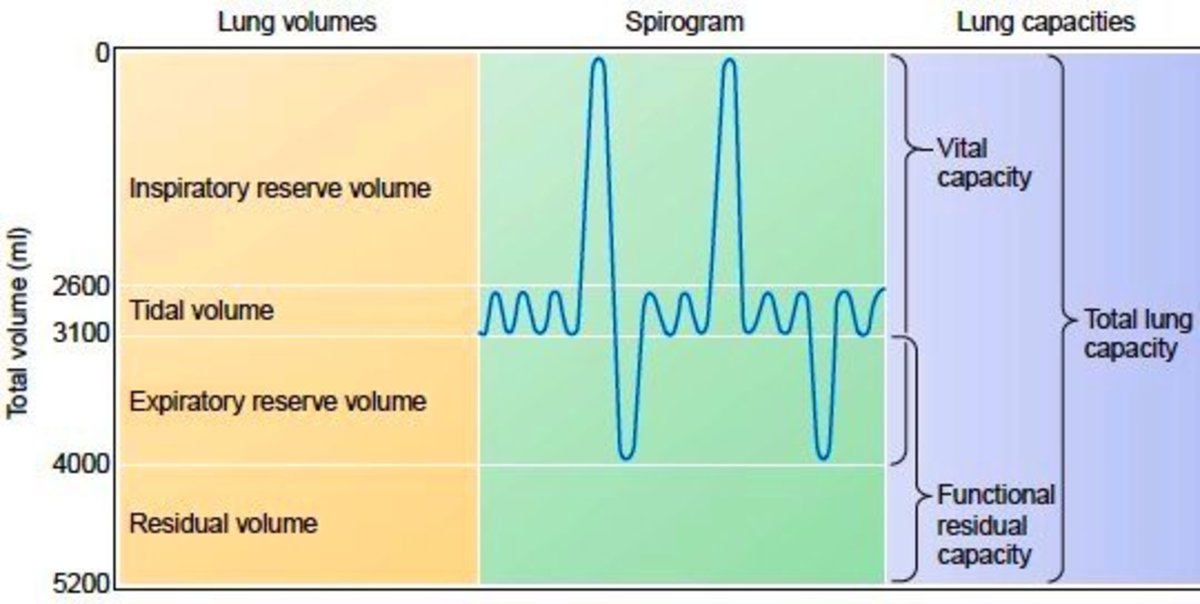
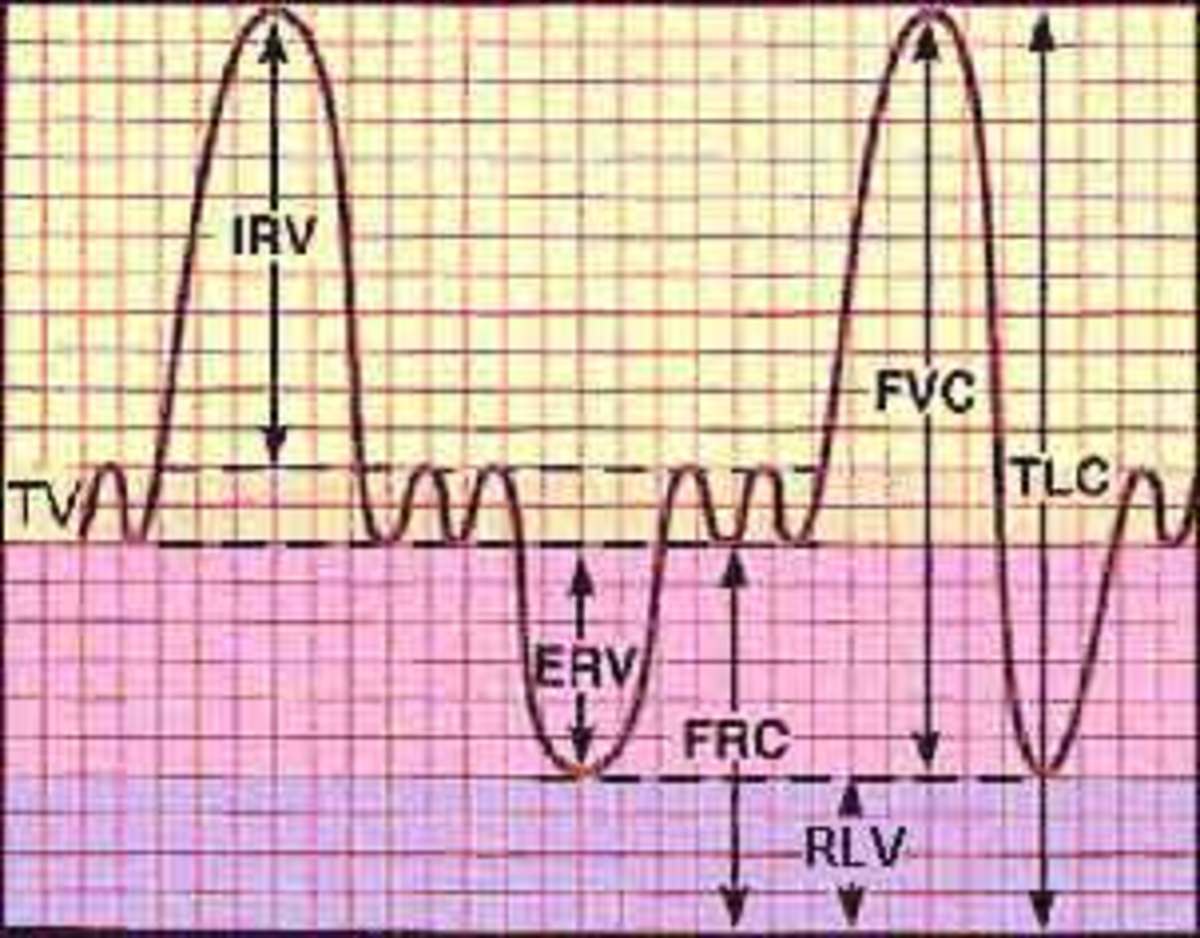
Lung Volumes and Lung Capacities in Health and Respiratory Diseases
Lung volumes and capacities tend to vary with age, sex, ethnicity and built. Alterations in the lung volumes are used to diagnose obstructive and restrictive lung diseases.
- 2
Lung Volumes and Capacities
Breathing (inspiration and expiration) occurs in a cyclical manner due to the movements of the chest wall and the lungs. The resulting changes in pressure, causes changes in lung volumes.
- 0
Pulmonary Mechanics
Bulk flow of air in between the environment and the lungs is an important respiratory function. Coordinated, active movements of the thorax and the diaphragm, result in inspiration and expiration.
- 10
Non-Respiratory Functions of the Respiratory System
In addition to serving the function of respiration, the respiratory system is involved in providing immunity, olfaction, phonation, and as a reservoir and a filter for CVS, among other things.
- 2
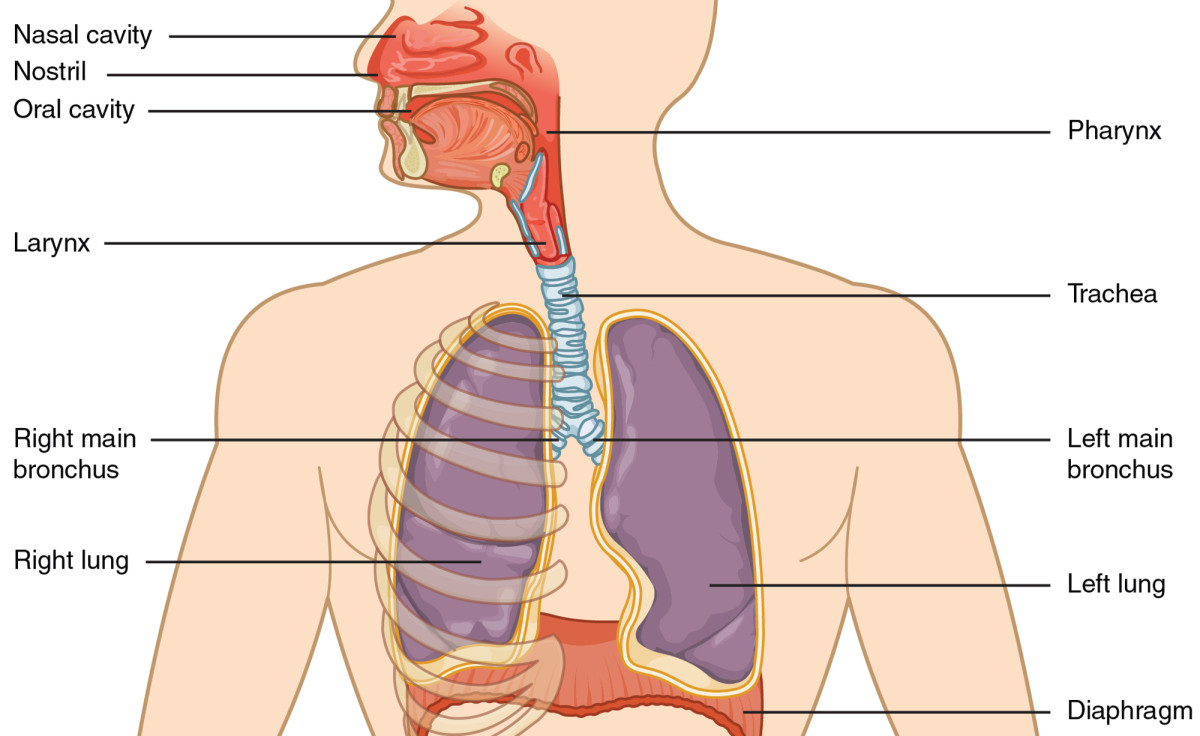
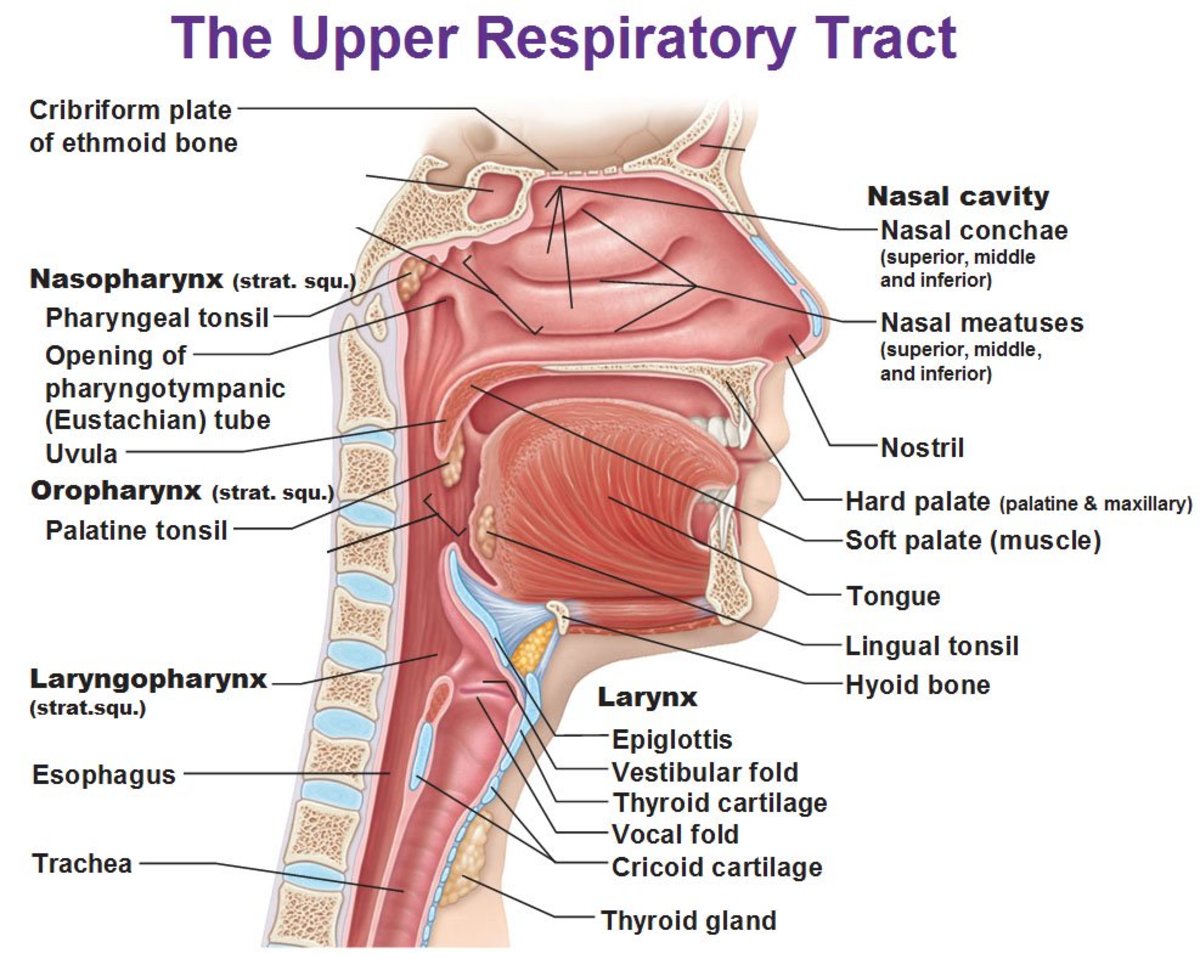
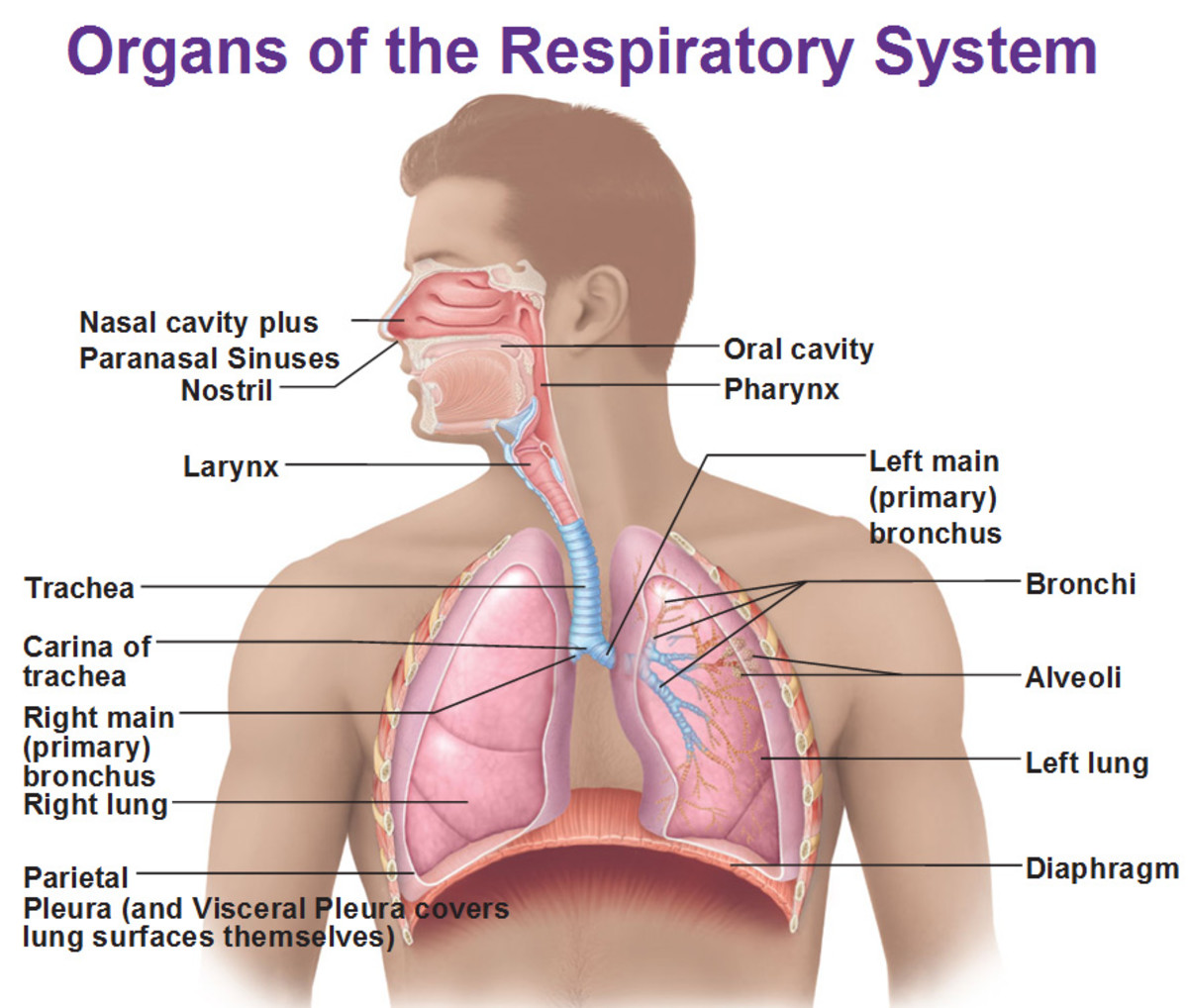
The Respiratory System: Anatomy and Physiology
The human respiratory system is comprised of special organs designed to take in oxygen for the air we breathe and expel carbon monoxide, keeping us alive. Let's take a closer look at these organs and explore respiratory physiology in more detail.