Horses and Their Sense of Vision
How a Horse Sees

The Amazing Vision of Horses
When we look at a horse, one of their most noticeable features is their big eyes, and their long noses. Ancient horses going back 55 million years ago had much shorter noses It is believed that horses noses got long through evolution because while they were grazing and eating, they could see higher and were more likely to see a predator coming.
A horse relies primarily on its vision to protect itself from predators and danger. Horses have the largest eyes of any land mammals. Only seals, whales, and ostrich have larger eyes.
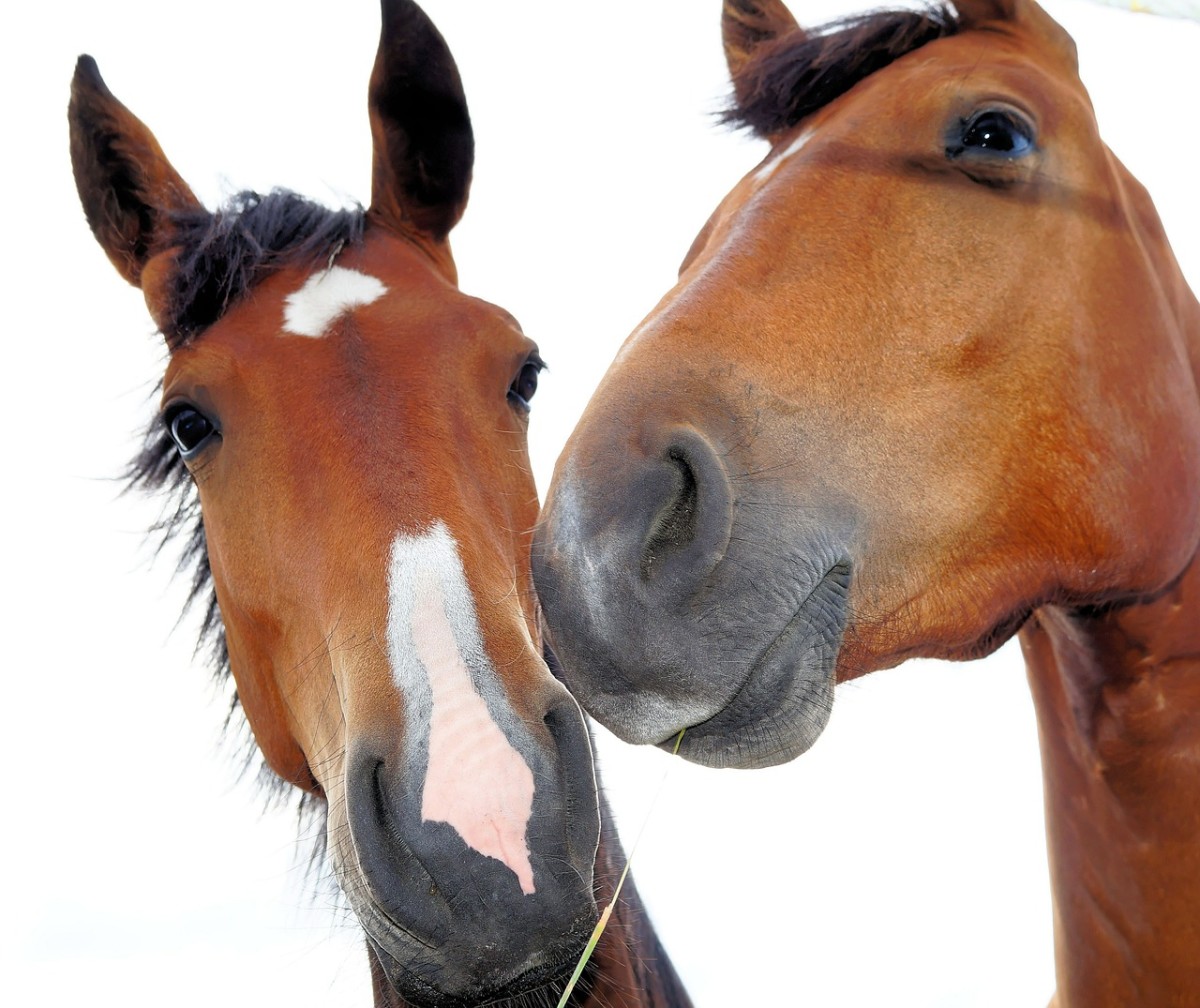
The eyes of a horse are located on the sides of their head, which gives them a panoramic view of what is going on around them.
Horses Have Superior Vision to People

Monocular and Binocular Vision
The large size of a horse's eye, give them a large circular view which allows a horse to see a predator coming upon at a distance and gives the horse enough time to run far away to safety.
Their monocular vision gives them an advantage of detecting animals that may try to sneak up on them or behind them. Monocular vision allows the horse to view what is around them from both sides with either eye. It gives them panoramic vision.
When a horse uses their binocular vision, it is directed down their nose, and the horse's forehead, they have a blind spot. This is how a horse's vision works. When a horse is grazing in an open field, they will be looking at the grass in front of them. A relaxed horse will be using their monocular vision. If the horse sees something that puts them on alert, the animal will raise its head and bring their binocular vision into focus. If the horse sees something from its side vision, the horse will turn and raise their head or whole body to get a better view. When the horse brings their binocular vision into focus, they also get better depth perception, so they know how far away something is. As a horse moves their heads up and down, they narrow their field of vision and get a clearer picture of what is in this narrow area. The horse will tilt its head to get a bigger glimpse of an object.
The features of the horse eye is particularly designed to allow this animal to see all around them with their monocular vision:
- large eyes helps see more of the landscape and capture more light
- curvature of the cornea gives a horse a panoramic view
- horizontal shape of the pupil helps a horse scan the horizon
- angular extent of the retina can detect motion in low lighting
- eyes are high up on their forehead
- elongated horizontal pupil that gives much wider lateral vision than the circular pupil of a person
Monocular vision is not three dimensional, it is flat vision used to identify movements from far away.
When horses use their binocular vision by looking straight ahead with both eyes, they can see in 3-D and also get depth perception.
A horse typically puts its nose down to see something and then lift its head to use their binocular vision. If the horse gets scared from something from behind, the horse will usually jump forward and then spin around to use its binocular vision. The horse can't use both binocular and monocular vision at the same time. It switches from one vision to another by positions of the eyes and movement of their head.
Why Do Horses Need Good Vision?
It used to be thought that horses had poor vision and were shortsighted. In actuality a horse's vision is better than that of a person. A horse relies heavily on their visual information for their survival. With their large retinas, it is believed their relative image magnification is 50% greater than a human.
Horses require large quantities of food to nourish the size of their bodies. To satisfy these needs, wild horses have been observed to spend about 50% to 60% of their time grazing on grass, bushes, etc in open fields, with their heads lowered and their eyes near the ground. This makes these prey animals vulnerable to predators. Horses do not have to worry about threats from birds and other aerial predators, but wolves, lions, snakes will go after horses. Horses will eat throughout the day, with their most active feeding times after dawn and before dusk. A horse's eyesight, therefore, needs to be a kind of early warning system so they can escape danger and also to allow them to see in lower light conditions at night.
Equines see well at night, which helps them flee from nocturnal predators. They can filter a substanial amount of light through their large eyes and they have internal reflectors which amplify the light. Horses can see better at night than people can, but they adjust slower to light changes than we do.
Horses have blind spots where the rider sits, and behind their tail, and under their nose.
Horses Grazing a Relaxing Video to Watch
Can Horses See in Color?
In research studies it is believed that horses have dichromatic vision, which means they can distinguish two main colors. People have trichromatic vision. This gives us the ability to distinguish three main colors. The colors horses do see are less intense than the colors people see.
Leblanc & Bouissou, two researchers, conducted a study in 1981 on maternal recognition of young in horses. Their research showed that mares who were shown, from a distance, their own foal and a different looking foal, were able to recognize their own offspring by recognizing the coat color. When they were looked with foals of similar coat colors, the mares used other sensory responses to identify their offspring.
What a Horse Sees

Horses Can See Different Things from Each Eye
People of course have their eyes in the front of their heads. We have what is called binocular vision. Both of our eyes focus on the same object. The brain combines the two images into one, to make on image. The images that the brain gets from the eyes are slightly different from each other. The brain uses these small differences to work out how far away an object is. This gives us our depth perception, and helps us figure out how fast something is moving towards or away from us.
People who do not have binocular vision have difficulties with depth perception difficulties and with visual measurement for distance.
A horse has both binocular and monocular vision. Equines can look straight ahead and focus on the object with both of their eyes. Horses mostly use monocular vision. They also can look at different things with each of their eyes. With monocular vision they can watch in front of them with one eye and in back of them with the other. This sense is actually a defense mechanism against predators.
Horses are pretty much defenseless creatures. They will fight if there are no choices, but their main defense is to run when there is danger. Their monocular vision allows them to see a predator before it gets closer to the horse and endangers it.
When a horse sees movement using monocular vision, he will usually turn his head to
see with both eyes, switching to monocular vision so that he can focus on the moving
object. Horses cannot use binocular and monocular vision at the same time. When a
horse switches from monocular vision to binocular vision, this causes objects to jump
and distort until he can focus his eyes again
Horses use their left and right eyes individually, and so they can see different things from each of their eyes. When they graze, they have one eye on the grass, and the other on the lookout for
Horses See Better than Humans

Horses Have an Almost 360 degree View Around Them
Predatory animals have their eyes in the front of their head so they can focus on their prey. Prey animals have their eyes on the side of their head, so they can see all around and protect themselves from danger. Horses are prey animals.
Because they can use each eye separately, they can get an almost 360 degree view of their surroundings. Horses have a blind spot in front and behind them. Horses rely on their exceptional ability to see to defend themselves against danger.A horse’s eyes are larger than most other animal’s eyes.
Their eyes can move independently, allowing the horse to see in panoramic vision. Horses can see in color.
The eyes of a horse have more movement receptors than human beings. They can perceive movement from a distance, but can’t see details that are close to them, unless they move their head up and down to get a better look at something.
Horses Eyes

Why Are Horses Eyes So Big?
Scientists have made a correlation between the size of an animal’s eyes and the size of the animal and the speed at which they run. In a study done at the University of Texas, in Austin found that animals with larger eyes usually see better.
If an animal is running fast, they need visual acuity to avoid collisions into things while running fast. The researchers found a very strong correlation between the diameter of an animal’s eye and their top running speed. This association was stronger than body size and eye size.
There of course is a relationship between animal size and eye size, just as an elephant, which is the biggest land animal will have bigger eyes than a mouse. The speed of the animal and body mass combination would explain why the eye of a horse is bigger than the eye of an elephant.
Some Horses Have Blue Eyes

Does Eye Color Affect Vision?
Most horses have brown eyes. The breeds that have a lot of white on their faces like the Appaloosas, Paints, and Pintos will often have blue eyes. The eye color does not affect the vision of the horses.
Horses superior sense of sight, and ability to see separately out of each eye has helped them survive over millions of years, as it gives them the ability to see an approaching predator and flee to safety in enough time. A horse’s vision is one of the five senses that helps protect this animal from the dangers in their environment.
Horse Trivia
view quiz statisticsHorses are Prey Animals

A Horse's Field of Vision Protects Them from Predators
Horses can only see certain colors or hues. They can’t see the difference between yellow, green and gray, but can differentiate blue and gray. They have poor depth perception because they mainly rely on monocular vision. When they use both eyes to see their perception improves by about five times. Horses are sensitive to movements and on windy days horses feel more threatened because more things are moving around. A horse can see fairly well at night too.
Because their eyes are placed on the sides of their heads, a horse has a very wide field of vision, much wider than people do, even though people have better perception than horses.
Horses can see almost 360 degrees except for a blind spot which is located almost where a rider sits on their back. Having a large field of vision provides better defense for prey animals since they can see a predator earlier and gives them more time to run away and escape. Also when horses travel together they can watch each other. Some breeds like English thoroughbreds and trotters have eyes that are placed more towards the corner of their heads and have less binocular vision. Arabians have eyes that are placed further down on their head and have bigger eyes giving them more binocular vision, which helps them determine distance better.
The width of a horse’s head and and body and the size and position of its eyes determine the front and rear vision of the horse. Horses with large wide set eyes can see more ahead and behind than other horses. All horses have blind spots in front and behind.
The horse has a second blind spot. It is about six feet directly behind its tail. They also can’t see under their nose.
Horses Sense of Vision

How Does a Horse's Vision Differ from People?
Horses have a larger visual field than people. A person’s visual field covers about 190 degrees. A horse’s visual field covers almost 360 degrees.
A horse can see things in three dimension, but is restricted to about 70 degrees directly in front of the horse. A person has a three dimensional field of 120 degrees. They have limited depth perception. A horse can’t estimate distances as well as a person.
Horses have depth perception, but it is limited compared to people’s vision.
A horse sees mostly in monocular vision. People use binocular vision (both eyes).
People have a blind spot of about 170 degrees. Horses have a blind spot behind them, approximately where the rider sits, and in front of them under their nose and another blind spot near their tail.
Horses can see at night better than people do. Horses do not have the ability to focus as well as a person can.
The ability of horse to adjust from dark to light is more difficult than for people.
A horse does not see as many colors as people do.
Although horses can see color, it is probably not vivid.
Horses need less light to see than people do, so their vision at dusk and dark works better than a person’s night vision. The structure of a horse’s eyes allows light to reflect on the retina, allowing them to make good use of the light that is available. The disadvantage for a horse is that they may have more difficulty adjusting to changes when going from dark to light.
Horses and Their Senses

Read More in the Series of Horses and Their 5 Senses
- Horses and Their Sense of Hearing
Horses have a superior sense of hearing compared to people. What a horse pays attention to can be seen by the direction their movable ears are pointing towards. This sense helps warn them of predators - Horses Their Ability to Feel and Their Sense of Touc...
Horses use their sense of touch to learn about their environment, to communicate, and to socialize, and as a defense against predators. A horse's sense of touch is more highly developed than peoples. - Horses and Their Sense of Taste
Horses have taste buds just like people do. But a horse's sense of taste can do much more than a human's. There are many similarities & many differences between a horse's sense of taste & a person's. - Horse Communication and Their Five Senses
Horses have been around for millions of years. As social animals they communicate with their five senses and with body language. Horses also use their five senses to protect themselves from predators - Horses and Their Sense of Smell
Horses use their 5 senses to understand their environment. A horse's sense of smell is one of the sharpest, besides a dog's sense of smell. Horses have two olfactory systems that pick up scents.