How to perform dog CPR

A variety of events such as serious illness, trauma, poisoning, severe blood loss or electrocution may cause an animal to stop breathing or go into cardiac arrest. Approximately 10% of animals revived from cardiac arrest exhibit long term survival, and survival is dependent on the initial cause of cardiac arrest and postresuscitation support. Even though this is a low survival rate, remember that all these animals will die without emergency treatment.
Even if an animal is still breathing, artificial respiration may be indicated to restore regular breathing. Signs indicating that artificial respiration may be needed are shallow breathing, blue gums, a glazed, staring expression or collapse. If your pet exhibits these symptoms, have a friend call your veterinarian while you initiate emergency treatment.
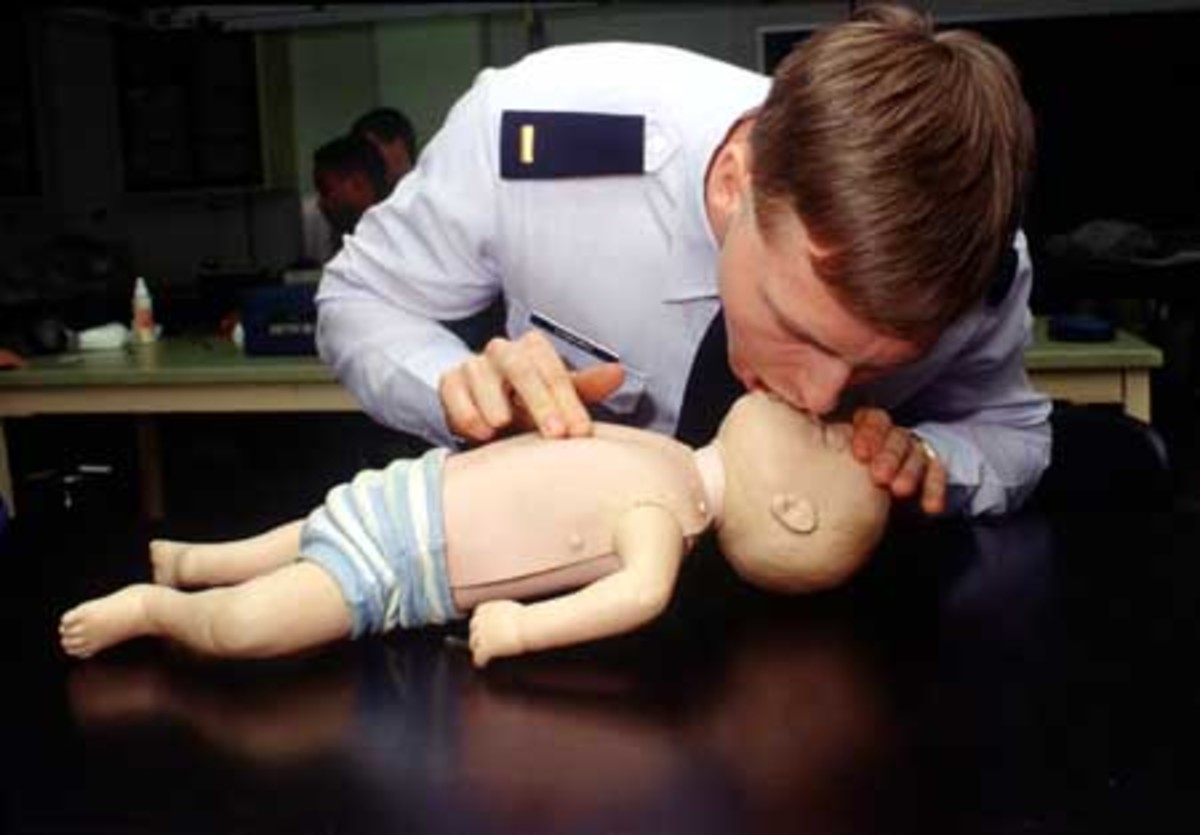
First, you must decide whether your pet's heart is beating by checking for a pulse. With the dog (or cat) laying on its side, place your hand just behind the pet's elbow on the side of the chest, and see if you can feel the heart beating. You can also check for a pulse on the upper middle inner thigh where the femoral artery is close to the skin surface. It would be a good idea to practice locating a pulse on your healthy pet so that in case of emergency, you know where to feel. Next, open the pet's mouth and check for any obstruction to breathing. If there are no obstructions, close the pet's mouth, and hold it shut with your hand. Inhale, place your mouth over the pet's nose (or entire muzzle if the pet is very small), and exhale. Remove your mouth from the nose to allow the chest to deflate. If the pet has a pulse, repeat this breathing procedure 12 to 15 times per minute, while someone drives you and your pet to your veterinarian. Periodically, you should recheck for a pulse. If breathing returns to normal, you can stop the artificial respiration.
If no pulse is detectable, cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) must be initiated immediately. When in doubt, it is better to administer CPR to a heart that has not actually stopped beating, than to not give CPR to a pet in cardiac arrest. CPR tries to simulate the pumping action of the heart, so that blood is forced out of the heart to the tissues.
First, place the animal on its side, preferably on a solid, firm surface. Do not place the animal tilted in a head down position, since this will cause the abdominal organs to fall toward the diaphragm, and decrease the effectiveness of CPR. A sharp thump to the chest may look good in the movies, but rarely will it cause a stopped heart to resume beating, and may actually result in damage to the heart. To initiate CPR, place the heel of one hand just behind the elbow on the side of the chest (where you checked for a pulse), and place your other hand on top of that hand. You should press firmly and quickly down on the chest approximately 60 to 80 times per minute.
Artificial respiration must also be carried out in time with CPR. Ideally, one breath should be given for every 5 chest compressions (about one per 5 seconds). One person performs CPR, while a second person does artificial respiration. However, if you are alone, one breath every 7 to 8 seconds can be given. If you have lots of help available, abdominal compression alternating with chest compressions helps improve blood return to the heart. The third person presses down on the side of the abdomen in between every heart compression. Periodically, one of your helpers should check for the return of a pulse while CPR is continued. If a pulse returns, CPR can be stopped, and the animal taken to your veterinarian for treatment and monitoring. If no pulse is still detected, CPR should be continued while en route to your veterinarian.
Summary
1. Check for breathing and a pulse. If your pet is not breathing, follow the following ABC's.
2. Airway: Check nose, mouth and throat for obstructions.
3. Breathe: Close your pet's mouth, place your mouth over the nose, and breathe into your pet.
4. CPR: Check for a pulse again. If there is no pulse, start chest compressions at a rate of 60 to 80 per minute. Give one breath for every 5 to 8 chest compressions. Get your pet to your veterinarian.