Digital Photography Lexicon
The Reason For Digital Camera Lexicon
Camera terminology can be complex and confusing, even to photographers. The more you are around digital cameras, the more you hear these terms. Below is a short list of the most common terms that refer to cameras or camera lenses.
The word, lexicon, intrigues me. It means "a wordbook or dictionary." While this is not truly a book or dictionary, it also can mean a collection of words related to a specific subject. I have been looking for a place to use it, and this seemed perfect. A bit of poetic license.
Aperture
Glossary of Digital Photography
Aberration - Basically, aberration is anything in the image that should not be there. Usually, it is the result of a a defect in a camera lens or lens system, due to flaws in design, material, or construction, that can distort the image. Examples include barrel distortion or pincushioning. These aberrations can ordinarily be corrected in post processing with software, such as Photoshop.
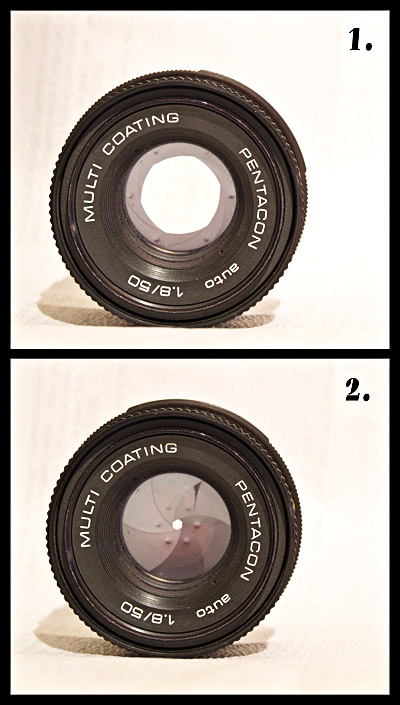
Aperture - Aperture is the size of the lens opening that controls the amount of light that is allowed to hit the image sensor. It is one of the elements that affects the exposure of the image. Aperture is also called f-stop. Smaller numbers indicate wider lens openings, and larger numbers refer to smaller openings. Example: f/2.8 is a small number, but it refers to one of the widest apertures, and f/22 is a large number that refers to a very small lens opening.
The larger the aperture (ie f/2.8) the less depth of field. Smaller apertures give images that have more of the image in focus.
Artifacts - These are imperfections in a digital image.They look like tiny polygonal shapes, and they are the caused by the optics of the lens, the way the sensor receives the image information, or the way the camera processes the image in its compression algorithm.
Barrel Distortion - This is a lens issue. It is the spherical appearance of a photograph. When you view the image, there is a curve where it should be straight. The most obvious example is done purposely when using a Fish-eye lens. However, when barrel distortion is mentioned in the review of a lens, it is usually in a negative connotation.
Chromatic Aberration - Chromatic aberration shows up as a kind of fringe of color where the there is a change in color inside your images. For instance, there may be a fringe of red around a purple flower. It is usually present where there is high levels of contrast in the image.
Digital Cameras With Wide Aperture
Depth of Field - The depth of field refers to that plane in the image that is in focus. This is more obvious when there is a shallow depth of field. For instance, when a portrait is taken, the photographer will want to have the subject's face in good focus, but the background will be blurred. This is the result of using a lens with a large aperture, such as f/2.8. A smaller aperture, such as f/16, produces a much broader (or deeper) focal plane resulting in more of the image being in focus.
Depth of Field

Digital Zoom - Digital zoom is a simulated zoom effect that is available on compact cameras to get more distance, or focal length, from the lens. The camera processes the image by enlarging the pixel size in the image. It may result in a photo that can not be printed at normal size without deterioration of the image because of the lower resolution of the image.
Dynamic Range - Dynamic range refers to the range of color tones that a camera is capable of processing at any given time. The camera sensor is not able to "see" as much range as the human eye can see, resulting in some images having areas that are either totally black or totally white, without any color at all. The term also refers to the light sensitivity of a sensor. There are sensors that have more dynamic range than others, resulting in a much more pleasing image.
Exposure - Exposure refers to the amount of light that is allowed to hit the camera sensor. It determines the lightness or darkness of the photo. It too much light is allowed to strike the sensor, the image is "over-exposed." Conversely, if an image is "under-exposed," not enough light was able to reach the sensor, making the photo too dark.
Focal Length - Focal length refers to how much magnification there is in a lens. A short focal length "sees" more of the area in front of the camera. Short focal lengths are called "wide-angle". A short focal length lens will be anywhere from about 18mm to 35mm.
Long focal length lenses magnify the scene. They are also know as telephoto lenses. A telephoto lens can be a medium telephoto lens which range from 50mm to 200mm. Telephoto lenses will be any length more than 200mm.
Prime lenses have a single focal length and can be wide angle or telephoto in length. Zoom lenses have variable focal lengths.
Image Stabilization (IS) - Image stabilization is a process whereby the lens or the camera compensate for movement of the camera when a photograph is being taken. The process uses gyroscopic sensors to detect the tiny movements of a camera and make adjustments by using the built-in camera or lens software. The result is less blur in the photo. IS can be built into either the camera or the lens.
ISO (Light Sensitivity) - The ISO rating is an indication of the light sensitivity in a camera. When the ISO is increased, the amount of light necessary to correctly expose an image is reduced. Therefore, a camera set to ISO 100 needs much more light to correctly expose an image than a camera set to ISO 800.
Raising the ISO can be very effective when taking pictures in areas where there is not enough light to get a normal picture. The trade-off is image noise. Raising the ISO usually raises the amount of image noise (noise is the little grainy dots you normally see in a newspaper photo).
JPEG (Joint Pictures Expert Group) - JPEG is a common file format for photographs. When a camera is set to take pictures in JPEG format, the camera uses a computer algorithm to compress the image. Compression can be very little to very severe, depending upon the image size that is chosen in the camera menu. Every digital camera has the option to process images in the JPEG format. These files can be read by every software program that processes digital images.



Macro - Macro is also know as close-up photography. It refers to a one-to-one or higher magnification of the image subject. It usually requires a special lens or camera setting to optimize the optical elements for this type of photograph. Macro lenses or settings on the camera will allow the camera to focus at a much closer range than when set at normal settings.
Megapixel - Megapixel is 1,000,000 (one milleion) pixels. Each pixel is a photosite, or photodiode, or light receptor. The pixels interpret the light that enters the camera through the lens to create the image. The size of a digital camera sensor is given in megapixels. People often think that the number of megapixels in a camera sensor determines the quality of the image that sensor produces. This is not necessarily true. It is possible that a 10 megapixel camera can have better image quality than a camera with twice the megapixels.
Noise - Camera noise looks like grain on a photograph. Noise is actually image artifacts that are variations in color. High amounts of noise make the photo less pleasing to the eye and therefore less desirable. Conditions that produce high levels of noise may be smaller sensors with a high number of megapixels which is common in many compact digital cameras, or another condition that results in high noise is increasing the ISO (in any camra) to extreme levels.
Perspective - This refers to the size of objects as they retreat into the image. For instance, when a road converges, getting smaller as it goes deeper into the image, this is perspective.
RAW - RAW is a picture format, or type of image capture that results in the retention of the most image information. There is no algorithym for compression when a camera is set to capture images in RAW. The resulting image is usually not as pleasing to the eye when it is downloaded from the camera as JPEG images because there is no camera processing (and no loss of pixels). RAW is available on Digital SLR cameras and some high end digital compacts. Special image processing software is necessary to open and process RAW images. Photoshop is the software of choice for many professionals.
Resolution - When referring to a digital image, resolution is the number of pixels in width and height. For instance the resolution of a photograph that is 640 x 480 pixels can be printed in a 4" x 3" photograph at 180 pixels per inch. The quality of such a picture would be less than the same picture with a resolution of 1200 x 900 pixels printed at 300 pixels per inch. The end result is the same size but better quality.
Shutter Speed - Shutter speed is just about what you would expect. It is the speed at which the shutter opens and closes. Fast shutter speeds let in less light than long shutter speeds. The more available light there is when a photograph is taken, the faster the shutter speed necessary to properly expose the image. Fast shutter speeds are necessary to "freeze" action such as in sports. Slower shutter speeds are used for photos taken in low light settings or to accomplish certain effects such as silky smooth water in a waterfall.
White Balance - White balance is a calibration of color temperature in degrees Kelvin. Most digital cameras have some auto settings for white balance to compensate for conditions like sunlight, tungsten lighting, fluorescent lighting, or shade which changes the Kelvin temperature in the image. Or a camera can be set to Auto White Balance, a setting that lets the camera interpret the light temperature. If the camera gets it wrong, it can be corrected with post processing software.
White Balance Correction

More Useful Digital Camera Information
- Canon EOS Lens Features (Vocabulary) |
It is sometimes confusing to try to figure out what the name of a lens means. On this page is a breakdown of lens nomenclature (lenses for Dummies). - Digital Photography Glossary of Terms
Digital photography glossary of terms.









