Electric bikes vs Motorcycles


If you haven't heard yet, electric bikes are here, they are basically battery powered, and rechargeable bikes that are also known as e-bikes or booster bikes. They work both electronically while riding, meaning they can ride on their own without the rider pedaling as well, they work with the help of the rider as a regular bike would. How fast they go is dependent on the laws of your country, however, they generally go up to 32 km/hr.
Motorcycles on the other hand are a lot more powerful. They work on fuel and are not rechargeable but go a lot faster than the electric bike. So, which one is right for you and how do they compare next to each other.
Let's break down the mechanics of an electric bike
So, when we hear the term electric bike it is almost elf explanatory as to how it works, but, let's break it down a little bit further.
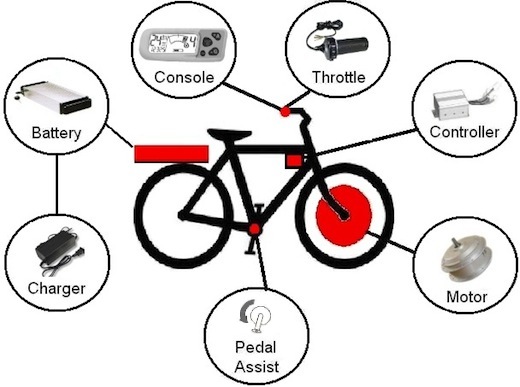
The above image gives a general and concise breakdown as to what makes a bike electric. Beginning with the motor. There are different types of motors and different ways to place them, which will make each type of electric bike perform differently.
- Front wheel drive
The motor is mounted to the front wheel. The disadvantage to this is the weight on the front of the bicycle throwing off the balance of the bicycle and causing an unpleasant and uneven ride, especially on uneven roads. On the plus side if the battery is mounted at the back of the bike the weight of the bike would then be more evenly distributed making the bike more functional. This also make it less prone to sudden acceleration.
- The rear wheel drive
The motor is mounted to the rear wheel. This mount type can cause stress on the rear wheels. Also, it can be prone to sudden bouts of acceleration. However, the rear wheel drive has good balance and traction in wet conditions, and because of the rear dive propulsion is great on off road rides as well.
- Chain drive
Also known as the mid drive, shaft drive, motorized bottom drive or crank drive. In this case the motor is mounted near the crank and powers the bike through the pedals.
- Friction Drive
This is one of the first types of motor placements used on the electric bike design, because of the many functional disadvantages of this motor placement. The shaft extended from the motor to the front or rear wheel of the bicycle, therefore when the shaft turned the bike moved forward. This design though it has since been superseded by many other more functional options can still be found and is an option if you are on a budget and not looking for speed or a lot of distance from your electric bike.

The Battery
This is where the electric bike gets it's power from, there are different types, with different performances, characteristics and costs. When choosing the right bike for you consider the voltage, capacity and type. Ask yourself also, does it charge quickly?, does it recharge when gong downhill?, What .type of maintenance will it require? and Does it come with any theft prevention mechanisms?

The controller
This is the brain of the electronic bike, it is connected to all the electronic parts of the electronic bike. It takes inputs from the electronic components of the bike and determine what the signal back should be. It is essentially connected to the pedal assist, the battery, the motor and the throttle.
The Throttle and Propulsion
With an electric bike, there is no need to pedal as they are designed to alter the power that the rider applies. Therefore the same amount of force required to propel a regular bike forward is not required of an electric bike. However, if you desire to move at a much faster pace, applying just a little more effort to the pedal will do so, However, if you do not desire to go very fast, the bike will move forward with no help required. The controller will determine the amount of power being sent to the motor simply by how much you move the trhottle. The throttle will either be a twist grip or a thumb press.
So, as you can see an electric bike is very cool alternative for those looking for something with more speed, but not willing to go the route of a motorcycle. Another fun perk of owning one of these is that it takes no license, registration or insurance is needed for this new inventive means of transportation. There are many different types as you can see in the video below, it's just about finding one that is the right fit for you. Now how does it stack up to the motorcycle, let's find out!
Are you interested in riding an electric bike?
The majestic motorcycle!

Crash course in motorcycles!
Motorcycles are motorized vehicles that are capable of transporting one or two people and generally have two wheels. The overall structure of a motorcycle is simple as well as the overall function of it.
Motorcycles have gasoline engines which converts the motion of the pistons into rotary motion, meanwhile the transmission system, transmits the motion to the back wheel. As the back wheel turns, it propels the motorcycle forward. In order to steer a motorcycle, use the handle bars to turn the front wheel, leaning the bike in the desired direction. Hand levers operate the clutch and the front brake while foot pedals change gears and control the rear brake.









