Transmission Control Module

As you already know from my previous hubs there are separate controllers for different areas in a vehicle. In this hub i'll try to explain the basics of how the auto-transmission works (not gearing stuff ... just the electronic aspects).
If you haven't gone through my previous articles then click the links below...
Understanding Car Computers, Sensors and Actuators
Types of Electronic Controllers in a Vehicle
If you just want to know about the transmission control module and the sensors / actuators involved then keep reading.
Some cars have a single ECU which controls both the transmission and the engine. Others, have specific transmission control modules.
Similar to the engine control module the main responsibility of this controller is to get information from sensors and run certain actuators, which will engage gears etc. In case of any errors arising the check engine light will light up on your dashboard.
Following the format of my previous hubs this hub discusses the where and why sensors are placed in certain positions and some insight as to how or what the sensors sense. If you are a DIY person then you could even open up the sensors yourself and clean them in order to obtain optimum signals.

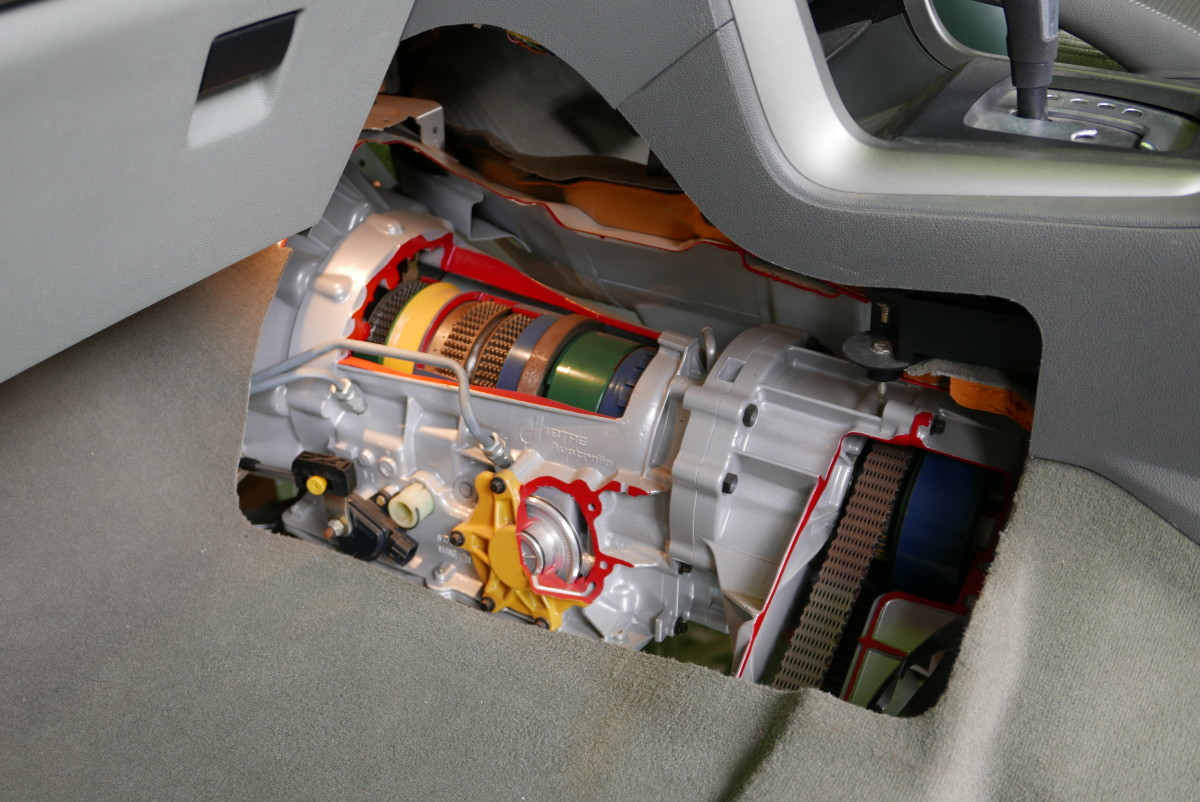
The location of the transmission control module (TCM) varies with every car and model therefore i cannot give you a fixed location for the TCM. In some instances the TCM is built-in to the ECU where the ECU will handle both the engine and the transmission.
The Sensors and Switches Linked with Transmission control module.
- Valve Body (Solenoids)
- Throttle Position Sensor (TPS)
- Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor (ECT)
- Vehicle Speed Sensor (VSS)
- Shift Solenoids
- Torque Converter Clutch Solenoid
- Gear Lever Switch
- Brake Pedal Switch
- Overdrive Switch
- Economy / Power / Sport - Switch
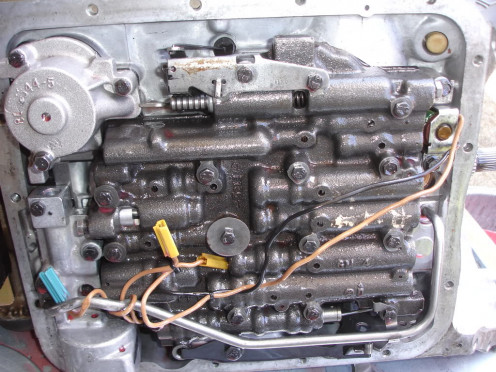
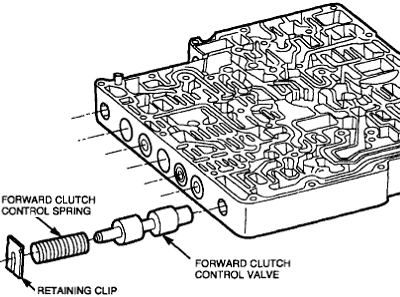
1. Valve Body
The valve body is basically a metal housing of several valves. These valves open and close according to the pressure of the automatic transmission fluid, as well as signals from the Transmission Control Module.
The next few sensors are already covered in my previous hub therefore i will not go into these.
2. Throttle Position Sensor
3. Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor
4. Vehicle Speed Sensor
For further details about these sensors check out my previous hub: Engine Control Module
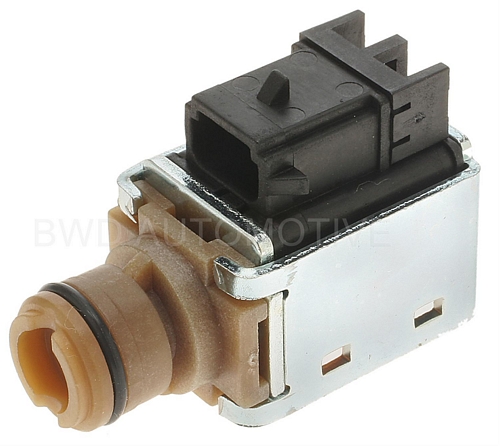

5. Shift Solenoids
the shift solenoids are used to control the flow of hydraulic fluid for shifting. Depending on the type of solenoid and valvebody it may either permit or block the flow of fluid when energized. These solenoids determine the correct upshift and downshift points for all driving conditions.
the transmission fluid enters the plastic circular end and exits through the rectangular edge (where the plastic meets the metal plate). There is a plunger within the metal housing which is pushed back with the pressure of the fluid which lets the TCM know the current pressure.
Located on the Valve body, these solenoids can malfunction mainly due to residue build up or metal shavings in the internal channel. You can use WD-40 or transmission fluid and compressed air to check if the paths are clear. If the problem lies in the plunger then you will have to replace the unit.

6. Torque Converter Clutch Solenoid
The torque converter clutch solenoid (TCCS)works in the same principle as the shift solenoids but this controls the fluid entering and exiting the torque converter clutch.
The TCCS is also located on the Valve body.
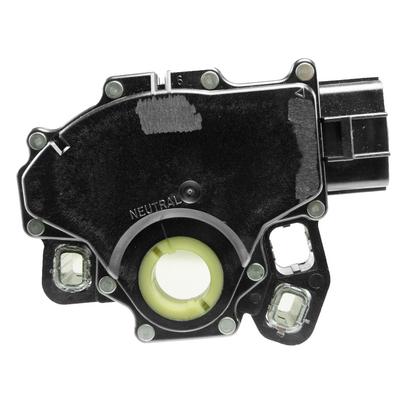


7. Gear Lever Switch
This is quite an obvious one. The unit is either linked mechanically as shown in the first picture or in the case of mercedes benz the gear lever switch is a complete unit.
Simple signals go from the lever to the Transmission control module which tells the TCM what mode to drive in.
A very simple way to detect errors with the gear switch :
Put the car in drive or reverse and the car is not moving then check the indicator on the dashboard to see if the correct lights are displayed. i.e. if you put in drive yet the dashboard shows neutral then know there is a problem with your switch.
If you are adventurous enough then open up the switch and use electrical contact cleaner on the points inside the gear switch.
Car Purchasing Tip :
Start the car, press the brake pedal and shift from neutral to Drive while noting the intensity of the jerk you feel. Move back into neutral and go into reverse. The larger the jerk the faster you should get away from that car, unless you love getting your gearbox replaced.
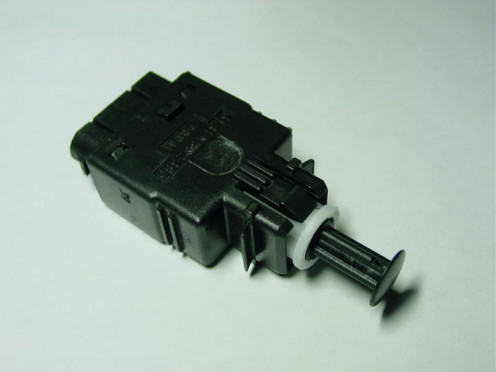
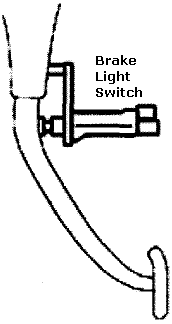
8. Brake Pedal Switch
The brake pedal switch is a simple on/off switch which is located either in front of or behind the brake pedal. This switch sends signals to the computer when depressed or released.
When the pedal is pressed the switch turns on therefore the brake lights turn on. The transmission converter clutch also disengages when the brakes are applied.
When the pedal is released the switch turns off and the brake lights turn off and the transmission converter clutch engages once again.
If you start your car and cannot shift into any gear while pressing the brake pedal then you may have a faulty switch.
If no components are broken inside then you can use electrical contact cleaner to fix the switch.


The last two switches are quite similar in function. I will be adding their information soon.
9. Overdrive Switch
10. Economy / Power / Sport Switch