Automobile Power Transmission System
Clutches
In cars with manual transmissions, the clutch serves as a vital link between the engine and the transmission. It's what allows you to smoothly shift gears, start from a stop, or stop the car while the engine is still running. When you press the clutch pedal, it disengages the engine from the transmission, letting the engine run independently. The most common type of clutch in passenger cars is the single dry-plate friction clutch. It consists of a disk sandwiched between the flywheel and the pressure plate. By gradually applying pressure, power is smoothly transmitted from the engine to the transmission.
The invention of the hydraulic coupling, or "fluid flywheel," paved the way for fully automatic transmissions. Unlike traditional clutches, which use friction disks, hydraulic couplings transfer power through fluid. Essentially, it operates like two fans facing each other—air from one fan spins the other, similar to how oil moves between the driving and driven members in a fluid flywheel, resulting in minimal slippage.
Manual Transmission
The manual transmission, also known as the gearbox, provides several forward speeds and reverse. In the United States, most passenger cars come with 3-speed transmissions, with 4-speeds available as an option. Each gear provides different ratios between the engine and the propeller shaft, affecting torque and speed. Synchronous meshing allows smooth shifting between gears without gear clash, making it easy for drivers of all skill levels to operate.
Automatic Transmissions
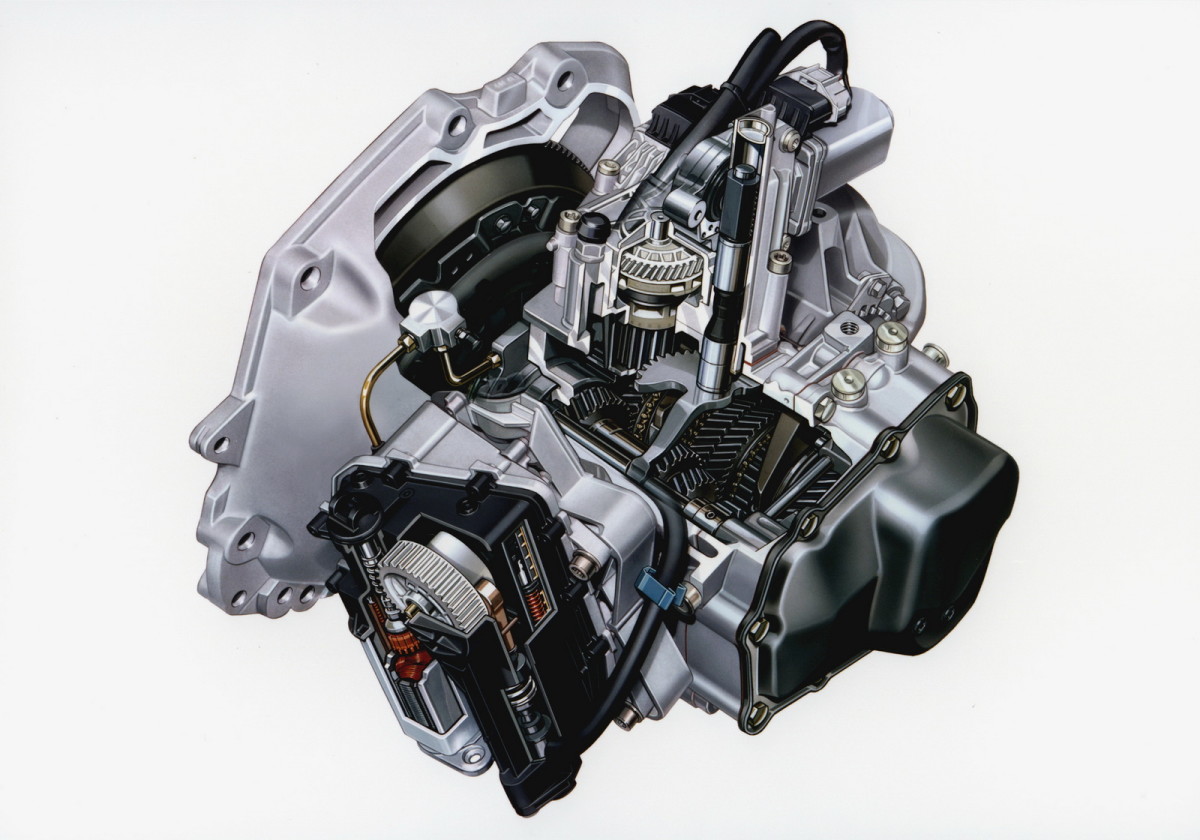
Fully automatic transmissions have undergone significant advancements since their introduction in 1939, evolving into a cornerstone feature of American automobiles. Offering unparalleled convenience, they have revolutionized the driving experience by simplifying gear shifting for drivers. Unlike manual transmissions where drivers manually shift gears using a clutch and gear stick, automatic transmissions automate this process, allowing drivers to focus solely on acceleration and braking.
There are two primary types of fully automatic transmissions: step-ratio shifter transmissions and hydraulic torque converter transmissions, each with its unique mechanisms and advantages.
Step-ratio shifter transmissions employ sophisticated governors to manage gear changes. These governors monitor various factors such as throttle position and vehicle speed, determining the optimal time to shift gears. When a gear change is required, the governors activate hydraulic mechanisms to lock specific sections of a planetary-gear set, seamlessly transitioning between gears. This mechanism ensures smooth shifting without any interruption in power delivery, enhancing both performance and comfort for the driver.
On the other hand, hydraulic torque converter transmissions utilize fluid dynamics to regulate torque delivery to the drive shaft. At the heart of this system is the torque converter, which functions similarly to a fluid coupling but incorporates additional components to enhance torque multiplication and facilitate gear changes. As the engine generates torque, the torque converter transmits this power through a fluid medium to the drive shaft, continuously adjusting the torque output to match driving conditions. This allows for a seamless range of gear ratios, adapting effortlessly to varying speeds and load demands.
Furthermore, hydraulic torque converter transmissions offer the added benefit of providing reverse gear, a crucial feature for maneuvering and parking. By harnessing the principles of fluid dynamics, these transmissions ensure smooth and efficient power delivery in both forward and reverse directions, enhancing overall drivability and versatility.
Overall, fully automatic transmissions represent a pinnacle of automotive engineering, offering unmatched convenience, performance, and reliability. Whether utilizing step-ratio shifter or hydraulic torque converter technology, these transmissions exemplify innovation in simplifying the driving experience while delivering superior performance on the road.
Propeller Shaft and Universal Joints
The propeller shaft carries power from the transmission to the rear axles. It may be exposed or enclosed in a torque tube. Universal joints accommodate the shaft's angular motion, allowing for changes in length. The double yoke and cross joint is commonly used, efficiently transmitting power through various angles. A slip joint compensates for changes in shaft length.
Final Drive and Differential
The final drive transfers power from the propeller shaft to the rear axles. It consists of a ring-gear-and-pinion set. Differential gears ensure equal power distribution to the rear wheels, crucial for turning corners smoothly. Limited-slip differentials, offered as optional equipment, enhance traction by directing power to the wheel with the most grip.
Rear Axle
Power from the differential is sent to the wheels through the rear axles. Most cars use semifloating axles, which distribute weight and bending stresses along the axle, providing stability and durability.
This content is accurate and true to the best of the author’s knowledge and is not meant to substitute for formal and individualized advice from a qualified professional.
© 2010 Sam Crow








