Effective Communication: Active Listening Skills
Learn to Become an Active Listener
I hear you...
Okay, so maybe you did hear what the speaker just said, but is that the same as listening? Is it even close to being active listening?
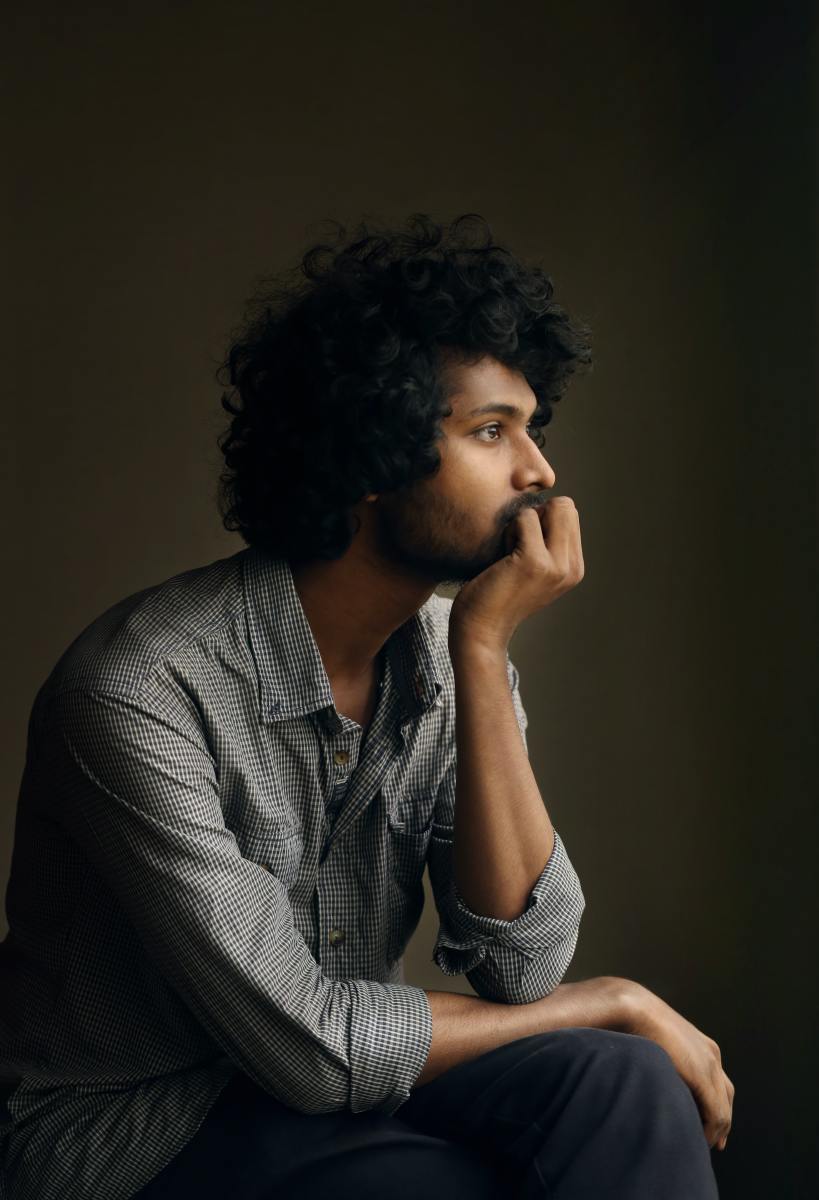
Active listening takes place when you, as the audience or "hear-ee" are paying attention to the speaker not only with your ears but with your eyes and your mind. Active listening requires that you have nothing else on your mind when the speaker is speaking. This is necessary for you to be an effective communicator because there are at least two sides to a conversation.
"Hearing" is more like being conscious that someone is speaking to you, but you are only partially engaged in what they are saying. You may or may not receive the message as it was intended by the speaker -- and this can lead to misunderstandings or hurt feelings that never had to happen.
Active listening is effective listening and an essential component in being an effective communicator.
How to Resolve Conflict and Create Connections
Understand Basic Body Language
Active listening involves some basic body language cues on your part that show the speaker you are open to them and to the message. You do this by facing the speaker squarely and assuming what is considered to be an "open" posture -- arms at rest, maintaining eye contact with the speaker and leaning slightly toward the speaker if the situation is appropriate.
Consider how you would feel about talking to someone who is in the open posture versus someone whose arms are crossed or someone who is busy looking at paperwork or avoiding eye contact with you. Wouldn't those body language signals make you feel like you were being ignored or that your message wasn't considered to be important?
Occasionally nodding your head or making a facial expression in response to something the speaker has said are also nuances of body language that indicate to the speaker you are engaged as a listener.
Six Effective LISTENing Skills
Three Basic Listening Modes
Just as there are different types of speakers, there are different modes of listening. The three modes are competitive/combative listening; passive/attentive listening and active/reflective listening.*
Competitive/Combative Listening occurs when you are more interested in promoting your own position or thoughts than in hearing what the speaker has to say. This is the listening mode that many people are in when in an argument with someone or trying to prove a point. Neither person is truly hearing what the other has to say because each person is instead intent on persuading or convincing the other.
Passive/Attentive Listening occurs when a person is attentively listening to what the other person has to say, but because the listener assumes he understands the spoken message, he does nothing to verify that understanding. This is considered to be passive listening.
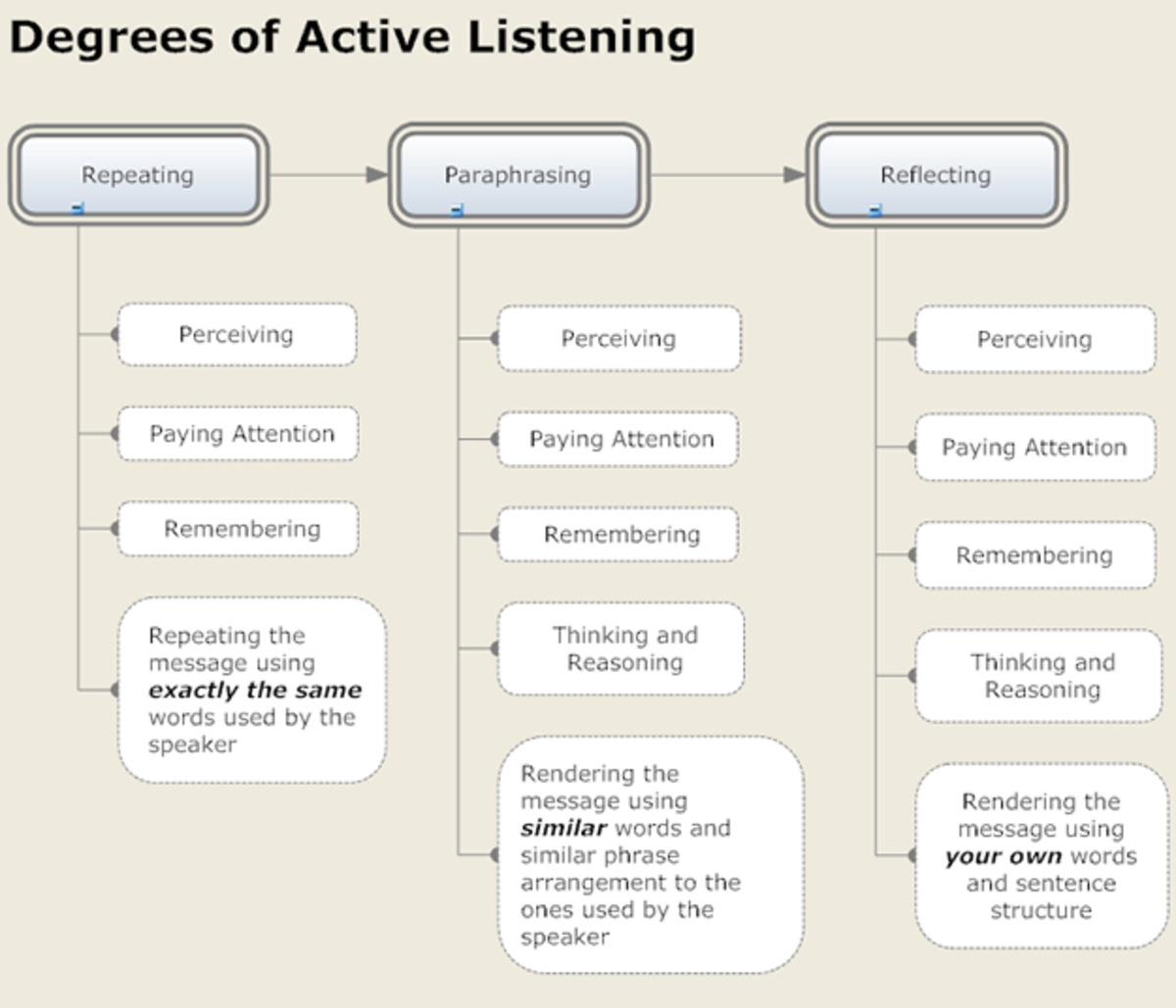
Active/Reflective Listening occurs when the listener is attentively listening to the speaker, but also monitoring the speaker's feelings, thoughts and intentions behind the message. To ensure the listener has understood the message accurately, the listener restates to the speaker what he understood the message to be, so that any misunderstanding or misinterpretation of the intended message can be clarified at once.
Of these three types of listening modes, the one that leads to the most effective communication is that of active/reflective listening.
*Larry Alan Nadig, Ph.D., Clinical Psychologist, http://www.drnadig.com/listening.htm
Reflective Listening Techniques
Clarifying
| To clear up an unclear information, to obtain more information
|
|---|---|
Summarizing
| Re-state key facts and ideas as you heard them
|
Perception Checking
| Ensuring any assumptions you made are correct
|
Paraphrasing
| Re-state the message, only briefly
|
Clarifying/Summarizing/Perception Checking
The "reflective" listener will use one of four methods to ensure he has understood the message as it was intended by the speaker. Clarifying, summarizing, perception checking and paraphrasing are the four methods that are used by an active, reflective listener.
Using at least one of these methods to make certain you understand the intended message is an important part of effective communication. It's something you should want to do and it's something that will show the person who's been speaking that you value what they've said.
These reflective techniques are used by the listener at the completion of the topic, or perhaps once or twice through an extended or complicated conversation.