How To Use Marketing Effectively-The 4 Step Process and 8 Stages of Product Introduction

What Is Marketing?
The term “marketing” refers to a form of communication from a producer or seller to a consumer audience. It is a type of management process that involves portraying an idea or concept in the aim of creating value for the consumer, enough for them to want to purchase this good. It is based on learning to understand the needs and wants of consumers and providing them with these products and services profitably. Creating a marketing strategy focusses a company’s attention on a particular target market thereby eliminating any unnecessary operating expenses that do not contribute to the growth of the company. This results in the company being efficient and profitable. Having this focused marketing strategy ensures a better chance of customer satisfaction, resulting in the gaining of market power (by the increasing number of consumers) and a positive reputation. It further promotes the innovation pursued by the company and the quality of the products and services being provided as these address the direct need of the consumers.
A company has to discover a way in which to fulfil the needs of customers through creation of marketing processes that aims at getting the desired products of sufficient quantity at the best possible time in the best possible place in the most efficient and profitable way for the company. The four steps involved in the marketing process are:

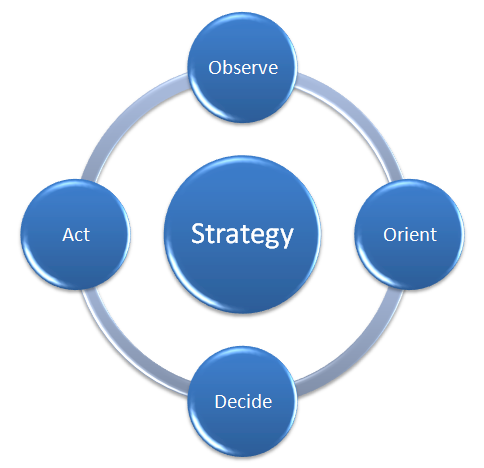
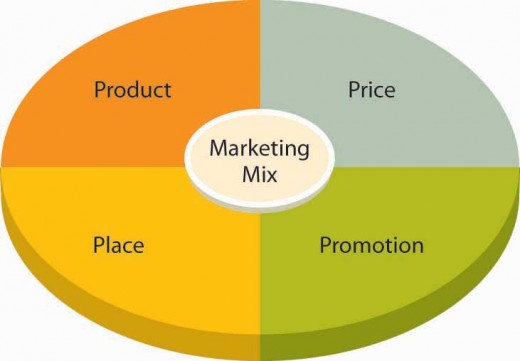
4 Steps of The Marketing Process
1.) The situational analysis
A firm has to identify problems and opportunities in which it can provide a much needed service or good to consumers. For a firm to do this successfully and efficiently it has to thoroughly analyse its external and internal environments and factors that affect this in the past, present and future as well as its own resources and capabilities for example a SWOT(strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats) analysis could be used in this process.
2.) The marketing strategy
Once an analysis has been completed and a need identified a strategy is needed to develop this pursuit of opportunity. This involves segmentation (identifying a market in different portions in order to better satisfy consumers) and target market.
3.) The marketing mix
This step involves certain tactical decisions based on the control of the products. For example: product development, decisions based on pricing of goods, distributing the products and getting it directly to the consumer as well as creating promotion campaigns.
4.) Implementation and control
At this stage of the process, a product has been created and launched therefore a problem has been addressed. However, consumer wants and needs adapt to the environment and should these change it may result in new innovations and product enhancements. This should be monitored closely in order to continue in order to maintain market share.

Product Introduction Into The Market
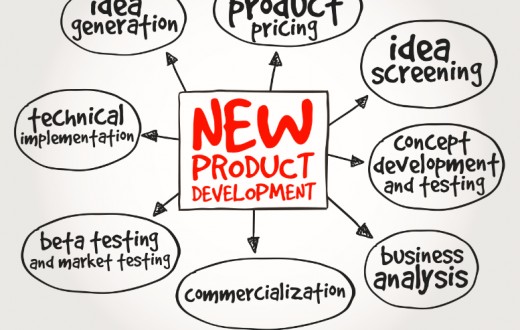
A company has to consistently change and develop new or enhance existing products in order to keep up with changing consumer preferences and environments if it wants to stay successful and profitable. This idea should fit the company’s vision and objectives. When companies develop new enhanced products it results in two outcomes. They give consumers a wider choice thus increasing the demand as well as increasing producer’s capabilities to shift towards market needs. The stages in which a company creates or recreates a product is as follows:

1.) Idea Generation
Before any new products are launched extensive research and information collection has to be done in order to see whether consumers would be interested in a product and whether it would be feasible to pursue it. This research is done in order for a firm to gain an understanding of the market place and the customers. Before Kitkat entered the market it would have had to conduct surveys and analyse consumer preferences. They would have had to gain information concerning what consumers are buying at the current time and would they be willing to pay for this?

2.) Idea Screening
The firm has to be selective on the ideas that they are willing to pursue as making the wrong choices and decisions will cost the company. Once they have found an idea that they see as profitable and feasible, they then eliminate any of the extra costs that they could have incurred. Kitkat chose the pursuit of new specialised flavours of their original chocolate. They saw this as profitable as they are still maintaining their original brand and quality but enhanced it enough to gain more consumers and maintain or even increase their market share.
3.) Concept Development and Testing
Once they have found a certain idea that they think would be a profitable opportunity they have to address the target market in order to see whether it would work. In Kitkats case they would have had to address their consumers and ask them whether they would be inclined to this concept and whether the change in flavours would encourage their choices towards buying their products over their rivals. This procedure helps to eradicate any previous unforeseen problems with their concept such as maybe if the flavours were different they would buy more of the product than the original suggestion?
4.) Business Analysis
After working through problems they may have overlooked they then would have had to address whether it was financially possible and feasible for them to pursue this opportunity. Kitkat would have had to draw up a business analysis in order to recognize the costs involved and the impact on the company’s cash flow. Will the products life span be sufficient enough to achieve the market share that they wish to achieve?
5.) Product Development
At this stage, using all the insight and information gained Kitkat would have created a prototype as such, a model of the product they intend to sell. They would have then had to introduce this product to their consumers in order to see whether what they have created met their expectation of what they intended to achieve.

6.) Test Marketing
After creating the complete product, after addressing their consumers, Kitkat would have launched their new flavours in a particular region or area and monitor the marketing mix (product, price, distribution or place and promotion), the market share changes and the revenue and progress of these products without the knowledge of their consumers. They would measure their sales against previous sales in order to see whether what they predicted to happen would actually occur. At this stage further product enhancements could be made in order to eliminate problems that they may have overlooked.
7.) Commercialisation
This is when Kitkat would have decided to nationally launch their new flavours. However, the way in which they do it is very important. They have to launch their product at an appropriate time in the correct manner and at a place that consumers would have the greatest access to in order maximise their success and gain the highest rewards.

8.) Monitoring and Evaluation
After the framework is completed it has to be evaluated in terms of the running of the process and the success rate of the product itself. Kitkat would have had to see whether their innovation and new products increased their market share and is on their way to achieving what they set out do or whether changes need to be made in their marketing strategy in order to further grow their business if there is a sudden consumer preference change.
How KitKat Uses Marketing To Refresh Sales
The problem faced by Kitkat was the fact that many of their competitors took their market share because of changing environments and the wants of consumers having changed to healthier options without them changing their products and adapting to this change of preference. With Kitkat being overtaken by competitors they identified the need for product innovation and to appeal to the changing wants of consumers in order to regain its market share. This resulted in them creating new products such as Kitkat Chunky and Kitkat Orange, to address this problem. By creating new additional products, they gave consumers a wider variety to choose from and portrayed a new image for themselves. This would have widened their scope and broadened their target market increasing their sales once again.
8 Stages Summary
Please feel free to leave your comments or any questions below! :)








